Map Interface In Java Javadsa
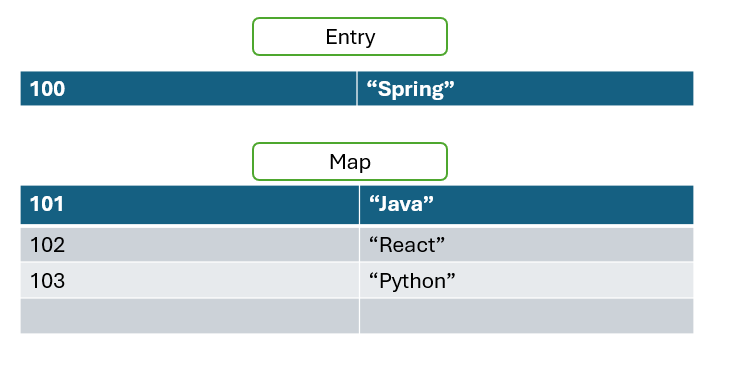
Map Interface In Java Javadsa An object that maps keys to values. a map cannot contain duplicate keys; each key can map to at most one value. this interface takes the place of the dictionary class, which was a totally abstract class rather than an interface. The map data structure in java is implemented by two interfaces: map interface; sortedmap interface; the three primary classes that implement these interfaces are, hashmap; treemap; linkedhashmap; now, let us go through a simple example first to understand the concept. example: java.
Map Interface In Java Javadsa In this tutorial, we will learn about the java map interface and its methods. in java, elements of map are stored in key value pairs. keys are unique values associated with individual values. To create a map in java, first, we have to include the interface in our program. we can use one of the following statements in the program to import the map functionality. we need to instantiate a concrete implementation of the map as it is an interface. the following statements create a map in java. The map interface is a part of the java collections framework and is used to store key value pairs. each key must be unique, but values can be duplicated. a map is useful when you want to associate a key (like a name or id) with a value (like an age or description). common classes that implement map:. The map interface in java is a way of representing a mapping between a key and a value. it is often misunderstood to be part of the collection interface. this article will help you understand how maps work in java.
Map Interface In Java Javadsa The map interface is a part of the java collections framework and is used to store key value pairs. each key must be unique, but values can be duplicated. a map is useful when you want to associate a key (like a name or id) with a value (like an age or description). common classes that implement map:. The map interface in java is a way of representing a mapping between a key and a value. it is often misunderstood to be part of the collection interface. this article will help you understand how maps work in java. The map interface provides three collection views, which allow a map's contents to be viewed as a set of keys, collection of values, or set of key value mappings. the order of a map is defined as the order in which the iterators on the map's collection views return their elements. In java, map is an interface in the collections framework that represents a mapping between keys and values. each key is associated with exactly one value, creating what's sometimes called a "dictionary" or "associative array" in other programming languages. Java map interface: java map interface tutorial presents you with the ultimate learnings about the concept. map interface in java offers methods for storing values based on a key basis. Hashmap class extends abstractmap and implements map interface. it uses a hashtable to store the map. this allows the execution time of get() and put() to remain same.
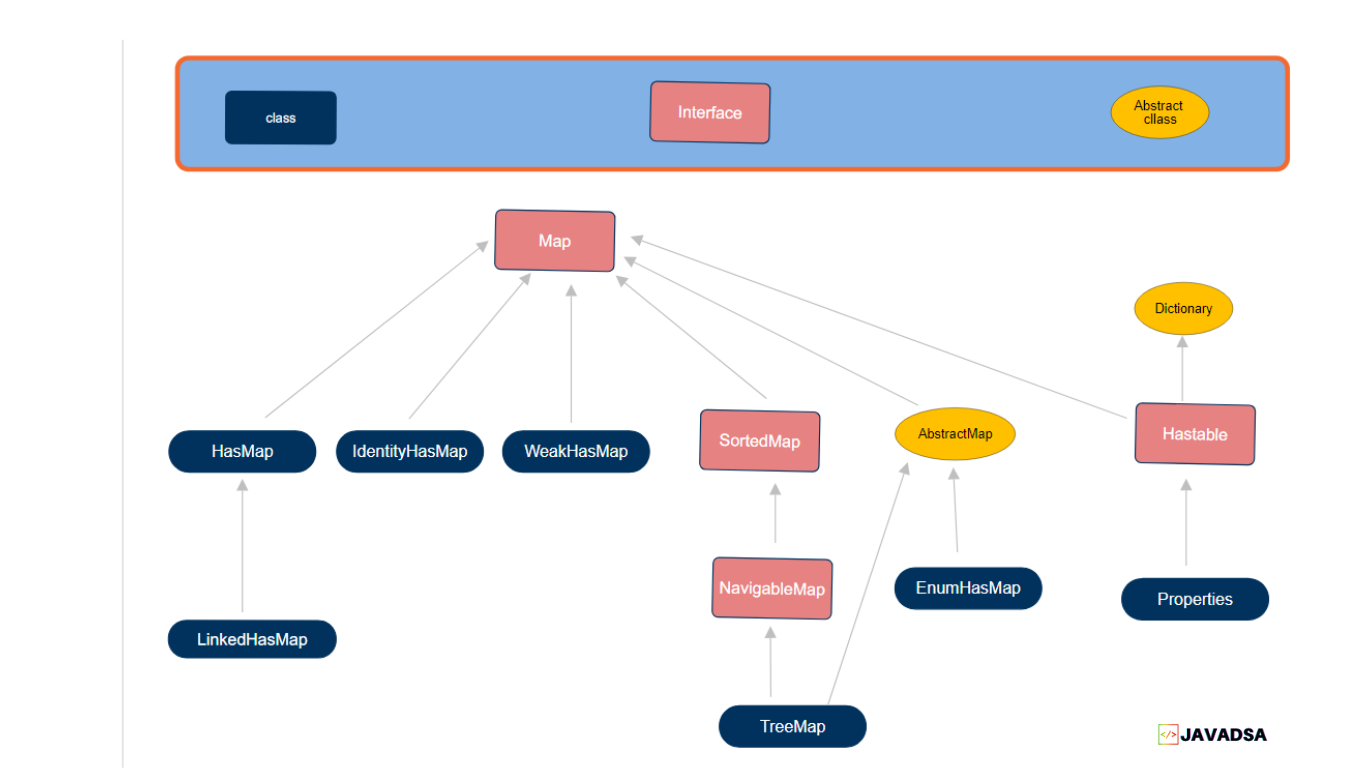
Map Interface In Java Javadsa The map interface provides three collection views, which allow a map's contents to be viewed as a set of keys, collection of values, or set of key value mappings. the order of a map is defined as the order in which the iterators on the map's collection views return their elements. In java, map is an interface in the collections framework that represents a mapping between keys and values. each key is associated with exactly one value, creating what's sometimes called a "dictionary" or "associative array" in other programming languages. Java map interface: java map interface tutorial presents you with the ultimate learnings about the concept. map interface in java offers methods for storing values based on a key basis. Hashmap class extends abstractmap and implements map interface. it uses a hashtable to store the map. this allows the execution time of get() and put() to remain same.
Comments are closed.