How To Read Topographical Maps Zone Numbers And Coordinates

How To Read Topographical Maps Zone Numbers And Coordinates To read topographic maps, look at the thicker contour lines and the number next to them to determine the elevation. you can also figure out the elevation change by looking at the space between the contour lines. For consistency, the top off a topographical maps is oriented to true north (which is not the same as magnetic north). in other words, unless clearly indicated otherwise, it is safe to assume that the top of the map represents north, the right side east, the bottom south, and the left west.

How To Read A Topographical Map For Hiking A topo map is an indispensable navigational tool, but only if you know how to read it. in this article, we'll teach you the basics. Master utm on topo maps: identify zones, read eastings and northings, plot precise coordinates, and integrate compass and gps for pinpoint accuracy. Learn how the utm grid system works and how to read it on usgs topographic maps. master map coordinates, navigation, and spatial accuracy using universal transverse mercator today. Utm zones are numbered consecutively beginning with zone 1, which includes the westernmost point of alaska, and progress eastward to zone 19, which includes maine. if utm ticks are shown on a usgs topographic map, the zone is indicated in the credit legend in the lower left corner of the map collar.

How To Read Topographic Maps Topozone Pdf Topography Contour Line Learn how the utm grid system works and how to read it on usgs topographic maps. master map coordinates, navigation, and spatial accuracy using universal transverse mercator today. Utm zones are numbered consecutively beginning with zone 1, which includes the westernmost point of alaska, and progress eastward to zone 19, which includes maine. if utm ticks are shown on a usgs topographic map, the zone is indicated in the credit legend in the lower left corner of the map collar. The fi rst features usually noticed on a topographic map are the area features, such as vegetation (green), water (blue), and densely built up areas (gray or red). The earth is divided into 60 (numbered 1 – 60) zones each 6º of longitude wide, starting at the international date line, and extends from 80º s to 84º n latitude. in polar regions the universal polar stereographic system is used. Each grid is identified by a number across the top called the zone number and a letter down the right hand side called the zone designator. for example, phoenix arizona is in utm grid 12 s. every spot within a zone can be defined by a coordinate system that uses meters. The next step in reading topographic maps is learning the elevations. elevations are provided on some of the brown contour lines. those are the darker lines, called index lines, which have round numbers (hundreds for example).
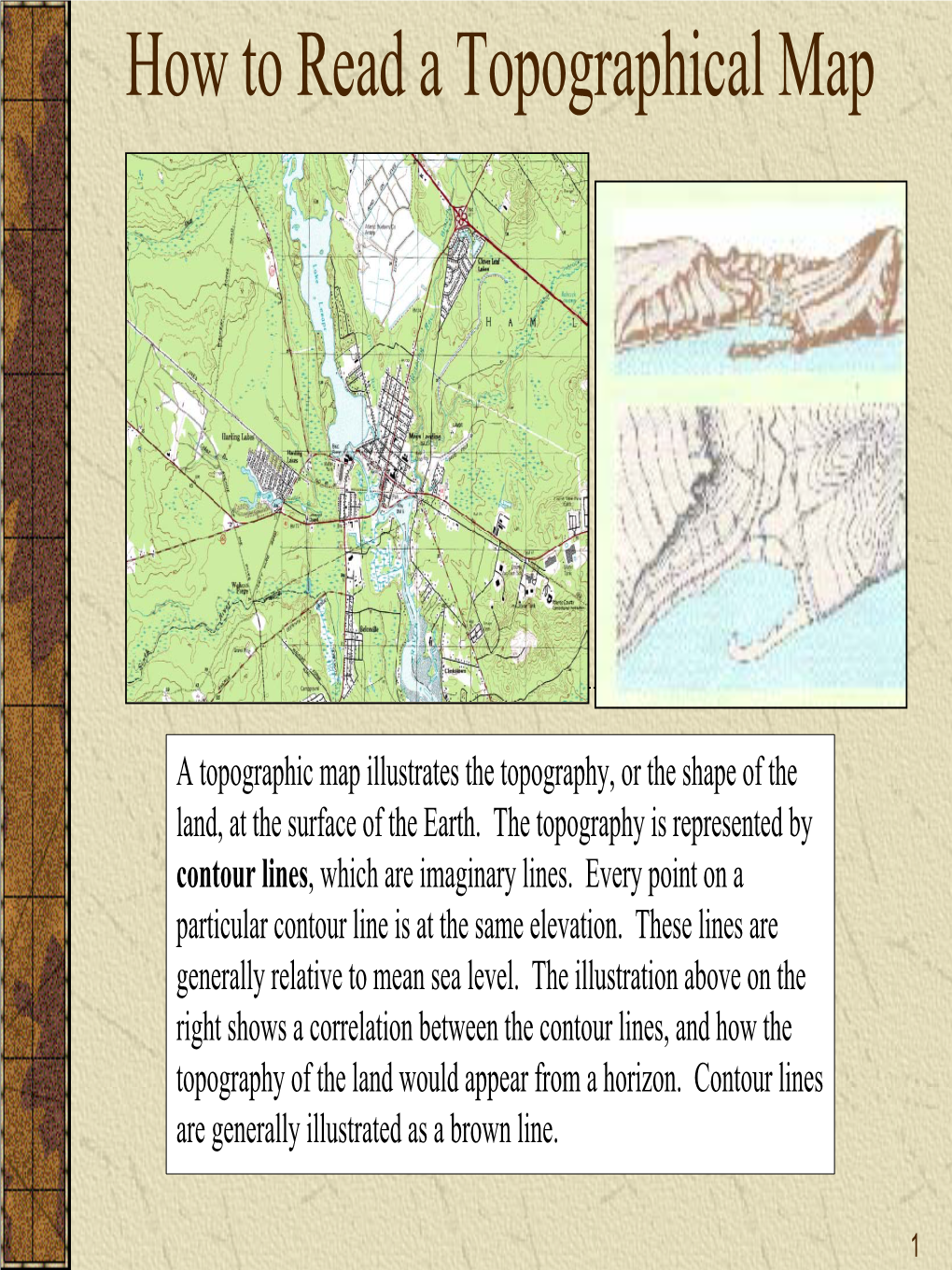
How To Read A Topographical Map Docslib The fi rst features usually noticed on a topographic map are the area features, such as vegetation (green), water (blue), and densely built up areas (gray or red). The earth is divided into 60 (numbered 1 – 60) zones each 6º of longitude wide, starting at the international date line, and extends from 80º s to 84º n latitude. in polar regions the universal polar stereographic system is used. Each grid is identified by a number across the top called the zone number and a letter down the right hand side called the zone designator. for example, phoenix arizona is in utm grid 12 s. every spot within a zone can be defined by a coordinate system that uses meters. The next step in reading topographic maps is learning the elevations. elevations are provided on some of the brown contour lines. those are the darker lines, called index lines, which have round numbers (hundreds for example).

Solution How To Read A Topographical Map Studypool Each grid is identified by a number across the top called the zone number and a letter down the right hand side called the zone designator. for example, phoenix arizona is in utm grid 12 s. every spot within a zone can be defined by a coordinate system that uses meters. The next step in reading topographic maps is learning the elevations. elevations are provided on some of the brown contour lines. those are the darker lines, called index lines, which have round numbers (hundreds for example).
Comments are closed.