Chapter 3 Learning Assessment E 3 18 Solution Mesh Analysis Linear Circuit Analysis
Mesh Analysis In Linear Circuits A Presentation #meshanalysis #loop #mesh #circuittheory #supernodalanalysis #supernode #nodalanalysis #chapter3 #unsolvedexamples #matlab #kcl #currentlaw #kirchhoffcurren. Engineering circuit analysis 9. 8th edition chapter three exercise solutions we note that kcl requires that if 7 a flows out of the “ ” terminal of the 2 v source, it flows left to right through r1.
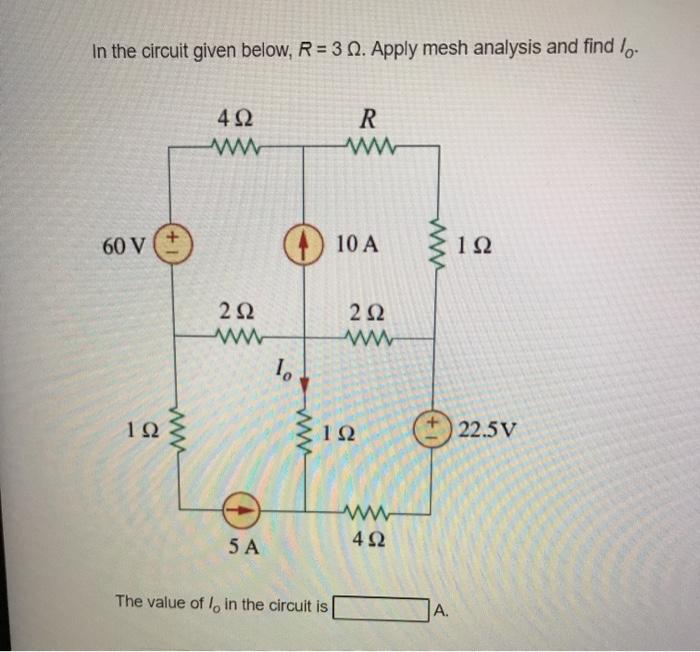
Solved In The Circuit Given Below R 3 Apply Mesh Analysis Chegg Enhance your mesh analysis skills with solved problems for better circuit comprehension and problem solving. Solution irwin 10th ch03.pdf free download as pdf file (.pdf), text file (.txt) or read online for free. the document contains solutions to 88 circuit analysis problems from chapter 3 on nodal and loop analysis techniques from the 10th edition of irwin's basic engineering circuit analysis textbook. Hence, va = 3ia = 1.98 v forming one supermesh from the remaining two meshes, we may write: 3 2.5 i 3 i 4 i = 0 1 2 2 and the supermesh kcl equation: i – i = 0.5 v = 0.5(1.98) = 0.99 2 1 a thus, we have two equations to solve: 2.5 i 7 i = 3 1 2 i1 i2 = 0.99 solving, we find that i = 413.7 ma and the voltage across the 2.5 Ω. Nodal analysis applies kcl to find unknown voltages in a given circuit, while mesh analysis applies kvl to find unknown currents. a mesh is a loop which does not contain any other loops within it. assign mesh currents i1, i2, , in to the n meshes. apply kvl to each of the n meshes.

Solved 3 Solve The Circuit Shown In Figure 3 Using Mesh Hence, va = 3ia = 1.98 v forming one supermesh from the remaining two meshes, we may write: 3 2.5 i 3 i 4 i = 0 1 2 2 and the supermesh kcl equation: i – i = 0.5 v = 0.5(1.98) = 0.99 2 1 a thus, we have two equations to solve: 2.5 i 7 i = 3 1 2 i1 i2 = 0.99 solving, we find that i = 413.7 ma and the voltage across the 2.5 Ω. Nodal analysis applies kcl to find unknown voltages in a given circuit, while mesh analysis applies kvl to find unknown currents. a mesh is a loop which does not contain any other loops within it. assign mesh currents i1, i2, , in to the n meshes. apply kvl to each of the n meshes. The two basic circuit analysis techniques described in this chapter follow this same pattern. nodal analysis is based on bal ancing currents coming into and out of nodes in the circuits. mesh or loop analysis is based on balancing voltage increases and drops around closed paths in the circuits. Question: 3.38 apply mesh analysis to the circuit in fig. 3.85 and obtain i ml 422 312 w anar 60 v 10 a 10 222 222 mu 12 312 22.5 v 5 a 422 figure 3.85 for prob. 3.38. there are 2 steps to solve this one. Each problem solution presents the circuit diagram and uses nodal or loop analysis to solve for unknown voltages and currents. the document contains solutions to 60 problems from chapter 3 on nodal and loop analysis techniques in irwin's basic engineering circuit analysis, 10th edition textbook. Find: the voltage across the 10 Ω resistor in the circuit of figure p3.14 using superposition. 3.34 g. rizzoni, principles and applications of electrical engineering problem solutions, chapter 3 analysis: (1) suppress voltage source vs1 . redraw the circuit.
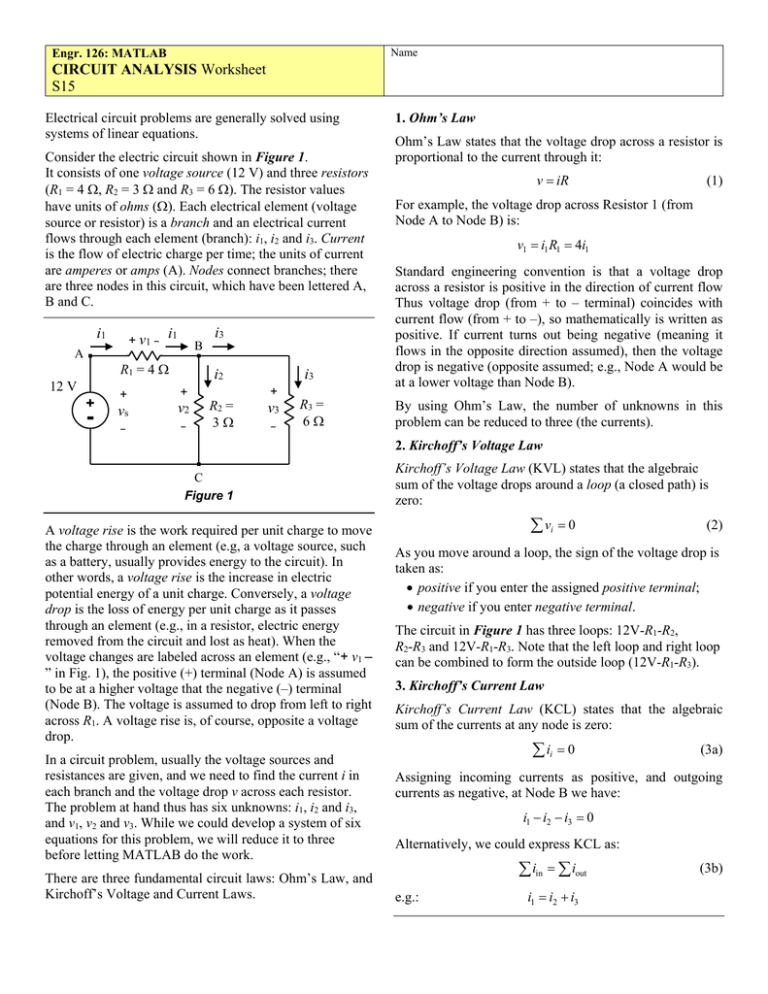
Circuit Mesh Analysis The two basic circuit analysis techniques described in this chapter follow this same pattern. nodal analysis is based on bal ancing currents coming into and out of nodes in the circuits. mesh or loop analysis is based on balancing voltage increases and drops around closed paths in the circuits. Question: 3.38 apply mesh analysis to the circuit in fig. 3.85 and obtain i ml 422 312 w anar 60 v 10 a 10 222 222 mu 12 312 22.5 v 5 a 422 figure 3.85 for prob. 3.38. there are 2 steps to solve this one. Each problem solution presents the circuit diagram and uses nodal or loop analysis to solve for unknown voltages and currents. the document contains solutions to 60 problems from chapter 3 on nodal and loop analysis techniques in irwin's basic engineering circuit analysis, 10th edition textbook. Find: the voltage across the 10 Ω resistor in the circuit of figure p3.14 using superposition. 3.34 g. rizzoni, principles and applications of electrical engineering problem solutions, chapter 3 analysis: (1) suppress voltage source vs1 . redraw the circuit.
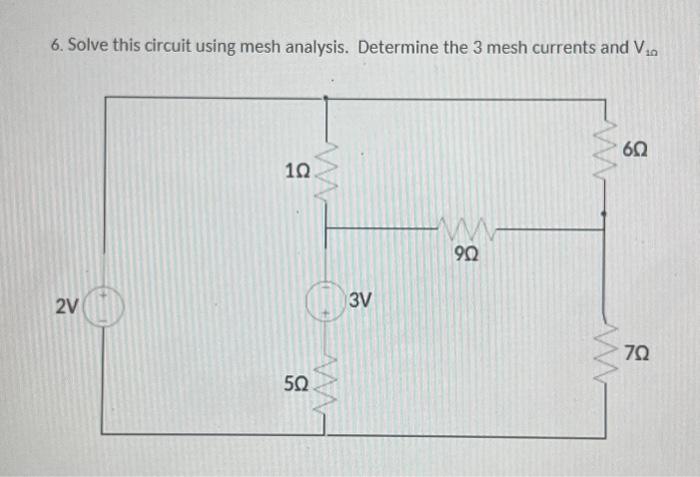
Solved 6 Solve This Circuit Using Mesh Analysis Determine Chegg Each problem solution presents the circuit diagram and uses nodal or loop analysis to solve for unknown voltages and currents. the document contains solutions to 60 problems from chapter 3 on nodal and loop analysis techniques in irwin's basic engineering circuit analysis, 10th edition textbook. Find: the voltage across the 10 Ω resistor in the circuit of figure p3.14 using superposition. 3.34 g. rizzoni, principles and applications of electrical engineering problem solutions, chapter 3 analysis: (1) suppress voltage source vs1 . redraw the circuit.
Comments are closed.