Python Compiler Interpreter Apk For Android Download

Download Python For Android Apk Newarmy In python this is simply =. to translate this pseudocode into python you would need to know the data structures being referenced, and a bit more of the algorithm implementation. some notes about psuedocode: := is the assignment operator or = in python = is the equality operator or == in python there are certain styles, and your mileage may vary:. There is no bitwise negation in python (just the bitwise inverse operator ~ but that is not equivalent to not). see also 6.6. unary arithmetic and bitwise binary operations and 6.7. binary arithmetic operations. the logical operators (like in many other languages) have the advantage that these are short circuited.
Python Programming Interpreter Apk For Android Download 96 what does the “at” (@) symbol do in python? @ symbol is a syntactic sugar python provides to utilize decorator, to paraphrase the question, it's exactly about what does decorator do in python? put it simple decorator allow you to modify a given function's definition without touch its innermost (it's closure). What does asterisk * mean in python? [duplicate] asked 16 years, 7 months ago modified 1 year, 6 months ago viewed 319k times. There are two operators in python for the "not equal" condition a.) != if values of the two operands are not equal, then the condition becomes true. (a != b) is true. I notice that i can do things like 2 << 5 to get 64 and 1000 >> 2 to get 250. also i can use >> in print: print >>obj, "hello world" what is happening here?.
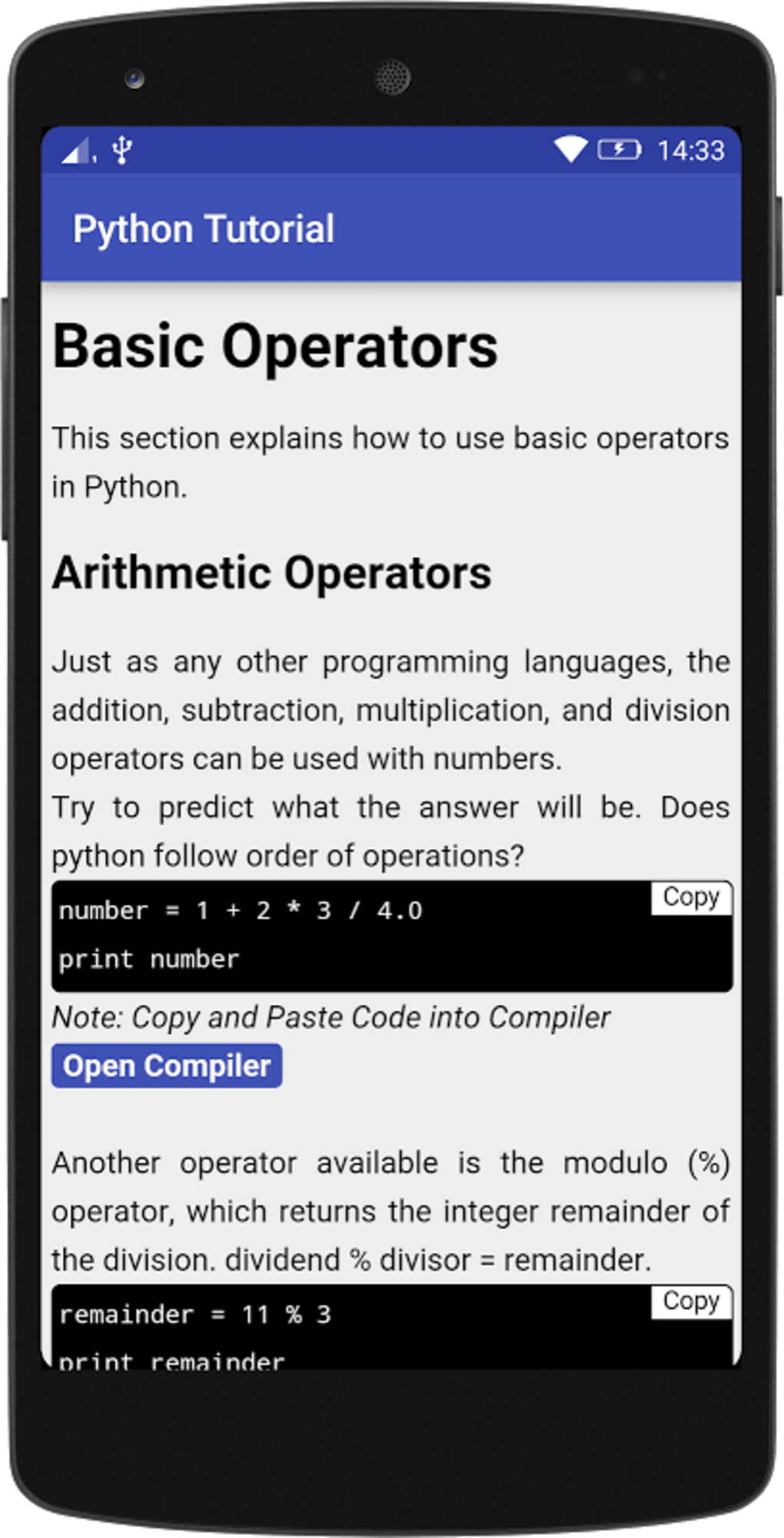
Python Tutorial And Compiler Apk For Android Download There are two operators in python for the "not equal" condition a.) != if values of the two operands are not equal, then the condition becomes true. (a != b) is true. I notice that i can do things like 2 << 5 to get 64 and 1000 >> 2 to get 250. also i can use >> in print: print >>obj, "hello world" what is happening here?. Since is for comparing objects and since in python 3 every variable such as string interpret as an object, let's see what happened in above paragraphs. in python there is id function that shows a unique constant of an object during its lifetime. this id is using in back end of python interpreter to compare two objects using is keyword. Python 2.4 adds the command line switch m to allow modules to be located using the python module namespace for execution as scripts. the motivating examples were standard library modules such as pdb and profile, and the python 2.4 implementation is fine for this limited purpose. Python slicing is a computationally fast way to methodically access parts of your data. in my opinion, to be even an intermediate python programmer, it's one aspect of the language that it is necessary to be familiar with. The simple answer is = is an assignment operator, == is a comparison operator. and you are wrong in saying that == can be used in any situation when = works. for example if i wanted to create the variable my string and set it equal to "something" i would use the = operator. my string = "something" i am assigning the variable to an object using that operator. if i want to compare two strings.
Abg Interpreter Apk For Android Download Since is for comparing objects and since in python 3 every variable such as string interpret as an object, let's see what happened in above paragraphs. in python there is id function that shows a unique constant of an object during its lifetime. this id is using in back end of python interpreter to compare two objects using is keyword. Python 2.4 adds the command line switch m to allow modules to be located using the python module namespace for execution as scripts. the motivating examples were standard library modules such as pdb and profile, and the python 2.4 implementation is fine for this limited purpose. Python slicing is a computationally fast way to methodically access parts of your data. in my opinion, to be even an intermediate python programmer, it's one aspect of the language that it is necessary to be familiar with. The simple answer is = is an assignment operator, == is a comparison operator. and you are wrong in saying that == can be used in any situation when = works. for example if i wanted to create the variable my string and set it equal to "something" i would use the = operator. my string = "something" i am assigning the variable to an object using that operator. if i want to compare two strings.
Comments are closed.