Normal Distribution Explained With Examples

Normal Distribution Notes And Examples Pdf In a normal distribution, data is symmetrically distributed with no skew. when plotted on a graph, the data follows a bell shape, with most values clustering around a central region and tapering off as they go further away from the center. normal distributions are also called gaussian distributions or bell curves because of their shape. Normal distribution, also known as the gaussian distribution, is a continuous probability distribution that is symmetric about the mean, depicting that data near the mean are more frequent in occurrence than data far from the mean.
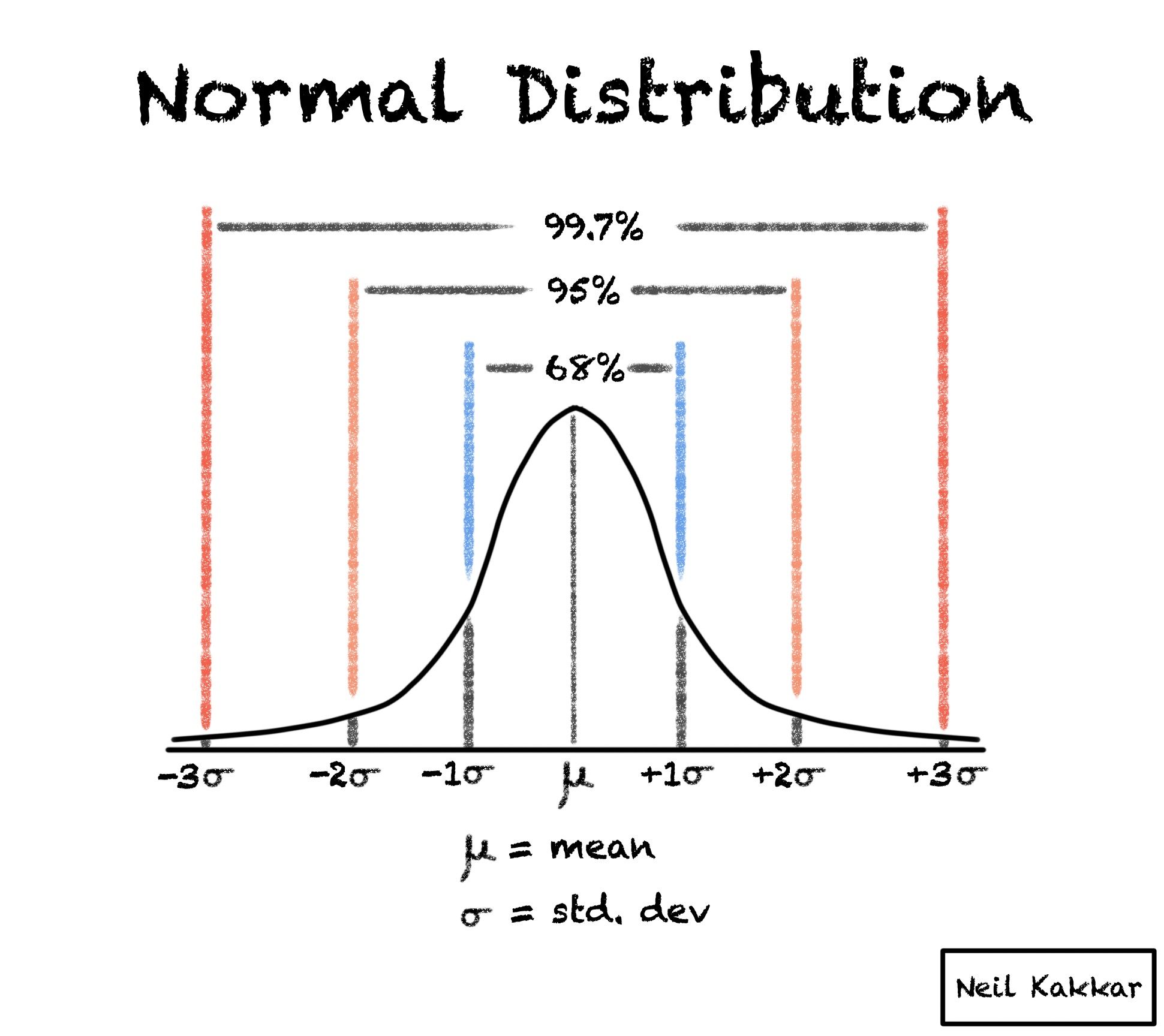
Normal Distribution Explained This tutorial provides several real life examples of the normal distribution, the most popular distribution in all of statistics. But in many cases the data tends to be around a central value, with no bias left or right, and it gets close to a "normal distribution" like this: the blue curve is a normal distribution. the yellow histogram shows some data that follows it closely, but not perfectly (which is usual). A bell shaped curve, also known as a normal distribution or gaussian distribution, is a symmetrical probability distribution in statistics. it represents a graph where the data clusters around the mean, with the highest frequency in the center, and decreases gradually towards the tails. In probability theory and statistics, a normal distribution or gaussian distribution is a type of continuous probability distribution for a real valued random variable.
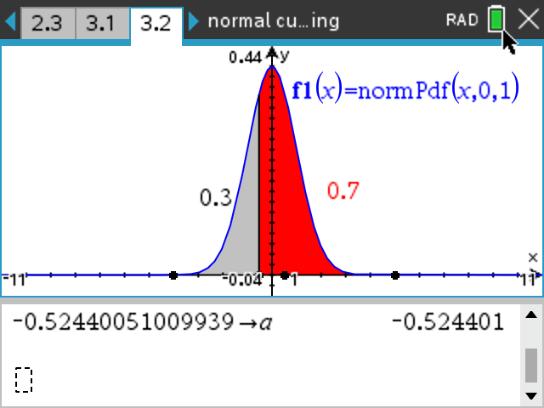
Normal Distribution Examples And Exam Questions Mathexams A bell shaped curve, also known as a normal distribution or gaussian distribution, is a symmetrical probability distribution in statistics. it represents a graph where the data clusters around the mean, with the highest frequency in the center, and decreases gradually towards the tails. In probability theory and statistics, a normal distribution or gaussian distribution is a type of continuous probability distribution for a real valued random variable. Learn about standard normal distribution, its properties, and how to calculate probabilities using z tables, charts, and real world examples. standard normal distribution explained with real world examples | codecademy. Normal distribution in real life plays a crucial role in understanding this phenomenon. from heights and test scores to errors in measurements, this statistical concept helps explain how variables behave under natural conditions. Learn how to calculate and interpret the normal distribution for continuous random variables. all this with some practical questions and answers. Normal distribution follows the central limit theory which states that various independent factors influence a particular trait. when these all independent factors contribute to a phenomenon, their normalized sum tends to result in a gaussian distribution.
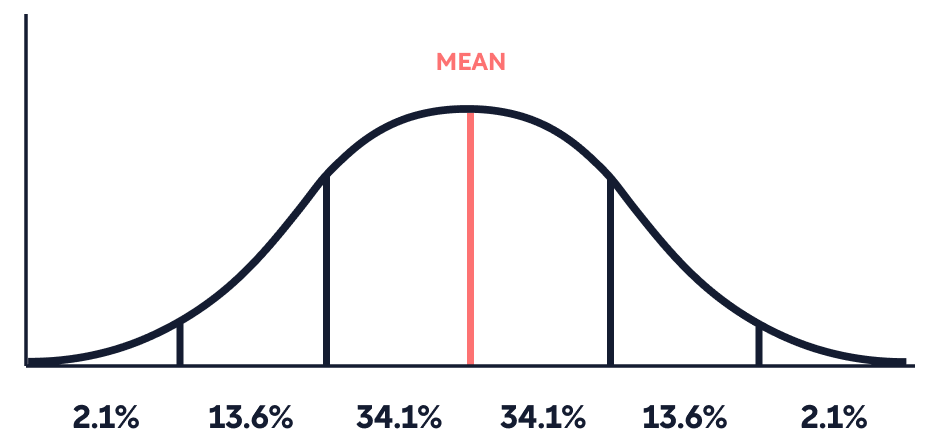
Normal Distribution Explained With Examples Shortform Books Learn about standard normal distribution, its properties, and how to calculate probabilities using z tables, charts, and real world examples. standard normal distribution explained with real world examples | codecademy. Normal distribution in real life plays a crucial role in understanding this phenomenon. from heights and test scores to errors in measurements, this statistical concept helps explain how variables behave under natural conditions. Learn how to calculate and interpret the normal distribution for continuous random variables. all this with some practical questions and answers. Normal distribution follows the central limit theory which states that various independent factors influence a particular trait. when these all independent factors contribute to a phenomenon, their normalized sum tends to result in a gaussian distribution.

Examples Of Normal Distribution In Real Life Explained Learn how to calculate and interpret the normal distribution for continuous random variables. all this with some practical questions and answers. Normal distribution follows the central limit theory which states that various independent factors influence a particular trait. when these all independent factors contribute to a phenomenon, their normalized sum tends to result in a gaussian distribution.
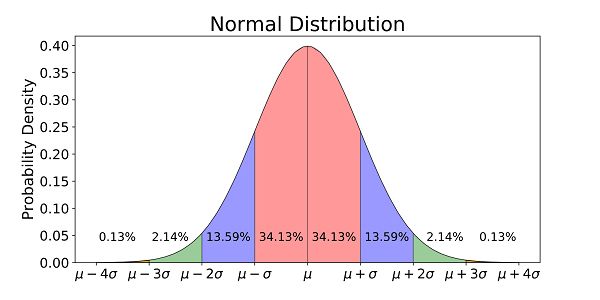
9 Real Life Examples Of Normal Distribution Studiousguy
Comments are closed.