Laws Of Exponents Product And Quotient Rules Properties Of Exponents Congruent Math

Laws Of Exponents Product And Quotient Rules Properties Of Exponents Congruent Math Exponent rules are those laws that are used for simplifying expressions with exponents. learn about exponent rules, the zero rule of exponent, the negative rule of exponent, the product rule of exponent, and the quotient rule of exponent with the solved examples, and practice questions. Use the guided notes to introduce the product and quotient rules in the properties of exponents. walk through the key points of the topic of the guided notes including keeping the base the same and adding the powers when multiplying exponents, and keeping the base the same and subtracting the powers when dividing exponents.

Laws Of Exponents Product And Quotient Rules Properties Of Exponents Congruent Math We need a more sophisticated way in multiplying expressions with exponents. hence, taking a look at example 6.1.1 , we can see the result is a5. notice we could have obtained this answer without expanding but by simply adding the exponents: a3 ⋅ a2 = a3 2 = a5. this is called the product rule of exponents. Exponents rules; exponents calculator; what is an exponent. the base a raised to the power of n is equal to the multiplication of a, n times: a n = a × a × × a n times. a is the base and n is the exponent. examples. 3 1 = 3. 3 2 = 3 × 3 = 9. 3 3 = 3 × 3 × 3 = 27. 3 4 = 3 × 3 × 3 × 3 = 81. 3 5 = 3 × 3 × 3 × 3 × 3 = 243. exponents. Exponent rules, also known as ‘laws of exponents’ or ‘properties of exponents, ’ are certain rules that help us to simplify expressions involving exponents that can be decimal numbers, fractions, or irrational numbers. it states that when we multiply two expressions with the same base, we add their exponents. mathematically,. To simplify such an expression, we use the power rule of exponents.
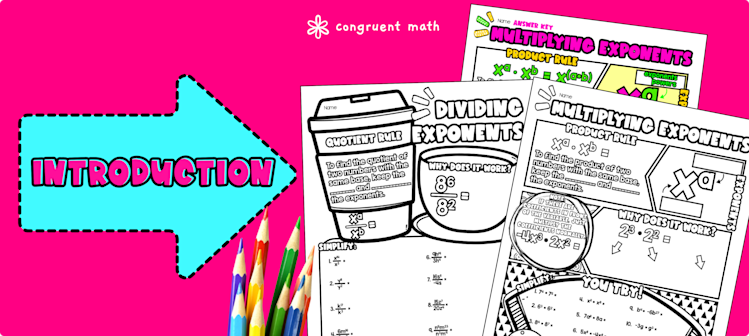
Laws Of Exponents Product And Quotient Rules Properties Of Exponents Congruent Math Exponent rules, also known as ‘laws of exponents’ or ‘properties of exponents, ’ are certain rules that help us to simplify expressions involving exponents that can be decimal numbers, fractions, or irrational numbers. it states that when we multiply two expressions with the same base, we add their exponents. mathematically,. To simplify such an expression, we use the power rule of exponents. This free guide to the rules of exponents including the negative exponent rule, product of powers rule with exponents, and other rules of exponents. each rule includes an explanation and examples. this guide also include a free printable exponent rules pdf guide that you can use as a reference. Laws explained. the first three laws above (x 1 = x, x 0 = 1 and x 1 = 1 x) are just part of the natural sequence of exponents. have a look at this:. There are many laws of exponents (often called the rules of exponents or properties of exponents) that are helpful in calculating values with high powers. solving two or more exponents is possible through the use of the exponent rules. The quotient property of exponents asks the questions: “where are there more copies of the base? how many more?” we’re looking for the difference in how many bases are in the numerator versus the denominator, so we subtract the exponents.
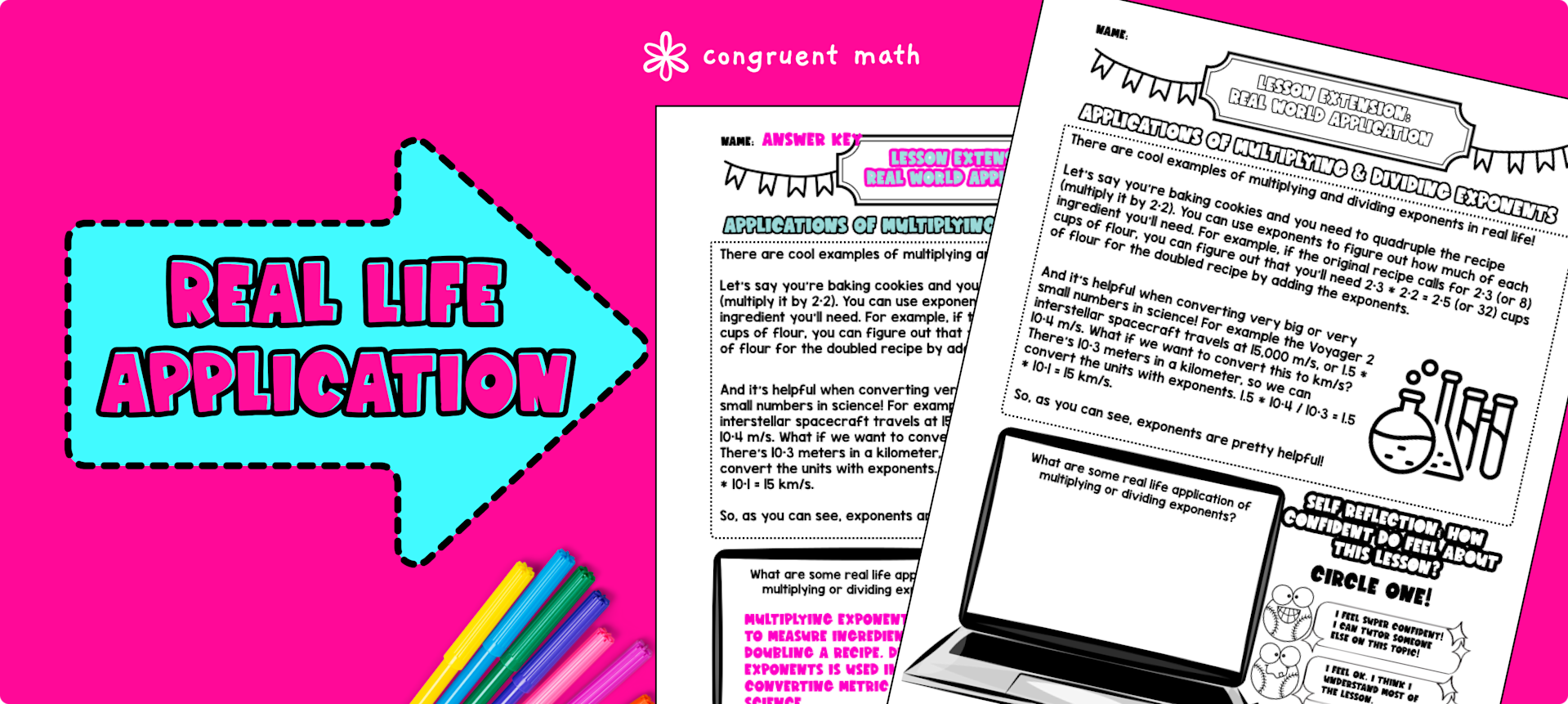
Laws Of Exponents Product And Quotient Rules Properties Of Exponents Congruent Math This free guide to the rules of exponents including the negative exponent rule, product of powers rule with exponents, and other rules of exponents. each rule includes an explanation and examples. this guide also include a free printable exponent rules pdf guide that you can use as a reference. Laws explained. the first three laws above (x 1 = x, x 0 = 1 and x 1 = 1 x) are just part of the natural sequence of exponents. have a look at this:. There are many laws of exponents (often called the rules of exponents or properties of exponents) that are helpful in calculating values with high powers. solving two or more exponents is possible through the use of the exponent rules. The quotient property of exponents asks the questions: “where are there more copies of the base? how many more?” we’re looking for the difference in how many bases are in the numerator versus the denominator, so we subtract the exponents.
Comments are closed.