Arctic Food Web

Arctic Food Web Arctic Tundra Learn how energy flows through the arctic ecosystem, from algae to polar bears, and how humans fit into the food web. explore the trophic levels, food chains, and food webs of the arctic with examples and diagrams. Learn about the different trophic levels and organisms in the arctic food chain of the ocean and the grassland. see how producers, consumers, and decomposers interact in the arctic circle that surrounds the north pole.
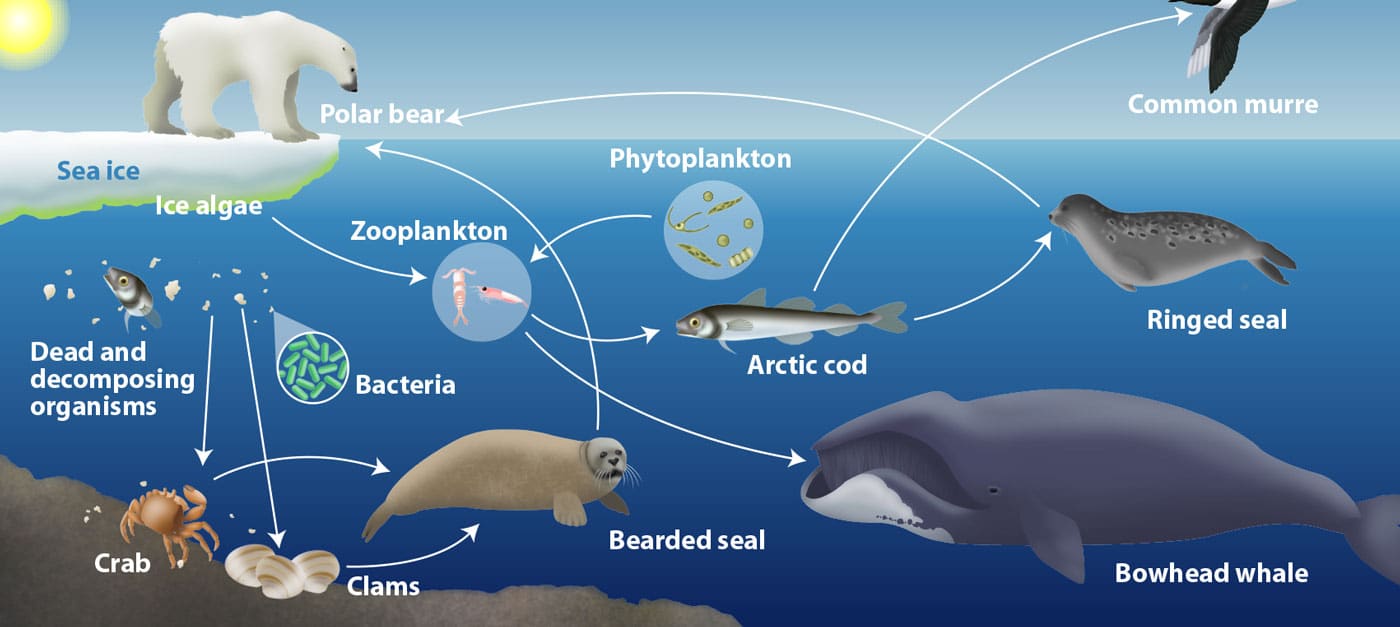
Arctic Food Web Erin E Hunter Learn about the unique characteristics, key components, and importance of arctic food webs, the complex system of interactions between producers, consumers, and decomposers in the arctic region. explore the adaptations, roles, and threats of various species that inhabit the arctic marine and terrestrial ecosystems. Learn about the arctic tundra food web, where producers are small shrubs and lichen, primary consumers are herbivores, and secondary consumers are carnivores. see how polar bears and seals fit into the marine food web, and how energy flows through the food chain. In the arctic ocean, this web of life unfolds in one of the planet’s most extreme environments, characterized by prolonged darkness and expansive sea ice. this system connects microscopic organisms, which form the base of the web, to the largest predators roaming the ice. Learn how plants, animals, and microbes form a delicate and resilient food web in the arctic, where life faces extreme challenges. discover the adaptations, strategies, and interactions of producers, consumers, and predators in this fascinating ecosystem.
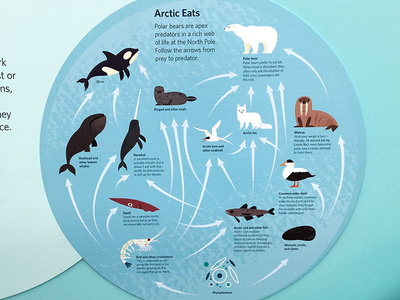
Arctic Food Web By Alexander Vidal Dribbble In the arctic ocean, this web of life unfolds in one of the planet’s most extreme environments, characterized by prolonged darkness and expansive sea ice. this system connects microscopic organisms, which form the base of the web, to the largest predators roaming the ice. Learn how plants, animals, and microbes form a delicate and resilient food web in the arctic, where life faces extreme challenges. discover the adaptations, strategies, and interactions of producers, consumers, and predators in this fascinating ecosystem. Learn how plankton, krill, fish, birds, seals, whales, and other animals form the arctic food chain. discover how climate change affects the survival and diversity of these species. One unusual feature of marine arctic food webs is that primary production can only occur during a very short period of the year. short winter days mean there is little or no sunlight to support photosynthesis. Learn about the biodiversity and ecosystems of the arctic and how energy transfers among producers, consumers, and decomposers. create food web models using coloring utensils, paper, and pre cut slips of different species. In the arctic tundra, the food web connects primary producers like phytoplankton and macroalgae to primary consumers (e.g., voles), secondary consumers (e.g., foxes), and tertiary consumers (e.g., polar bears), each level relying on the one below.
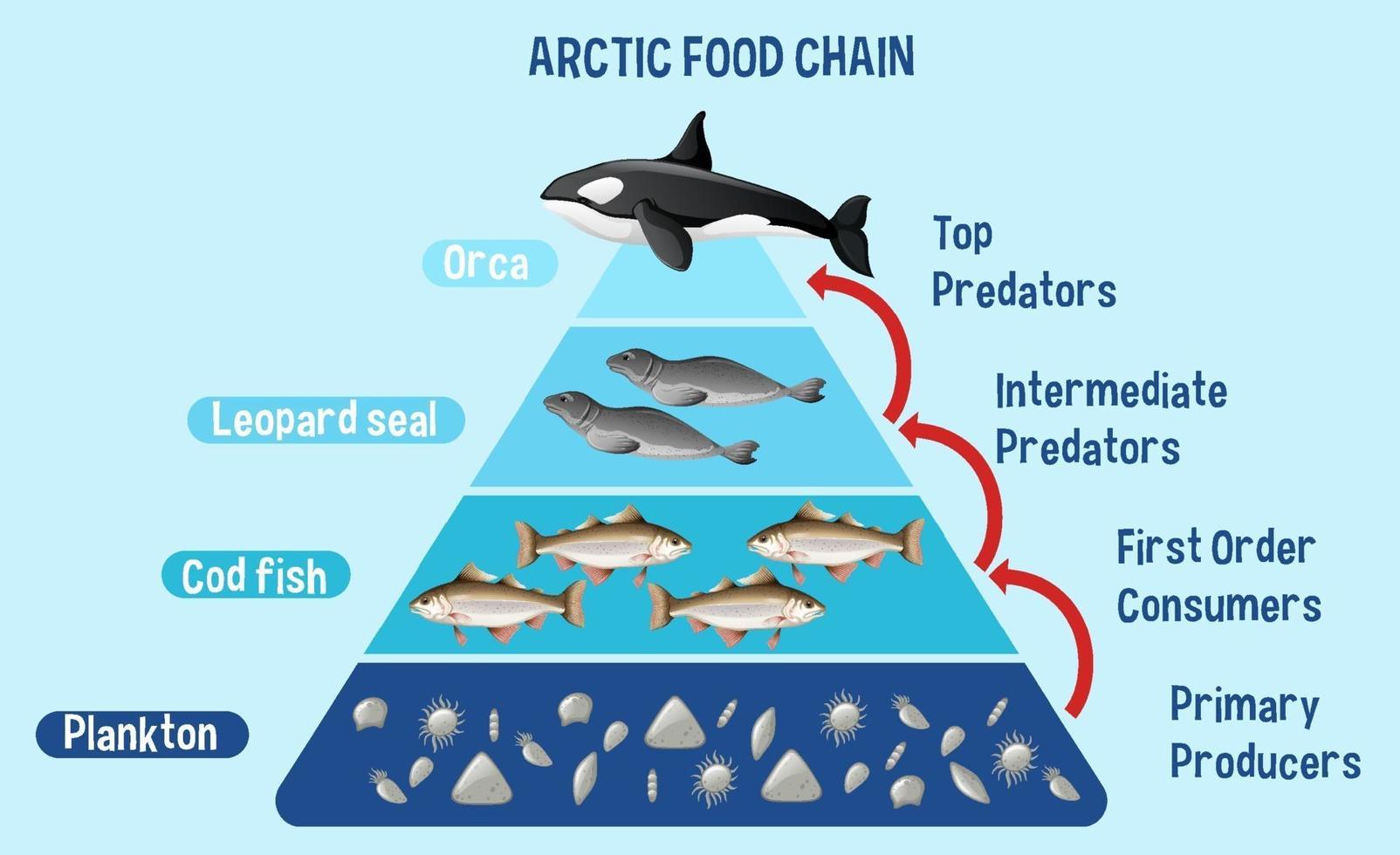
Build A Food Web Arctic Ocean Food Web Arctic Ocean A Vrogue Co Learn how plankton, krill, fish, birds, seals, whales, and other animals form the arctic food chain. discover how climate change affects the survival and diversity of these species. One unusual feature of marine arctic food webs is that primary production can only occur during a very short period of the year. short winter days mean there is little or no sunlight to support photosynthesis. Learn about the biodiversity and ecosystems of the arctic and how energy transfers among producers, consumers, and decomposers. create food web models using coloring utensils, paper, and pre cut slips of different species. In the arctic tundra, the food web connects primary producers like phytoplankton and macroalgae to primary consumers (e.g., voles), secondary consumers (e.g., foxes), and tertiary consumers (e.g., polar bears), each level relying on the one below.

Arctic Food Web Pdf Learn about the biodiversity and ecosystems of the arctic and how energy transfers among producers, consumers, and decomposers. create food web models using coloring utensils, paper, and pre cut slips of different species. In the arctic tundra, the food web connects primary producers like phytoplankton and macroalgae to primary consumers (e.g., voles), secondary consumers (e.g., foxes), and tertiary consumers (e.g., polar bears), each level relying on the one below.
Comments are closed.