Graph Database Vs Relational Database Explained
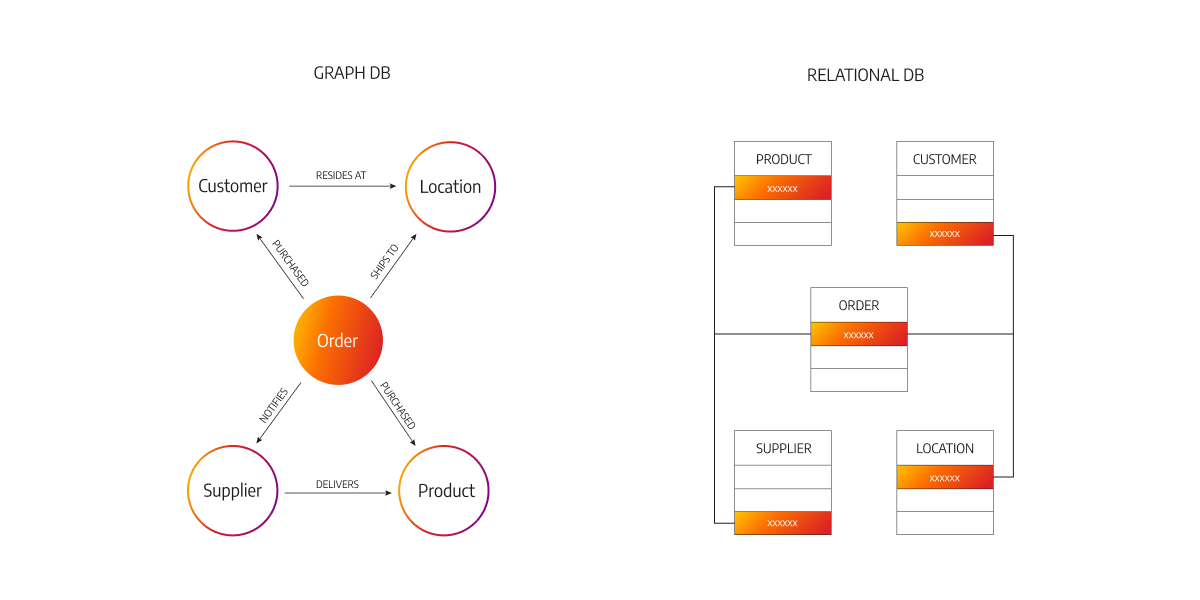
Graph Database Vs Relational Database 53 Off In the diagram below you can see the overall difference in what it takes a graph database vs relational database to assemble and process the same information. the above may be enough to give you a sense of the differences if you are just looking at the highest level. In this article, we will explain the key differences between graph databases and relational databases, giving a clearer understanding of which database type is best along with their advantages and disadvantages.
Graph Database Vs Relational Database 53 Off Relational databases organize data into structured tables with rows and columns, making them ideal for well defined and structured data. in contrast, graph databases employ nodes and edges to represent data relationships, a better fit for complex, interconnected data. Both graph and relational databases store information and represent relationships between data. however, the relational model prioritizes data entities while the graph model prioritizes relationships between the entities. Graph databases offer plenty of advantages for enterprises, but relational databases still top the market. both emphasize relationships between data, but how do they compare? relational databases are a staple across industries, but graph databases offer different capabilities that may fit enterprise needs better. This article explores the difference between relational database vs graph database, including structure, querying, scalability, and use cases.

Graph Database Vs Relational Database Graph databases offer plenty of advantages for enterprises, but relational databases still top the market. both emphasize relationships between data, but how do they compare? relational databases are a staple across industries, but graph databases offer different capabilities that may fit enterprise needs better. This article explores the difference between relational database vs graph database, including structure, querying, scalability, and use cases. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the key distinctions between relational databases and graph databases, helping you choose the right database model for your specific. Inspired by a small movie data set used by neo4j as a guided introduction to graph querying, we are going to look at side by side examples and equivalents of what a data model or query would look like in both a graph database, and a relational database. Unlike traditional relational databases that rely on tables, a graph database organizes data using nodes and edges. these nodes represent entities like people or objects, while edges depict the relationships between them. this structure allows for intricate and highly connected data representations. Relational databases efficiently handle large volumes of data by handling relationships between records through joins and utilizing a predefined structure (schema). graph databases, on the other hand, store relationships explicitly at the record level, making them suitable for scenarios with complex and dynamic relationships.

Graph Database Vs Relational Database In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the key distinctions between relational databases and graph databases, helping you choose the right database model for your specific. Inspired by a small movie data set used by neo4j as a guided introduction to graph querying, we are going to look at side by side examples and equivalents of what a data model or query would look like in both a graph database, and a relational database. Unlike traditional relational databases that rely on tables, a graph database organizes data using nodes and edges. these nodes represent entities like people or objects, while edges depict the relationships between them. this structure allows for intricate and highly connected data representations. Relational databases efficiently handle large volumes of data by handling relationships between records through joins and utilizing a predefined structure (schema). graph databases, on the other hand, store relationships explicitly at the record level, making them suitable for scenarios with complex and dynamic relationships.
Comments are closed.