Foramina In The Base Of The Adult Skull Internal Aspect Of Base Of Skull Orifices Foramina Of
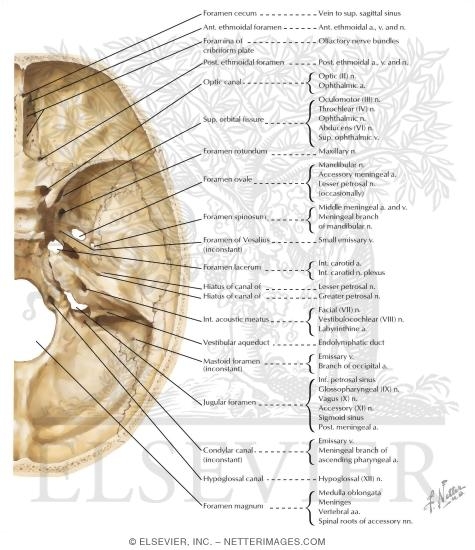
Foramina In The Base Of The Adult Skull Internal Aspect Of Base Of Skull Orifices Foramina Of Foraminal stenosis is like what happens to an electrical cord when you shut a door on it, wedging it between the door and frame. eventually, the pressure on the cord can damage it, affecting how it conducts electricity. likewise, foraminal stenosis can put pressure on affected nerves. The spinal canal houses your spinal cord. there are other openings on the stacked vertebrae called the foramina (singular foramen), where the nerve roots branch out of the spinal cord. at every level of the spine, a pair of spinal nerves exits the spinal column through the foramina.
Foramina In The Base Of The Adult Skull Internal Aspect Of Base Of Skull Orifices Foramina Of In human anatomy, a foramen is a natural opening or passage, with the plural form being foramina. found most often in bone, these openings are integral components of the skeletal structure. these passages vary in size and shape, depending on their location and the structures they accommodate. The skulls of vertebrates have foramina through which nerves, arteries, veins, and other structures pass. the human skull has many foramina, collectively referred to as the cranial foramina. Foraminal stenosis is the narrowing or tightening of the openings between the bones in your spine. these small openings are called the foramen. foraminal stenosis is a specific type of spinal. A foramen (pl. foramina) is an opening that allows the passage of structures from one region to another. in the skull base, there are numerous foramina that transmit cranial nerves, blood vessels and other structures – these are collectively referred to as the cranial foramina.
Foramina In The Base Of The Adult Skull Internal Aspect Of Base Of Skull Orifices Foramina Of Foraminal stenosis is the narrowing or tightening of the openings between the bones in your spine. these small openings are called the foramen. foraminal stenosis is a specific type of spinal. A foramen (pl. foramina) is an opening that allows the passage of structures from one region to another. in the skull base, there are numerous foramina that transmit cranial nerves, blood vessels and other structures – these are collectively referred to as the cranial foramina. Sciatic foramen either of two openings (the greater and smaller sciatic foramina), formed by the sacrotuberal and sacrospinal ligaments in the sciatic notch of the hip bone. A foramen (plural foramina) is an opening or hole through tissue, usually bone, allowing nerves and blood vessels to pass through. The human skull has numerous foramina through which cranial nerves, arteries, veins, and other structures pass. the skull bones that contain foramina include the frontal, ethmoid, sphenoid, maxilla, palatine, temporal, and occipital lobes. Foraminal refers to the openings between vertebrae that allow nerves to exit the spinal column, crucial for nerve function. foraminal spaces are critical components of the vertebral column. these openings, known as intervertebral foramina, are situated between adjacent vertebrae.

Skull Foramina Internal Aspect Diagram Quizlet Sciatic foramen either of two openings (the greater and smaller sciatic foramina), formed by the sacrotuberal and sacrospinal ligaments in the sciatic notch of the hip bone. A foramen (plural foramina) is an opening or hole through tissue, usually bone, allowing nerves and blood vessels to pass through. The human skull has numerous foramina through which cranial nerves, arteries, veins, and other structures pass. the skull bones that contain foramina include the frontal, ethmoid, sphenoid, maxilla, palatine, temporal, and occipital lobes. Foraminal refers to the openings between vertebrae that allow nerves to exit the spinal column, crucial for nerve function. foraminal spaces are critical components of the vertebral column. these openings, known as intervertebral foramina, are situated between adjacent vertebrae.
Comments are closed.