Computer Arithmetic

3 Arithmetic For Computers Pdf Computer Architecture Arithmetic Computer arithmetic is the branch of computer science that deals with the representation and manipulation of numerical quantities in a computer system. here are some basic concepts and operations involved in computer arithmetic:. Learn about the scientific field of computer arithmetic, which deals with number representation and arithmetic operations on computers. explore the different types of arithmetic, such as fixed point, floating point, interval, modular, finite field and matrix arithmetic.

Computer Arithmetic Learn about the basic arithmetic operations, data types, and memory hierarchy in digital computers. see examples of signed magnitude representation, addition and subtraction algorithms, and memory address map. Learn how computers represent and manipulate numbers using binary and floating point systems. this web page covers topics such as signed integers, rounding, exceptions, and special operations. Learn the basics of binary and hexadecimal representations, two's complement encoding, and floating point numbers. see examples, definitions, and algorithms for arithmetic operations and conversions. Learn how computers represent and perform operations on numbers, and the challenges and implications of computer arithmetic. explore chapters and articles on topics such as floating point arithmetic, software, and storage systems.

Computer Arithmetic Volume Ii Coderprog Learn the basics of binary and hexadecimal representations, two's complement encoding, and floating point numbers. see examples, definitions, and algorithms for arithmetic operations and conversions. Learn how computers represent and perform operations on numbers, and the challenges and implications of computer arithmetic. explore chapters and articles on topics such as floating point arithmetic, software, and storage systems. Learn about number representation, basic arithmetic operations and evaluation of functions in digital computers. the lecture notes cover topics such as radix, digit set, redundancy, complement, overflow, carry and more. Learn how computer arithmetic performs addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, and logical operations on binary numbers. see examples, illustrations, and mips code for various arithmetic and logic units (alu). Learn about different ways of representing integers in binary, such as fixed point, sign magnitude and 2's complement. also, see how to perform addition, subtraction and multiplication using binary adder and multiplier units. Examine inputs and outputs to find earliest place where value is wrong. typically, trace backwards from bad outputs, forward from inputs. look at values at intermediate points in circuit. do not rip up, debug!.

Computer Arithmetic Learn about number representation, basic arithmetic operations and evaluation of functions in digital computers. the lecture notes cover topics such as radix, digit set, redundancy, complement, overflow, carry and more. Learn how computer arithmetic performs addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, and logical operations on binary numbers. see examples, illustrations, and mips code for various arithmetic and logic units (alu). Learn about different ways of representing integers in binary, such as fixed point, sign magnitude and 2's complement. also, see how to perform addition, subtraction and multiplication using binary adder and multiplier units. Examine inputs and outputs to find earliest place where value is wrong. typically, trace backwards from bad outputs, forward from inputs. look at values at intermediate points in circuit. do not rip up, debug!.
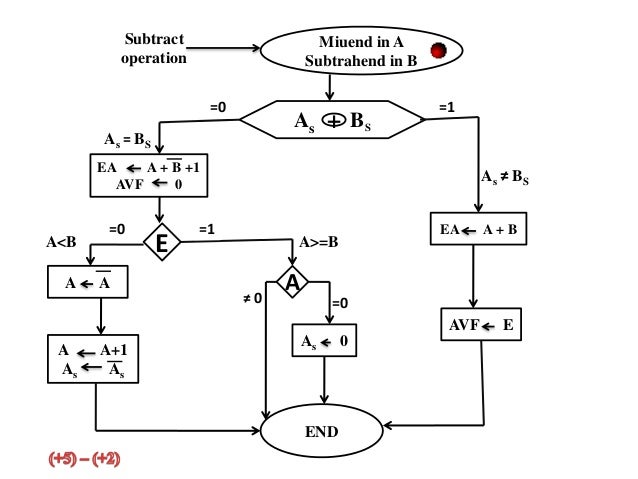
Computer Arithmetic Learn about different ways of representing integers in binary, such as fixed point, sign magnitude and 2's complement. also, see how to perform addition, subtraction and multiplication using binary adder and multiplier units. Examine inputs and outputs to find earliest place where value is wrong. typically, trace backwards from bad outputs, forward from inputs. look at values at intermediate points in circuit. do not rip up, debug!.

Computer Arithmetic
Comments are closed.