0 Ecc2 E1 B 3 E5 F 48 A2 8 Cee 69 D7 E73 Cbc8 B Postimages

E 0 B 8 A 7 E 0 B 8 A 8 Pdf Possible duplicate: prove 0! = 1 0! = 1 from first principles why does 0! = 1 0! = 1? all i know of factorial is that x! x! is equal to the product of all the numbers that come before it. the product of 0 and anything is 0 0, and seems like it would be reasonable to assume that 0! = 0 0! = 0. i'm perplexed as to why i have to account for this condition in my factorial function (trying to learn. 0i = 0 0 i = 0 is a good choice, and maybe the only choice that makes concrete sense, since it follows the convention 0x = 0 0 x = 0. on the other hand, 0−1 = 0 0 1 = 0 is clearly false (well, almost —see the discussion on goblin's answer), and 00 = 0 0 0 = 0 is questionable, so this convention could be unwise when x x is not a positive real.

E 0 B 8 A 5 E 0 B 8 B 7 E 0 B 988 E 0 B 8 Pdf Is there a consensus in the mathematical community, or some accepted authority, to determine whether zero should be classified as a natural number? it seems as though formerly $0$ was considered i. 0 0 = x 0 0 = x 0x = 0 0 x = 0 x x can be any value, therefore 0 0 0 0 can be any value, and is indeterminate. 1 0 = x 1 0 = x 0x = 1 0 x = 1 there is no such x x that satisfies the above, therefore 1 0 1 0 is undefined. is this a reasonable or naive thought process? it seems too simple to be true. 10 several years ago i was bored and so for amusement i wrote out a proof that 0 0 0 0 does not equal 1 1. i began by assuming that 0 0 0 0 does equal 1 1 and then was eventually able to deduce that, based upon my assumption (which as we know was false) 0 = 1 0 = 1. Is a constant raised to the power of infinity indeterminate? i am just curious. say, for instance, is $0^\\infty$ indeterminate? or is it only 1 raised to the infinity that is?.

E0 B8 A0 E0 B8 B2 E0 B8 A9 E0 B8 B2 E0 B8 9e E0 B8 B2 E0 B8 97 E0 B8 B5 E0 B8 9a E0 B8 97 E0 10 several years ago i was bored and so for amusement i wrote out a proof that 0 0 0 0 does not equal 1 1. i began by assuming that 0 0 0 0 does equal 1 1 and then was eventually able to deduce that, based upon my assumption (which as we know was false) 0 = 1 0 = 1. Is a constant raised to the power of infinity indeterminate? i am just curious. say, for instance, is $0^\\infty$ indeterminate? or is it only 1 raised to the infinity that is?. How can i prove from first principles that $0!$ is equal to $1$?. The above picture is the full background to it. it does not invoke "indeterminate forms". it does not require you to write 0 0 0 0 and then ponder what that might mean. we don't divide by zero anywhere. it is just the case where limx→a g(x) = 0 lim x → a g (x) = 0 is out of scope of the above theorem. however, it is very common, in mathematical education, to talk about "indeterminate forms. 92 the other comments are correct: 1 0 1 0 is undefined. similarly, the limit of 1 x 1 x as x x approaches 0 0 is also undefined. however, if you take the limit of 1 x 1 x as x x approaches zero from the left or from the right, you get negative and positive infinity respectively. In the set of real numbers, there is no negative zero. however, can you please verify if and why this is so? is zero inherently "neutral"?.
B8b3e9d3f14e604dec7e06bceb65b7b7e427fdd0 B8b How can i prove from first principles that $0!$ is equal to $1$?. The above picture is the full background to it. it does not invoke "indeterminate forms". it does not require you to write 0 0 0 0 and then ponder what that might mean. we don't divide by zero anywhere. it is just the case where limx→a g(x) = 0 lim x → a g (x) = 0 is out of scope of the above theorem. however, it is very common, in mathematical education, to talk about "indeterminate forms. 92 the other comments are correct: 1 0 1 0 is undefined. similarly, the limit of 1 x 1 x as x x approaches 0 0 is also undefined. however, if you take the limit of 1 x 1 x as x x approaches zero from the left or from the right, you get negative and positive infinity respectively. In the set of real numbers, there is no negative zero. however, can you please verify if and why this is so? is zero inherently "neutral"?.

A 1 B 8 C 0 D 2 E 0 F 5 G 0 H 0 I 7 There Is In Chegg 92 the other comments are correct: 1 0 1 0 is undefined. similarly, the limit of 1 x 1 x as x x approaches 0 0 is also undefined. however, if you take the limit of 1 x 1 x as x x approaches zero from the left or from the right, you get negative and positive infinity respectively. In the set of real numbers, there is no negative zero. however, can you please verify if and why this is so? is zero inherently "neutral"?.
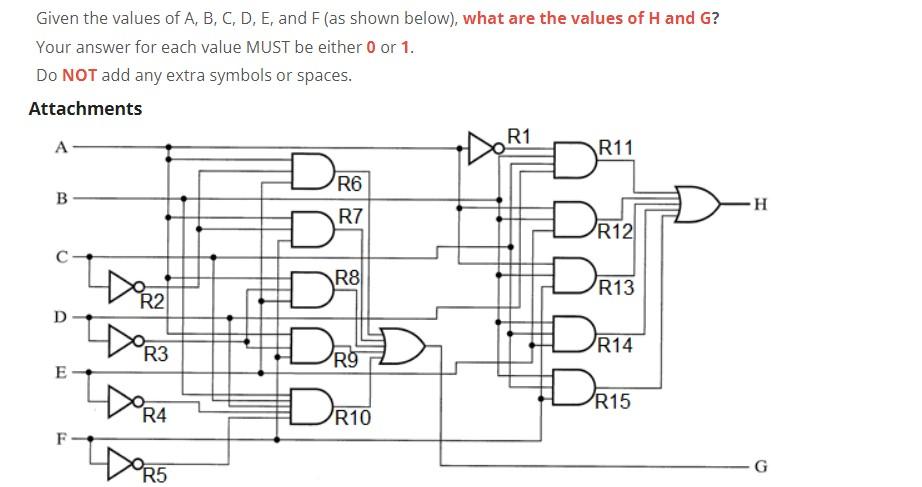
Solved When A 0 B 1 C 1 D 1 E 0 And F 0 Chegg
Comments are closed.