Presumptive Atypical Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Pa Colonies And Their Download Scientific Diagram

Presumptive Atypical Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Pa Colonies And Their Download Scientific Diagram Download scientific diagram | presumptive atypical pseudomonas aeruginosa (pa) colonies and their confirmation results from publication: comparison of the. Explore the unique colony morphology and characteristics of pseudomonas aeruginosa, including pigment production, shape, texture, and elevation.

Presumptive Atypical Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Pa Colonies And Their Download Scientific Diagram Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a ubiquitous, motile, gram negative bacterium that has been recently identified as a multi drug resistant pathogen in critical need of novel therapeutics. of the approximately 5,000 strains, pao1 and pa14 are common. To confirm presumptive ( ) colonies as positive pseudomonas aeruginosa or other species the appropriate morphological and biochemical tests must be performed on representative colonies by an experienced laboratory. In cystic fibrosis (cf), pseudomonas aeruginosa (pa) is a major pathogen that can persistently colonize patients. genetic studies showed a high diversity of pa , the success of widespread or ‘international’ clones and described epidemic clones in cf and epidemic high risk (erh) clones. We prospectively investigated the sources of pa, the clinical impact of pa colonization upon admission and the dynamics of colonization at different body sites throughout the intensive care unit stay.
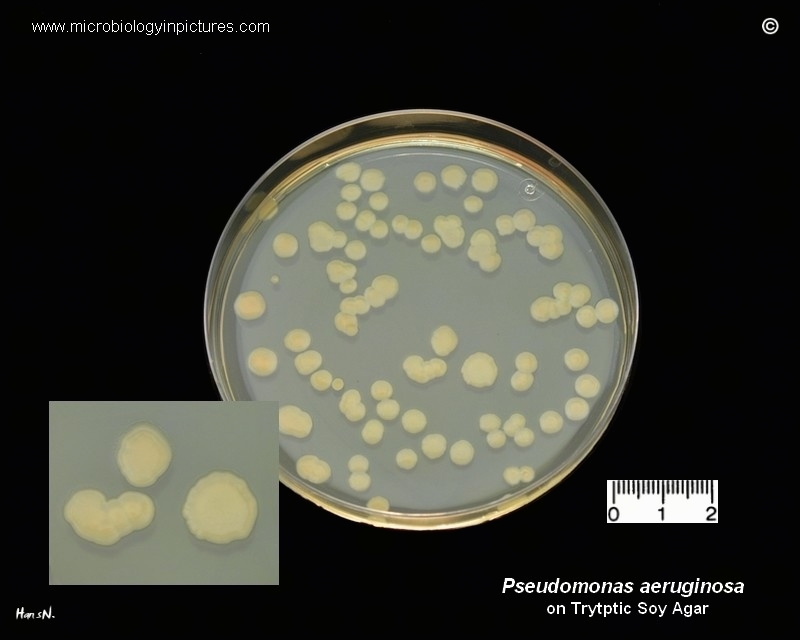
Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Pure Culture In Petri Dish With Tryptic Soy Agar Character Of Growth Of In cystic fibrosis (cf), pseudomonas aeruginosa (pa) is a major pathogen that can persistently colonize patients. genetic studies showed a high diversity of pa , the success of widespread or ‘international’ clones and described epidemic clones in cf and epidemic high risk (erh) clones. We prospectively investigated the sources of pa, the clinical impact of pa colonization upon admission and the dynamics of colonization at different body sites throughout the intensive care unit stay. Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a major pathogen in burn wound infections. we present one of the first reports of small colony variant (scv) emergence of p. aeruginosa, taken from a patient under aminogl. Pseudomonas aeruginosa (pa) is a leading pathogen in intensive care units (icus). surveillance for pa may improve empiric antimicrobial therapy, since colonizing strains may subsequently cause infections. The diversity of colonial types of pseudomonas aeruginosa which may be encountered is described, together with a series of biochemical tests and the application of serological and pyocine typing which are of use in identifying atypical strains. Explore the complex dynamics and adaptive strategies of pseudomonas aeruginosa colonies, including biofilm formation and antibiotic resistance.

Colonies Of Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Download Scientific Diagram Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a major pathogen in burn wound infections. we present one of the first reports of small colony variant (scv) emergence of p. aeruginosa, taken from a patient under aminogl. Pseudomonas aeruginosa (pa) is a leading pathogen in intensive care units (icus). surveillance for pa may improve empiric antimicrobial therapy, since colonizing strains may subsequently cause infections. The diversity of colonial types of pseudomonas aeruginosa which may be encountered is described, together with a series of biochemical tests and the application of serological and pyocine typing which are of use in identifying atypical strains. Explore the complex dynamics and adaptive strategies of pseudomonas aeruginosa colonies, including biofilm formation and antibiotic resistance.
Comments are closed.