Optics Ordering Points To Identify The Clustering Structure Clustering Example In Python
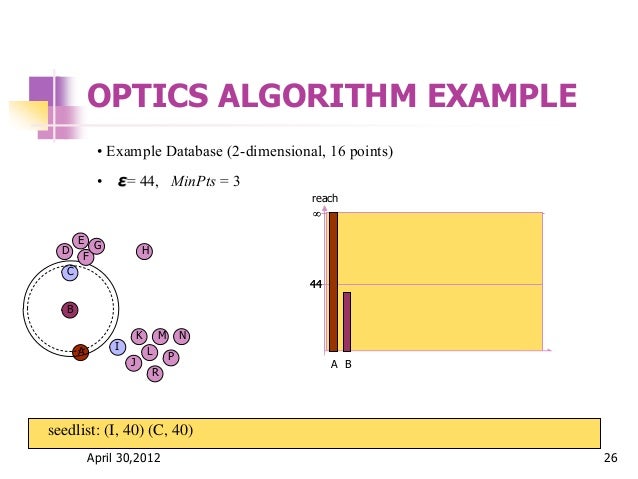
Optics Ordering Points To Identify The Clustering Structure Optics (ordering points to identify the clustering structure) is a clustering algorithm used to find clusters of different shapes and densities in a dataset. it works like dbscan but gives better results when data has clusters with varying densities. why we use optics instead of dbscan?. Estimate clustering structure from vector array. optics (ordering points to identify the clustering structure), closely related to dbscan, finds core samples of high density and expands clusters from them [1]. unlike dbscan, it keeps cluster hierarchy for a variable neighborhood radius.
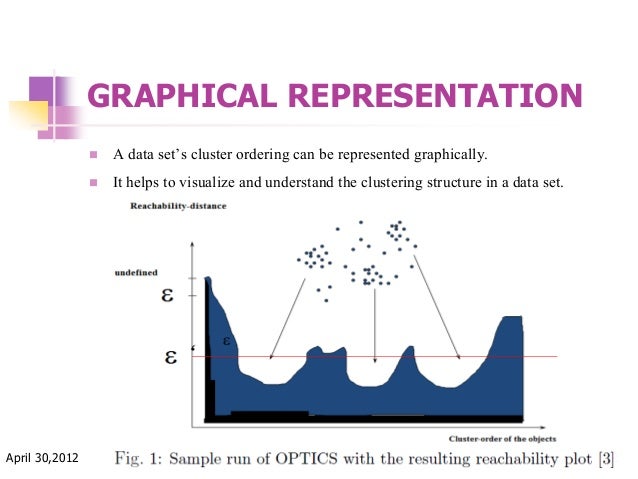
Optics Ordering Points To Identify The Clustering Structure Dbscan’s relatively algorithm is called optics (ordering points to identify cluster structure). it will create a reachability plot which is used to extract clusters and while an input, maximum epsilon is available used to speed up the computation time. That’s it! with just a few lines of code, you can use optics clustering to identify clusters in your data. In this article, we will explore optics clustering as implemented in scikit learn, a popular machine learning library in python. we will go through the fundamentals of the algorithm, how it differs from other clustering methods, and how you can apply it in practice. Interpretation of results: the reachability plot and the extracted clustering structure can be difficult to interpret, especially for those unfamiliar with the algorithm. sample code. here's an example of how to use the optics clustering algorithm with python's scikit learn library:.
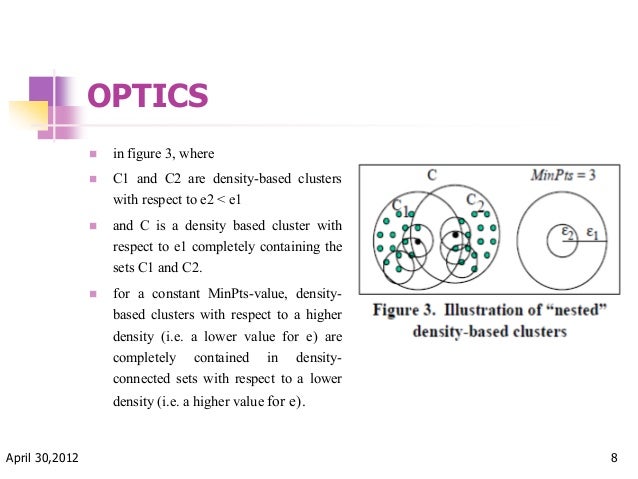
Optics Ordering Points To Identify The Clustering Structure In this article, we will explore optics clustering as implemented in scikit learn, a popular machine learning library in python. we will go through the fundamentals of the algorithm, how it differs from other clustering methods, and how you can apply it in practice. Interpretation of results: the reachability plot and the extracted clustering structure can be difficult to interpret, especially for those unfamiliar with the algorithm. sample code. here's an example of how to use the optics clustering algorithm with python's scikit learn library:. In the original optics paper, a reachability plot is created to aid the identification of clusters. kmeans is often used on real world data. sometimes the data is not isotropically distributed, meaning the real world clusters are not circular and uniformly distributed in all directions. Using this step by step example, you will learn how to create an optics based clustering model with python. Optics (ordering points to identify the clustering structure) is a density based clustering algorithm similar to dbscan clustering. unlike dbscan which struggles with varying densities. optics does not directly assign clusters but instead creates a reachability plot which visually represents clusters. the key concepts in optics are:. We introduce a new algorithm for the purpose of cluster analysis which does not produce a clustering of a data set explicitly; but instead creates an augmented ordering of the database representing its density based clustering structure.
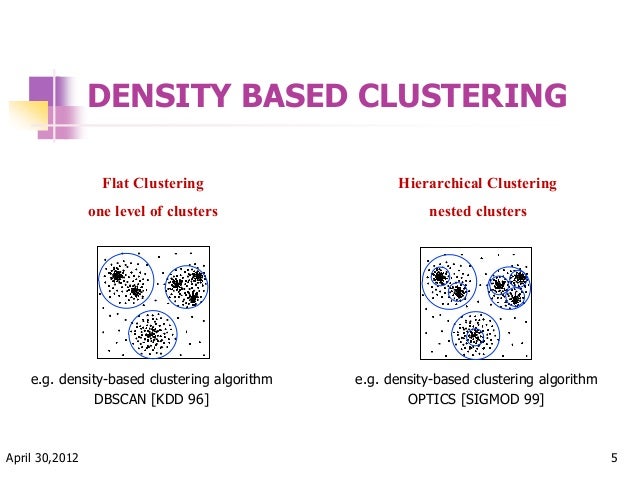
Optics Ordering Points To Identify The Clustering Structure In the original optics paper, a reachability plot is created to aid the identification of clusters. kmeans is often used on real world data. sometimes the data is not isotropically distributed, meaning the real world clusters are not circular and uniformly distributed in all directions. Using this step by step example, you will learn how to create an optics based clustering model with python. Optics (ordering points to identify the clustering structure) is a density based clustering algorithm similar to dbscan clustering. unlike dbscan which struggles with varying densities. optics does not directly assign clusters but instead creates a reachability plot which visually represents clusters. the key concepts in optics are:. We introduce a new algorithm for the purpose of cluster analysis which does not produce a clustering of a data set explicitly; but instead creates an augmented ordering of the database representing its density based clustering structure.

Optics Ordering Points To Identify The Clustering Structure Optics (ordering points to identify the clustering structure) is a density based clustering algorithm similar to dbscan clustering. unlike dbscan which struggles with varying densities. optics does not directly assign clusters but instead creates a reachability plot which visually represents clusters. the key concepts in optics are:. We introduce a new algorithm for the purpose of cluster analysis which does not produce a clustering of a data set explicitly; but instead creates an augmented ordering of the database representing its density based clustering structure.
Comments are closed.