Classification Of Arthropods

Classification Of Arthropods Play Online On Flash Museum рџ пёџ The phylum arthropoda is commonly divided into four subphyla of extant forms: chelicerata (arachnids), crustacea (crustaceans), hexapoda (insects and springtails), and myriapoda (millipedes and centipedes). Arthropods ( ˈɑːrθrəˌpɒd ar thrə pod) [3][4] are invertebrates in the phylum arthropoda. they possess an exoskeleton with a cuticle made of chitin, often mineralised with calcium carbonate, a body with differentiated (metameric) segments, and paired jointed appendages.
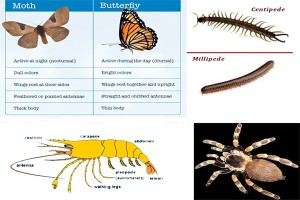
Classification Of Arthropods Archives Microbiology Notes Classification of arthropoda with identification characters for each sub phylum and class arthropods are classified into five sub phylum and each then subdivide into classes (a total of 16 classes according to recent classification of animal taxa). Phylum arthropoda and its various groups have been classified differently by different workers. the classification here is followed by vandal (1949), snodgrass (1960), and strorer (1979). In this article, we’ll delve into the fascinating world of arthropoda, exploring its characteristics, classification, evolutionary history, and its importance in ecosystems. Spider, tick, mite chi. opoda (c. pedes d. plopoda (diplo two; poda appendage)e.g. . ch. restrial ter. ma. y terr. , . t. is. o. ra. r . in. h . ear. amo. larva numph adult.
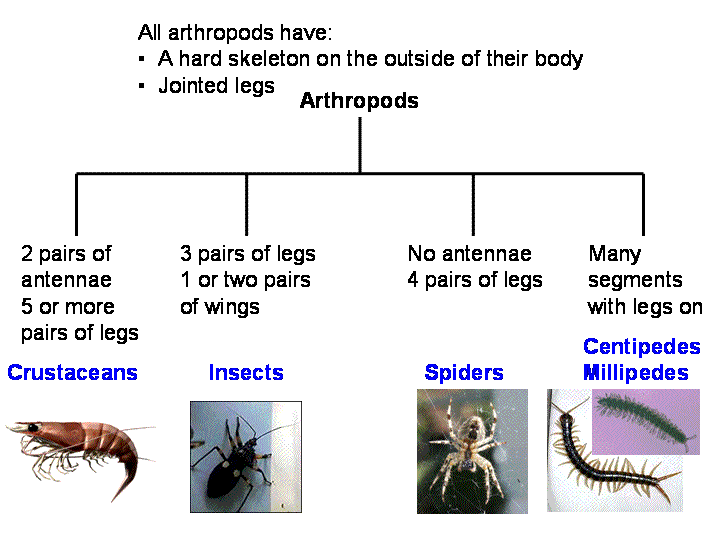
Arthropods Tambopata In this article, we’ll delve into the fascinating world of arthropoda, exploring its characteristics, classification, evolutionary history, and its importance in ecosystems. Spider, tick, mite chi. opoda (c. pedes d. plopoda (diplo two; poda appendage)e.g. . ch. restrial ter. ma. y terr. , . t. is. o. ra. r . in. h . ear. amo. larva numph adult. Large numbers of arthropods live as parasites, and structural changes occur in them to adjust with the peculiar mode of life. many arthropods are well known for their habit of migration. some of them can produce sound and nearly all are equipped with efficient sense organs. Defining features of arthropods arthropods share fundamental characteristics. a defining feature is their exoskeleton, a rigid external covering made primarily of chitin, a complex polysaccharide. this exoskeleton provides physical protection, structural support, and helps prevent water loss, which is beneficial for terrestrial species. The classification of phylum arthropoda can be broadly outlined by dividing it into several subphyla, each characterized by unique anatomical and physiological features. Arthropod insects, crustaceans, arachnids: arthropod classes are based on criteria such as modification, specialization, number, and appearance of body segments and appendages. their relationships both within the phylum and with other animal phyla are uncertain.

Taxonomic Classifications Used By The Division Of Arthropods Museum Of Southwestern Biology Large numbers of arthropods live as parasites, and structural changes occur in them to adjust with the peculiar mode of life. many arthropods are well known for their habit of migration. some of them can produce sound and nearly all are equipped with efficient sense organs. Defining features of arthropods arthropods share fundamental characteristics. a defining feature is their exoskeleton, a rigid external covering made primarily of chitin, a complex polysaccharide. this exoskeleton provides physical protection, structural support, and helps prevent water loss, which is beneficial for terrestrial species. The classification of phylum arthropoda can be broadly outlined by dividing it into several subphyla, each characterized by unique anatomical and physiological features. Arthropod insects, crustaceans, arachnids: arthropod classes are based on criteria such as modification, specialization, number, and appearance of body segments and appendages. their relationships both within the phylum and with other animal phyla are uncertain.

Protect Health Protect Life Classification Of Arthropods The classification of phylum arthropoda can be broadly outlined by dividing it into several subphyla, each characterized by unique anatomical and physiological features. Arthropod insects, crustaceans, arachnids: arthropod classes are based on criteria such as modification, specialization, number, and appearance of body segments and appendages. their relationships both within the phylum and with other animal phyla are uncertain.
Comments are closed.