Data Representation Pdf Digital Technology Computer Architecture

Data Representation Architecture 1 Pdf Byte Computer Data Storage Data representation refers to the form in which data is stored, processed, and transmitted. devices such as smartphones, ipods, and computers store data in digital formats that can be handled by electronic circuitry. Section 1 computer systems a – data representation and computer structure how data is represented in a computer system data as bit pattern representations a bit is the smallest unit of data in computing or the digital world. a bit can only be in one of two ‘binary’ states: ‘0’ or ‘1.
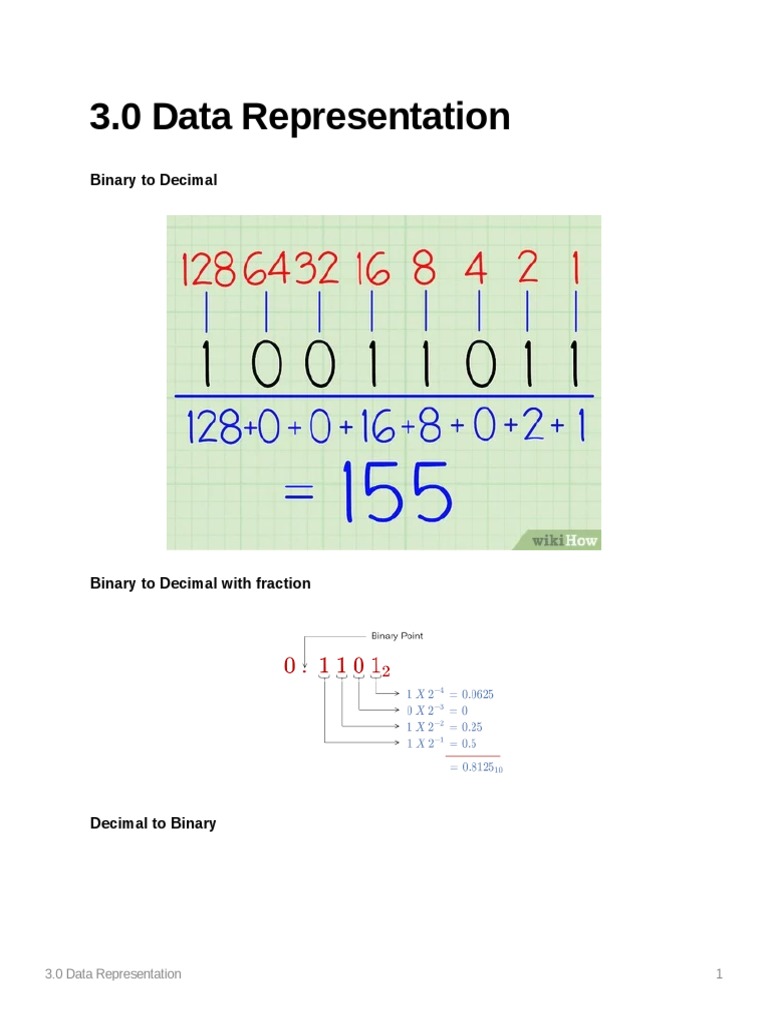
Data Representation Pdf Integer Computer Science Decimal Digital computer represents all kinds of data and information in the binary system. binary number system consists of two digits 0 (l ow voltage) and 1 (hi gh voltage). its base or radix is 2. each digit or bit in binary number system can be 0 or 1. the positional values are expressed in power of 2. example: 1011(2 ), 111(2 ), 100001(2 ). • digital systems can process data in discrete form only • continuous, or analog, information is converted into digital form by means of an analog to digital converter. Computer architecture 2019 2020 #3 : data representation 3 • variable length encodings: utf 8 (one to four 8 bit code units), utf 16 (one or two 16 bit code units). Recall representation does not affect the calculated result , but it can affect its ease of use. since we'll convert to decimal before showing numbers to humans,.

Introduction To Data Representation Pdf Data Type Integer Computer Science Computer architecture 2019 2020 #3 : data representation 3 • variable length encodings: utf 8 (one to four 8 bit code units), utf 16 (one or two 16 bit code units). Recall representation does not affect the calculated result , but it can affect its ease of use. since we'll convert to decimal before showing numbers to humans,. •bits:all digital data are sequences of 0s and 1s (binary) •amenable to high low on off electromagnetism •data types: first layer of abstraction to interpret a bit sequence with human understandable category of information •example data types: boolean, byte, integer, floating point number (float), character, string •data structures: a. • byte: it is a unit of digital information, usually comprising 8 bits • the smallest addressable unit of memory in many, but not all, computer architectures. The significance of data representation is underscored by its role in applications ranging from scientific computing to multimedia processing. for example, a digital calculator uses numeric data to perform arithmetic operations, while a text editor utilizes alphanumeric data to facilitate text input and editing. • the hardware structure of a computer combines individual bits into larger units. in most modern architectures, the smallest unit on which the hardware operates is a sequence of eight consecutive bits called a byte. the following diagram shows a byte containing a combination of 0s and 1s: binary notation.
Comments are closed.