How Did Early Humans Compare To Other Primates Teachnthrive

How Did Early Humans Compare To Other Primates Teachnthrive Though there are many ways in which early humans differed from other primates, it’s important to remember that they were still very similar. they shared a common ancestor with all other primates and had many of the same features. Well, if these groups are indeed early humans, then the human chimp ancestor must have formed very quickly, and just as quickly split to begin the human line; all within 1 or 2 million years.
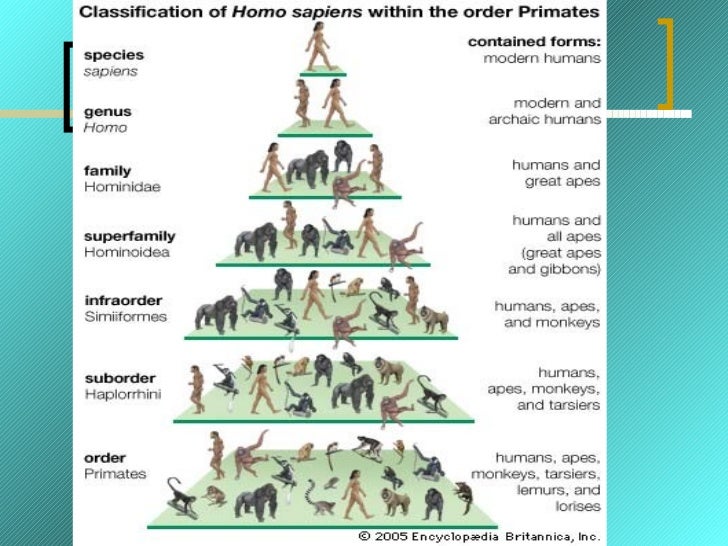
Humans And Other Primates Humans did not evolve from apes, gorillas or chimps. we share a common ancestor and have followed different evolutionary paths. Strong evidence supports the branching of the human lineage from the one that produced great apes (orangutans, chimpanzees, bonobos, and gorillas) in africa sometime between 6 and 7 million years ago. evidence of toolmaking dates to about 3.3 million years ago in kenya. Many primates live in complex social groups, displaying extended periods of parental care, allowing offspring more time to develop and learn. the first true primates. the earliest evidence of primate like mammals, often referred to as proto primates, dates back approximately 66 million years to the late paleocene epoch. The first true primates date to about 55 mya in the eocene epoch. they were found in north america, europe, asia, and africa. these early primates resembled present day prosimians such as lemurs. evolutionary changes continued in these early primates, with larger brains and eyes, and smaller muzzles being the trend.
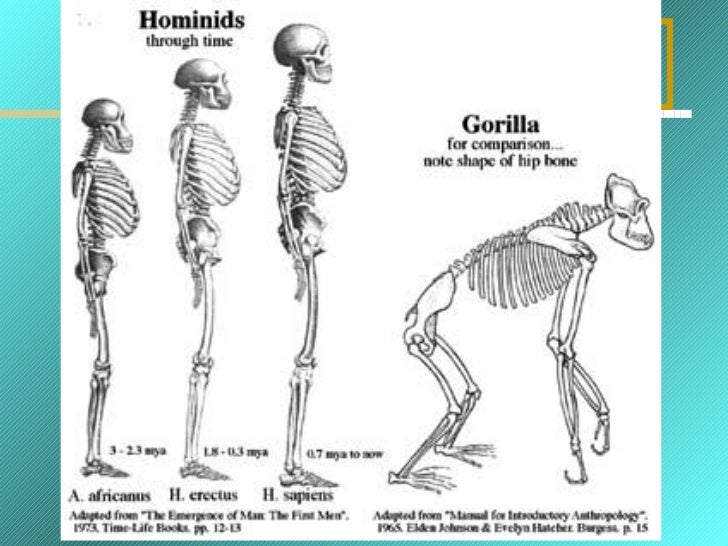
Humans And Other Primates Many primates live in complex social groups, displaying extended periods of parental care, allowing offspring more time to develop and learn. the first true primates. the earliest evidence of primate like mammals, often referred to as proto primates, dates back approximately 66 million years to the late paleocene epoch. The first true primates date to about 55 mya in the eocene epoch. they were found in north america, europe, asia, and africa. these early primates resembled present day prosimians such as lemurs. evolutionary changes continued in these early primates, with larger brains and eyes, and smaller muzzles being the trend. Humans are the only primate capable of living in virtually any environment of the world, all because of culture, our learned behaviors. humans belong to the order primates. all living primates, including humans, evolved from earlier primates that are now extinct. In the first part of this review, several differences between humans' and other primates' brains were presented. they may explain why other primates do not develop a similar language to ours. Early primates left humans an anatomical legacy: arboreal adaptations such as grasping hands, fingernails, and binocular vision. they also left a legacy of sociality, as most living primates form long term social bonds that include mutual grooming. Human evolution. the family hominidae of order primates includes chimpanzees and humans. evidence from the fossil record and from a comparison of human and chimpanzee dna suggests that humans and chimpanzees diverged from a common hominoid ancestor approximately 6 million years ago.
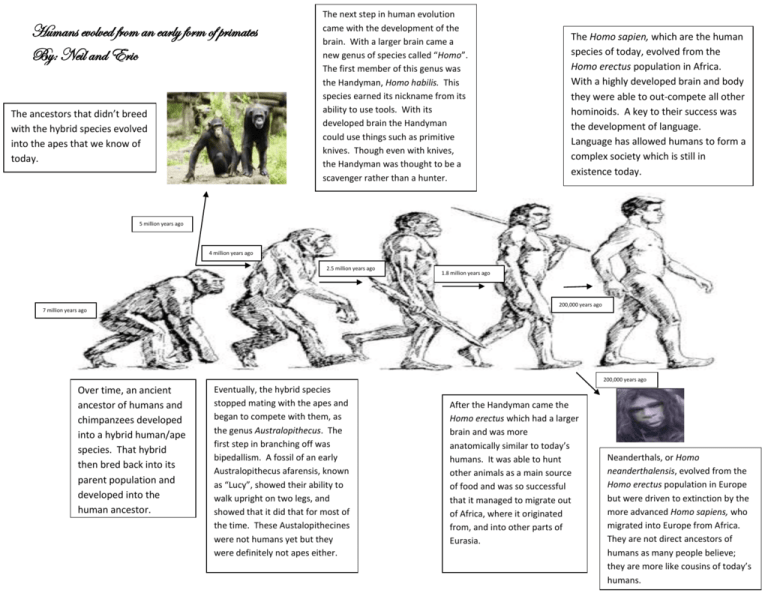
Human Evolution From Primates To Homo Sapiens Humans are the only primate capable of living in virtually any environment of the world, all because of culture, our learned behaviors. humans belong to the order primates. all living primates, including humans, evolved from earlier primates that are now extinct. In the first part of this review, several differences between humans' and other primates' brains were presented. they may explain why other primates do not develop a similar language to ours. Early primates left humans an anatomical legacy: arboreal adaptations such as grasping hands, fingernails, and binocular vision. they also left a legacy of sociality, as most living primates form long term social bonds that include mutual grooming. Human evolution. the family hominidae of order primates includes chimpanzees and humans. evidence from the fossil record and from a comparison of human and chimpanzee dna suggests that humans and chimpanzees diverged from a common hominoid ancestor approximately 6 million years ago.

Earliest Primate Evolution Fossils And Anthropoids Course Hero Early primates left humans an anatomical legacy: arboreal adaptations such as grasping hands, fingernails, and binocular vision. they also left a legacy of sociality, as most living primates form long term social bonds that include mutual grooming. Human evolution. the family hominidae of order primates includes chimpanzees and humans. evidence from the fossil record and from a comparison of human and chimpanzee dna suggests that humans and chimpanzees diverged from a common hominoid ancestor approximately 6 million years ago.

Study Humans Primates Age In Similar Ways Cbs News
Comments are closed.