Metallic Susceptibility Artifact On Mri
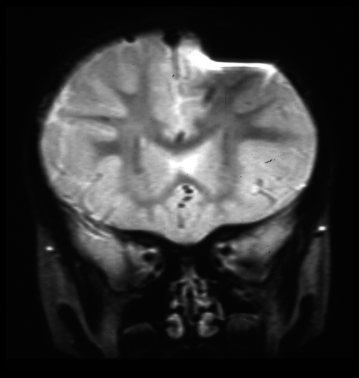
Susceptibility Artifact Questions And Answers In Mri Examples of ferromagnetic metals include iron, nickel, and cobalt, all of which distort magnetic fields, thereby causing severe artifacts on mr images. Explore magnetic susceptibility in mri: learn its physics, impact on image quality, and techniques to mitigate metal related artifacts.
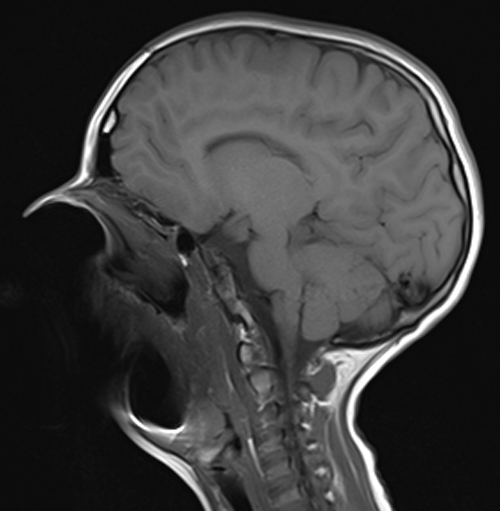
Susceptibility Artifact Questions And Answers In Mri In this article, we review some of the basic principles of imaging, and how metal induced susceptibility artifacts originate in images. we describe common ways to reduce or modify artifacts using readily available imaging techniques. A gallery of various susceptibility artifacts is provided below (click on any picture to enlarge and read caption). since ferromagnetic materials have the largest susceptibilities, field distortions and mr artifacts are usually prominent around metal objects and implants. When a material with high susceptibility, like blood or metal, is placed in a magnetic field, it distorts the field around it, like a pebble in a pond. this magnetic distortion creates susceptibility artifacts, which are those pesky distortions and signal dropouts we see on mri images. The presence of any metal (ferromagnetic or not) causes large distortions in the magnetic field and significant susceptibility artifacts. the range of signal loss depends on the metal and on the pulse sequence (spin echo, gradient echo).
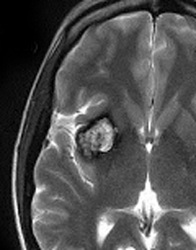
Susceptibility Artifact Questions And Answers In Mri When a material with high susceptibility, like blood or metal, is placed in a magnetic field, it distorts the field around it, like a pebble in a pond. this magnetic distortion creates susceptibility artifacts, which are those pesky distortions and signal dropouts we see on mri images. The presence of any metal (ferromagnetic or not) causes large distortions in the magnetic field and significant susceptibility artifacts. the range of signal loss depends on the metal and on the pulse sequence (spin echo, gradient echo). We reviewed the literature about overcoming artifacts from metallic orthopaedic implants at high field strength mri imaging and multi detector ct. the evolution of multichannel ct has made available new techniques that can help minimizing the severe beam hardening artifacts. The main reasons for artifacts in mr imaging with metal implants are due to differences in the magnetic susceptibility between metal implants and the surrounding tissue. Artifacts are caused by a variety of factors that may be patient related, such as voluntary and physiologic motion, metallic implants or foreign bodies. finite sampling, k space encoding, and fourier transformation may cause aliasing and gibbs artifact. Spin echo techniques are employed to mitigate metal artifacts in magnetic resonance imaging (mri). by utilizing a 180° refocusing pulse, these techniques counteract signal loss caused by rapid variations in the static magnetic field near metal implants or objects.
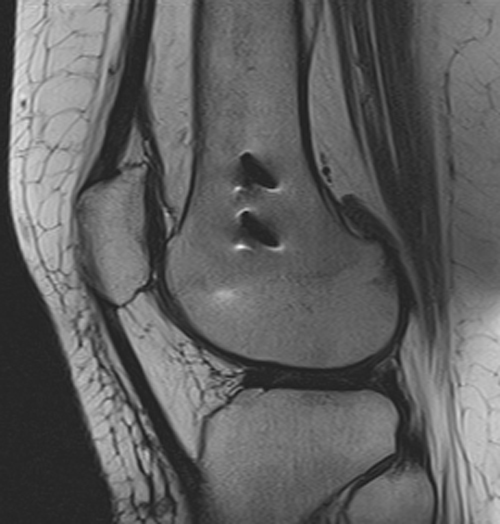
Susceptibility Artifact Questions And Answers In Mri We reviewed the literature about overcoming artifacts from metallic orthopaedic implants at high field strength mri imaging and multi detector ct. the evolution of multichannel ct has made available new techniques that can help minimizing the severe beam hardening artifacts. The main reasons for artifacts in mr imaging with metal implants are due to differences in the magnetic susceptibility between metal implants and the surrounding tissue. Artifacts are caused by a variety of factors that may be patient related, such as voluntary and physiologic motion, metallic implants or foreign bodies. finite sampling, k space encoding, and fourier transformation may cause aliasing and gibbs artifact. Spin echo techniques are employed to mitigate metal artifacts in magnetic resonance imaging (mri). by utilizing a 180° refocusing pulse, these techniques counteract signal loss caused by rapid variations in the static magnetic field near metal implants or objects.
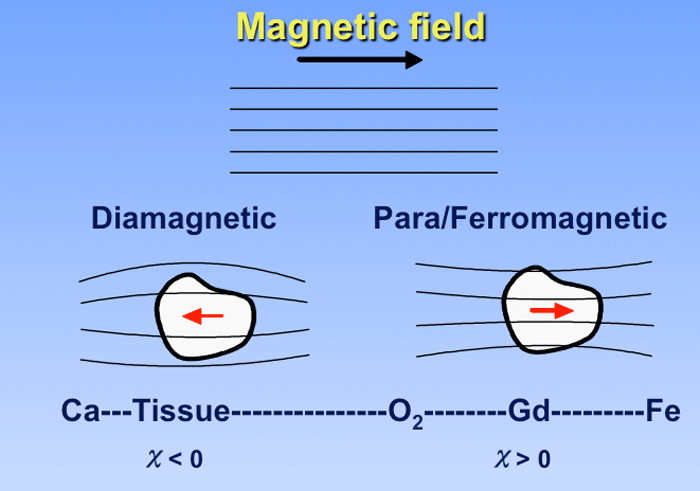
Susceptibility Artifact Questions And Answers In Mri Artifacts are caused by a variety of factors that may be patient related, such as voluntary and physiologic motion, metallic implants or foreign bodies. finite sampling, k space encoding, and fourier transformation may cause aliasing and gibbs artifact. Spin echo techniques are employed to mitigate metal artifacts in magnetic resonance imaging (mri). by utilizing a 180° refocusing pulse, these techniques counteract signal loss caused by rapid variations in the static magnetic field near metal implants or objects.
Comments are closed.