Angular Momentum And Spin Pdf Spin Physics Eigenvalues And Eigenvectors

Angular Momentum And Spin Pdf Spin Physics Eigenvalues And Eigenvectors Although we will develop the spin eigenvalues and eigenvectors for any value of the spin, spin 1 2 particles will dominate our discussion. we can represent the operators of the spin spaces in subspaces. Just as an electron possess a magnetic moment associated with its orbital angular momentum, it also possesses a moment associated with its spin angular momentum.

3 Angular Momentum And Spin Download Free Pdf Spin Physics Eigenvalues And Eigenvectors Angular momentum and spin free download as pdf file (.pdf), text file (.txt) or read online for free. 1) the document introduces angular momentum and spin through commutation relations. Remember: 0 = ↑ = state representing ang. mom. w z comp. up 1 = ↓ = state representing ang. mom. w z comp. down so we have derived the eigenvectors and eigenvalues of the spin for a spin 1 2 system, like an electron or proton: 0 and 1 are simultaneous eigenvectors of s2 and sz. Hence, handling spin is often simpler than handling normal operators because there are not infinite numbers of eigenvalues and hence eigenstates. allowing for these differences, then spin acts just like other angular momentum. In the following we provide a brief introduction to the group of three dimensional rotation matrices. we will also introduce the generators of this group and their algebra as well as the representation of rotations through exponential operators.
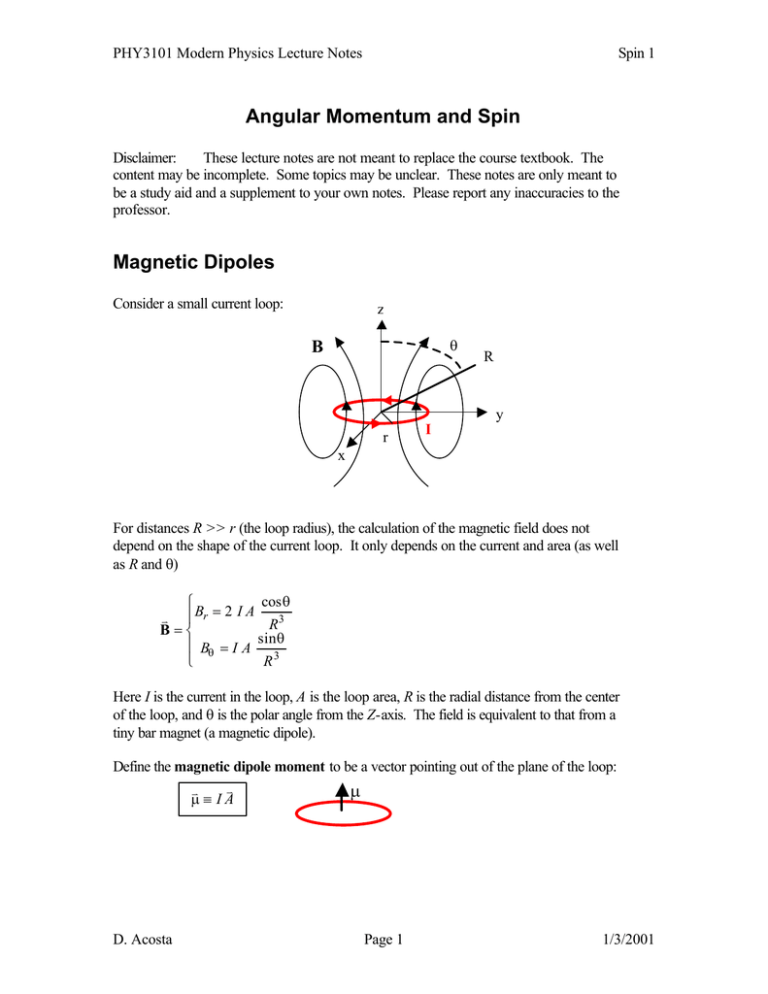
Angular Momentum And Spin Hence, handling spin is often simpler than handling normal operators because there are not infinite numbers of eigenvalues and hence eigenstates. allowing for these differences, then spin acts just like other angular momentum. In the following we provide a brief introduction to the group of three dimensional rotation matrices. we will also introduce the generators of this group and their algebra as well as the representation of rotations through exponential operators. A more powerful approach is to solve the angular momentum eigenfunction problem using operator methods analogous to the creation and annihilation operators we have used in the harmonic oscillator problem. these notes provide details about the operator approach. Example the x component of the spin angular momentum of an electron is denoted by the pauli spin operator 0 1 1 x 1 0 find the eigenvalues and eigenvectors of x. This defini tion is valid for both the orbital angular momentum and the spin. a compact way of writing these expressions, using the levi civita tensor, is explained in appendix 13.1.

Lecture 11 Spin Orbital And Total Angular Momentum 1 Lecture 11 Spin Orbital And Total A more powerful approach is to solve the angular momentum eigenfunction problem using operator methods analogous to the creation and annihilation operators we have used in the harmonic oscillator problem. these notes provide details about the operator approach. Example the x component of the spin angular momentum of an electron is denoted by the pauli spin operator 0 1 1 x 1 0 find the eigenvalues and eigenvectors of x. This defini tion is valid for both the orbital angular momentum and the spin. a compact way of writing these expressions, using the levi civita tensor, is explained in appendix 13.1.
Comments are closed.