Foreign Exchange Management Act Fema Foreign Exchange Regulation Act Fera Banking Awareness

An Analysis Of The Evolution Of Foreign Exchange Regulation In India From Fera To Fema Pdf In this comprehensive video, afreen delves into the essential aspects of fema and fera, shedding light on their significance, evolution, and implications in the realm of foreign exchange. Subsequently, foreign exchange regulation act (fera) was enacted in 1947 which was later replaced with 'the foreign exchange regulation act, 1973' (fera). the act has been made effective from 1st june, 2000. this act enables management of foreign exchange reserves for the country.

What Exactly Is The Foreign Exchange Regulation Act Fera The foreign exchange management act (fema), enacted in 1999, replaced the foreign exchange regulation act (fera) to streamline and liberalize foreign exchange regulations in india. The shift from the foreign exchange regulation act (fera) to the foreign exchange management act (fema) in 1999 signifies a important transformation in india’s approach to foreign exchange governance. Fera stands for the foreign exchange regulation act. it was an indian law that came into effect in 1973 with the primary objective of regulating foreign exchange transactions and conserving the country’s foreign exchange resources. Foreign exchange regulation act, 1973 (fera) was replaced by the foreign management act, 1999 (fema). fema was enacted by parliament of india and it came into force on 1st june, 2000. there are a total of 49 sections divided into 7 chapters.

Foreign Exchange Management Act Fema Law Aimers Fera stands for the foreign exchange regulation act. it was an indian law that came into effect in 1973 with the primary objective of regulating foreign exchange transactions and conserving the country’s foreign exchange resources. Foreign exchange regulation act, 1973 (fera) was replaced by the foreign management act, 1999 (fema). fema was enacted by parliament of india and it came into force on 1st june, 2000. there are a total of 49 sections divided into 7 chapters. The foreign exchange management act (fema), enacted in 1999 to replace the restrictive foreign exchange regulation act (fera) of 1973, regulates foreign exchange transactions in india. The foreign exchange management act represents a landmark evolution in india’s approach to external sector regulation. by transitioning from the restrictive fera to the facilitative fema, india signaled its maturity as an economy confident enough to engage with global markets on more liberal terms. Fema replaced the more stringent and control oriented fera, which treated most foreign exchange violations as criminal offenses. fema adopts a more liberal and management based approach, treating violations as civil offenses, thereby enabling a more facilitative regulatory framework. In response to these changes and to facilitate smoother external trade and payments, fema was enacted in 1999, replacing fera. this act signified a transition from a regulatory to a management approach in handling foreign exchange, aligning with global economic practices.
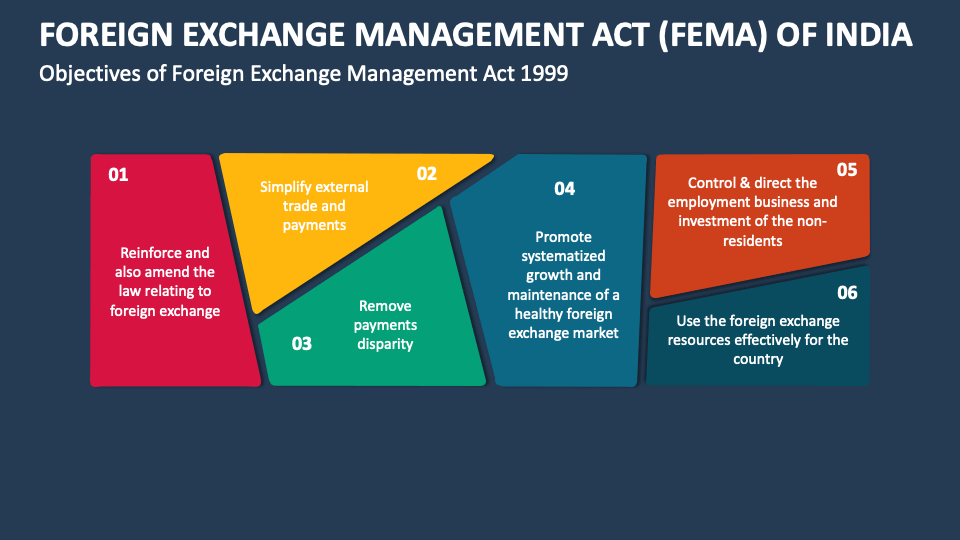
Foreign Exchange Management Act Fema Of India Powerpoint And Google Slides Template Ppt Slides The foreign exchange management act (fema), enacted in 1999 to replace the restrictive foreign exchange regulation act (fera) of 1973, regulates foreign exchange transactions in india. The foreign exchange management act represents a landmark evolution in india’s approach to external sector regulation. by transitioning from the restrictive fera to the facilitative fema, india signaled its maturity as an economy confident enough to engage with global markets on more liberal terms. Fema replaced the more stringent and control oriented fera, which treated most foreign exchange violations as criminal offenses. fema adopts a more liberal and management based approach, treating violations as civil offenses, thereby enabling a more facilitative regulatory framework. In response to these changes and to facilitate smoother external trade and payments, fema was enacted in 1999, replacing fera. this act signified a transition from a regulatory to a management approach in handling foreign exchange, aligning with global economic practices.
Comments are closed.