Difference Between Primary Key And Foreign Key

Difference Between Primary Key And Foreign Key A foreign key is a column (or set of columns) in a second table whose value is required to match the value of the primary key in the original table. usually a foreign key is in a table that is different from the table whose primary key is required to match. a table can have multiple foreign keys. the primary key cannot accept null values. Foreign key. foreign key is a field in the table that is primary key in another table. foreign key can accept multiple null value. foreign key do not automatically create an index, clustered or non clustered. you can manually create an index on foreign key. we can have more than one foreign key in a table.
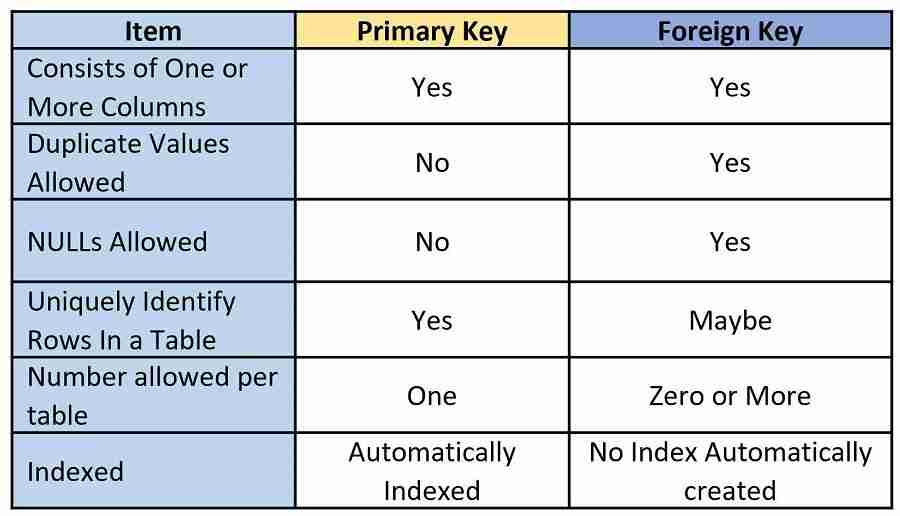
Foreign Key Vs Primary Key What Is The Difference Essential Sql Primary key: is a single field chosen by the designer to uniquely identify a record in a table (relation), cannot be null (empty unassigned). foreign key: is the primary key one table appearing (cross referenced) in another table. secondary (or alternative) key: is any field in the table that isn't selected to be any of the two types above. The primary key will probably be implemented with a primary key constraint; the candidate keys will probably be implemented with unique constraints. a foreign key is an instance of one entity's candidate key in another entity, representing a relationship between the two entities. The primary key for the table is a unique index, and usually only has one column. a foreign key is a value in a table that references a unique index in another table. it is used as a way to relate to tables together. for example, a child table can look up the one parent row via its column that is a unique index in the parent table. From sql foreign key constraint. to allow naming of a foreign key constraint, and for defining a foreign key constraint on multiple columns, use the following sql syntax. create table orders ( o id int not null, orderno int not null, p id int, primary key (o id), constraint fk perorders foreign key (p id) references persons(p id) ).

Difference Between Primary And Foreign Key In Table Sql Java67 The primary key for the table is a unique index, and usually only has one column. a foreign key is a value in a table that references a unique index in another table. it is used as a way to relate to tables together. for example, a child table can look up the one parent row via its column that is a unique index in the parent table. From sql foreign key constraint. to allow naming of a foreign key constraint, and for defining a foreign key constraint on multiple columns, use the following sql syntax. create table orders ( o id int not null, orderno int not null, p id int, primary key (o id), constraint fk perorders foreign key (p id) references persons(p id) ). A surrogate key is typically a numeric value. within sql server, microsoft allows you to define a column with an identity property to help generate surrogate key values. the primary key constraint uniquely identifies each record in a database table. primary keys must contain unique values. a primary key column cannot contain null values. Difference between candidate key vs primary key: ) both primary and candidate keys can uniquely identify records in a table on database. 2) both primary and candidate keys are has constraints unique and not null. 3) primary key or candidate keys can be either single column or combination of multiple columns in a table. When you create a table, in addition to the table name, you must specify the primary key of the table. the primary key uniquely identifies each item in the table, so that no two items can have the same key. dynamodb supports two different kinds of primary keys: partition key – a simple primary key, composed of one attribute known as the. Foreign key a foreign key is an attribute or combination of attribute in a relation whose value match a primary key in another relation. the table in which foreign key is created is called as dependent table. the table to which foreign key is refers is known as parent table.
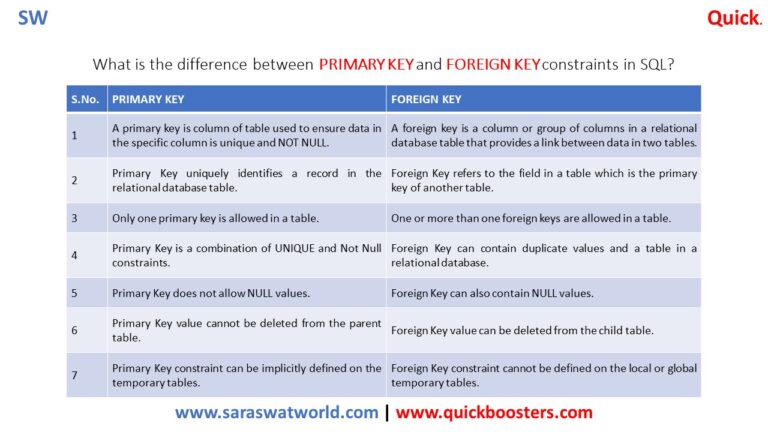
What Is The Difference Between Primary Key And Foreign Key In Sql Quickboosters A surrogate key is typically a numeric value. within sql server, microsoft allows you to define a column with an identity property to help generate surrogate key values. the primary key constraint uniquely identifies each record in a database table. primary keys must contain unique values. a primary key column cannot contain null values. Difference between candidate key vs primary key: ) both primary and candidate keys can uniquely identify records in a table on database. 2) both primary and candidate keys are has constraints unique and not null. 3) primary key or candidate keys can be either single column or combination of multiple columns in a table. When you create a table, in addition to the table name, you must specify the primary key of the table. the primary key uniquely identifies each item in the table, so that no two items can have the same key. dynamodb supports two different kinds of primary keys: partition key – a simple primary key, composed of one attribute known as the. Foreign key a foreign key is an attribute or combination of attribute in a relation whose value match a primary key in another relation. the table in which foreign key is created is called as dependent table. the table to which foreign key is refers is known as parent table.
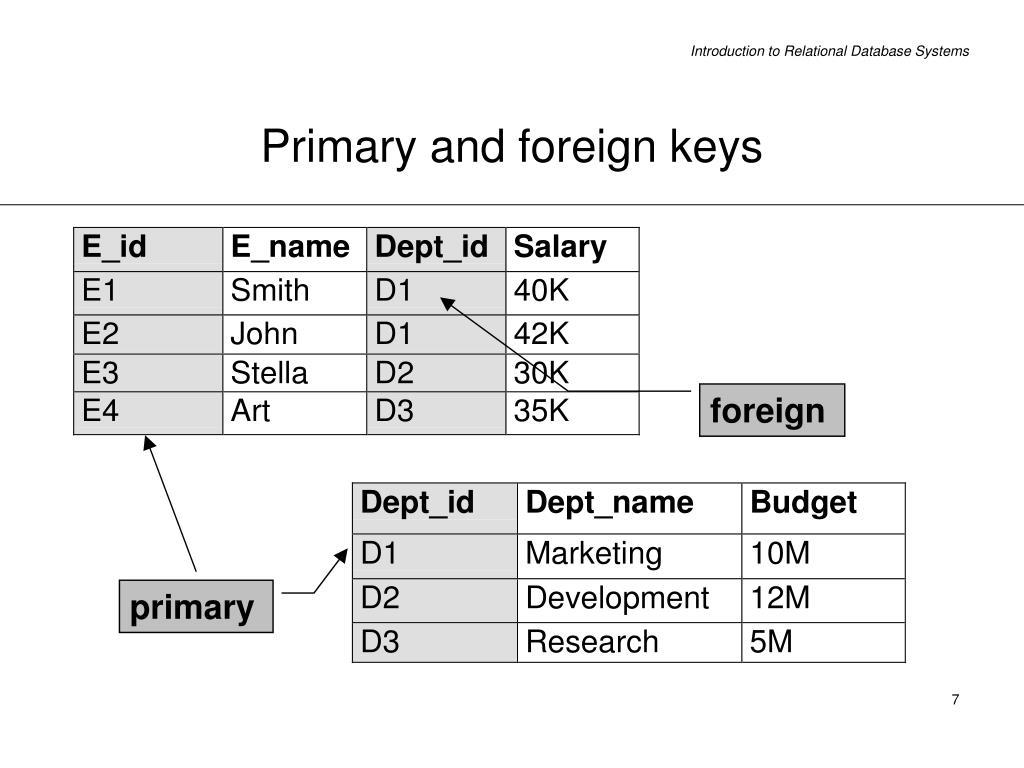
Ppt Introduction To Relational Database Systems Powerpoint Presentation Id 714913 When you create a table, in addition to the table name, you must specify the primary key of the table. the primary key uniquely identifies each item in the table, so that no two items can have the same key. dynamodb supports two different kinds of primary keys: partition key – a simple primary key, composed of one attribute known as the. Foreign key a foreign key is an attribute or combination of attribute in a relation whose value match a primary key in another relation. the table in which foreign key is created is called as dependent table. the table to which foreign key is refers is known as parent table.
Comments are closed.