Order And Degree Of Differential Equations Geeksforgeeks
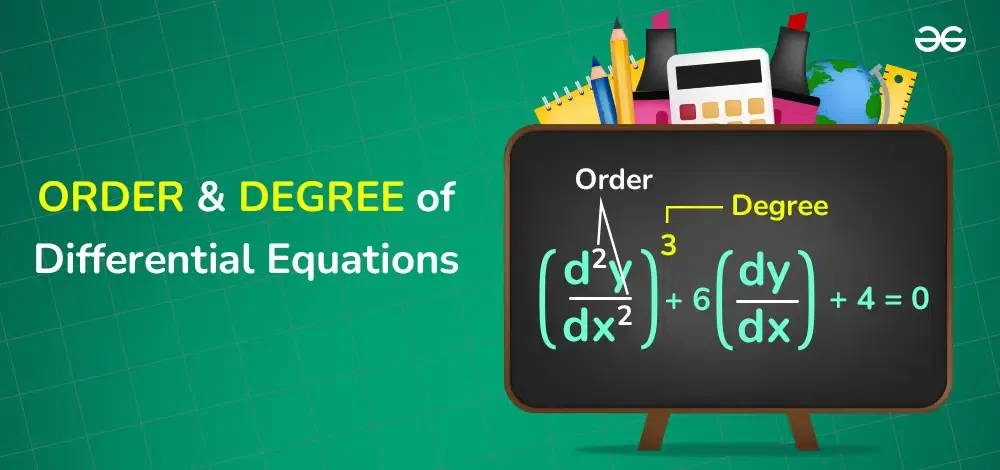
Order And Degree Of Differential Equations Geeksforgeeks Order and degree of differential equations indicate the degree of complexity and the number of independent variables in the differential equations. the highest derivative sets the order of the equation and offers important information about the function's behaviour and evolution. In this article, you will learn the definition of the order and degree of differential equations and how to find the order and degree of a given differential equation, along with solved examples. differential equations are classified on the basis of the order.

Order And Degree Of A Differential Equations Youtube In this video you will learn how to find the order and degree of the differential equation. also you will learn how to identify if the differential equation is linear or. The order of a differential equation is the order of the highest derivative occurring in the equation. the degree of a differential equation is the degree (exponent) of the derivative of the highest order in the equation after the equation is freed from negative and fractional powers of the derivatives . Linear differential equation: a differential equation in which the dependent variable and its derivatives occur only in the first degree and are not multiplied together is called a linear differential equation. The degree of an ordinary differential equation (ode) is defined as the highest power to which the derivative of the dependent variable appears in the equation. it represents the order of the highest derivative involved in the equation.

рџ µ02 Order And Degree Of A Differential Equation Exercise Youtube Linear differential equation: a differential equation in which the dependent variable and its derivatives occur only in the first degree and are not multiplied together is called a linear differential equation. The degree of an ordinary differential equation (ode) is defined as the highest power to which the derivative of the dependent variable appears in the equation. it represents the order of the highest derivative involved in the equation. (𝑑^4 𝑦) (𝑑𝑥^4 ) 𝑠𝑖𝑛(𝑦^′′′ )=0 (𝑑^4 𝑦) (𝑑𝑥^4 ) 𝑠𝑖𝑛(𝑦^′′′ )=0 𝒚^′′′′ 𝒔𝒊𝒏(𝒚^′′′ )=𝟎 highest order of derivative = 4 ∴ order = 𝟒 degree since 𝑦^′′′ is in sin〖 (𝑦^′′′ )〗 it is not a polynomial equation ∴ degree is not defined. Order and degree (if defined) of a differential equation are always positive integers. an ordinary differential equation involves function and its derivatives. it contains only one independent variable and one or more of its derivatives with respect to the variable. In this video, we break down the concepts of order and degree of differential equations with easy to follow explanations and solved examples. understanding t. Thus, the order of the differential equation is 2 and degree is 1. (2) consider the differential equation. since this equation involves fractional powers, we must first get rid of them. on squaring the equation, we get. now, we can clearly make out that the highest order derivative is 3.

Order And Degree Of Differential Equations With Solved Examples Youtube (𝑑^4 𝑦) (𝑑𝑥^4 ) 𝑠𝑖𝑛(𝑦^′′′ )=0 (𝑑^4 𝑦) (𝑑𝑥^4 ) 𝑠𝑖𝑛(𝑦^′′′ )=0 𝒚^′′′′ 𝒔𝒊𝒏(𝒚^′′′ )=𝟎 highest order of derivative = 4 ∴ order = 𝟒 degree since 𝑦^′′′ is in sin〖 (𝑦^′′′ )〗 it is not a polynomial equation ∴ degree is not defined. Order and degree (if defined) of a differential equation are always positive integers. an ordinary differential equation involves function and its derivatives. it contains only one independent variable and one or more of its derivatives with respect to the variable. In this video, we break down the concepts of order and degree of differential equations with easy to follow explanations and solved examples. understanding t. Thus, the order of the differential equation is 2 and degree is 1. (2) consider the differential equation. since this equation involves fractional powers, we must first get rid of them. on squaring the equation, we get. now, we can clearly make out that the highest order derivative is 3.

Order And Degree Of A Differential Equation Example Solved Problems With Answer Solution Formula In this video, we break down the concepts of order and degree of differential equations with easy to follow explanations and solved examples. understanding t. Thus, the order of the differential equation is 2 and degree is 1. (2) consider the differential equation. since this equation involves fractional powers, we must first get rid of them. on squaring the equation, we get. now, we can clearly make out that the highest order derivative is 3.
Comments are closed.