How To Find The Domain Of A Function
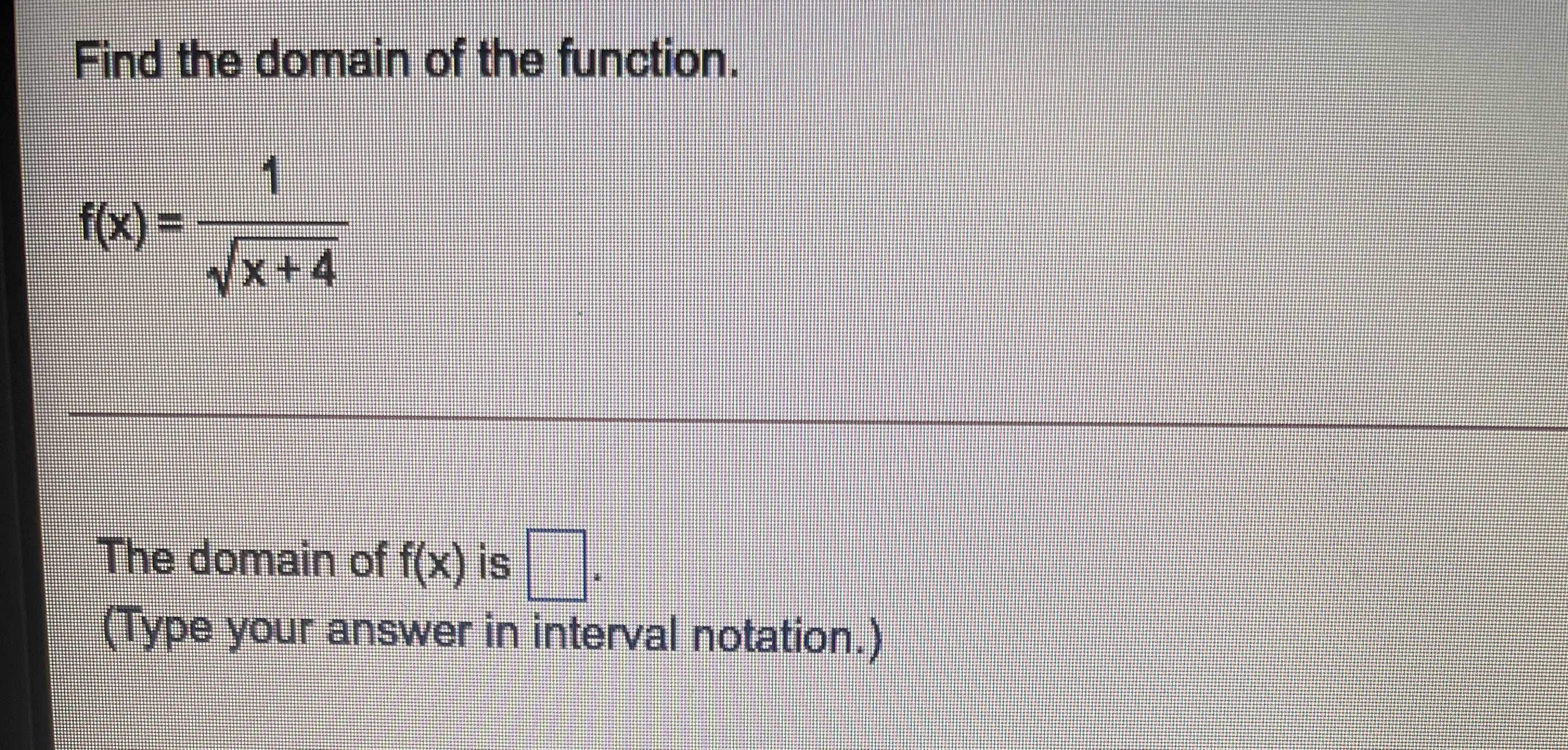
Find The Domain Of The Function F X Fra Cameramath If you want to know how to find the domain of a function in a variety of situations, just follow these steps. the domain of a function is the set of input values (x) for which the function produces an output value (y). solve for the domain depending on things like whether there is a variable in the denominator or inside a radical sign. Learn how to find the domain of a function for different types of functions, such as linear, rational, and square root. follow the steps to identify the function type, check for restrictions, and write the domain in interval notation.

How To Find The Domain Of A Function K 12 Math Problems The domain of a function is the set of all possible input values (usually x) that the function can accept without causing any issues, such as division by zero or taking the square root of a negative number. How do i find domain of function? to find the domain of a function, consider any restrictions on the input values that would make the function undefined, including dividing by zero, taking the square root of a negative number, or taking the logarithm of a negative number. Functions assign outputs to inputs. the domain of a function is the set of all possible inputs for the function. for example, the domain of f (x)=x² is all real numbers, and the domain of g (x)=1 x is all real numbers except for x=0. we can also define special functions whose domains are more limited. want to join the conversation?. This algebra video tutorial explains how to find the domain of a function that contains radicals, fractions, and square roots in the denominator using interv.

6 Ways To Find The Domain Of A Function Wikihow Functions assign outputs to inputs. the domain of a function is the set of all possible inputs for the function. for example, the domain of f (x)=x² is all real numbers, and the domain of g (x)=1 x is all real numbers except for x=0. we can also define special functions whose domains are more limited. want to join the conversation?. This algebra video tutorial explains how to find the domain of a function that contains radicals, fractions, and square roots in the denominator using interv. In algebra, every function can be represented as a graph on the coordinate plane. the graph of a function provides a visually representation of how the function behaves and gives you important information—including its domain and range. Let’s turn our attention to finding the domain of a function whose equation is provided. oftentimes, finding the domain of such functions involves remembering three different forms. first, if the function has no denominator or an even root, consider whether the domain could be all real numbers. What is the domain of the function f (x) = 2 (7x – 1) ? the domain means what real number can you plug in that would still make the function work. for this case, we have to worry about the denominator so that it does not equal 0, so we solve the following. 7x – 1 = 0, 7x = 1, x = 1 7, so when x ≠ 1 7 the function will work. Learn how to find the domain of a function without the graph by looking for the bad x values that make the function undefined. see examples with fractions, square roots, and absolute values.
Comments are closed.