Rational And Irrational Numbers Geeksforgeeks
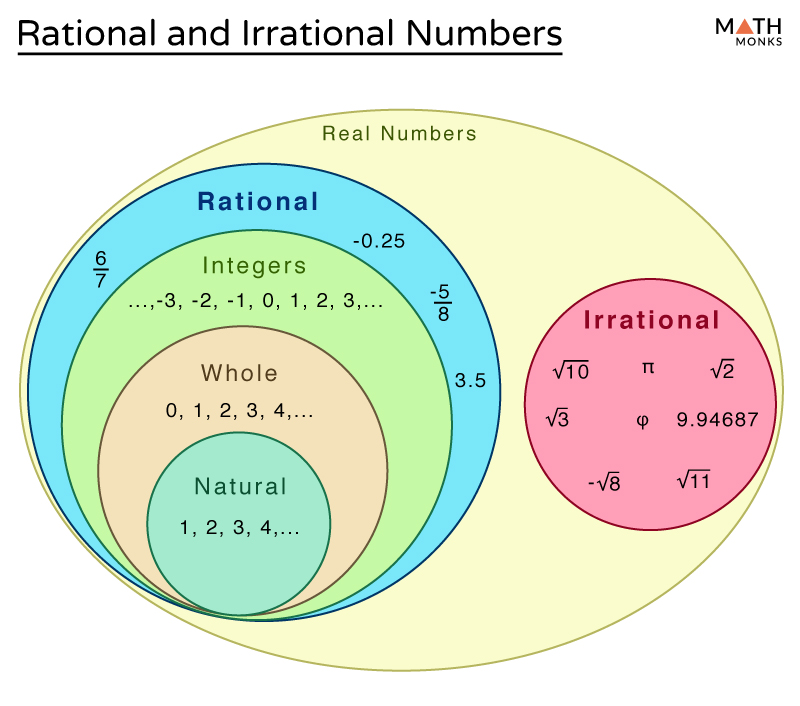
Rational And Irrational Numbers Differences Examples Rational numbers include familiar values like fractions, whole numbers, and repeating decimals. irrational numbers include numbers like π and √2 , which have infinite non repeating decimal expansions. Learn the differences between rational and irrational numbers explained with definition, differences, solved examples.
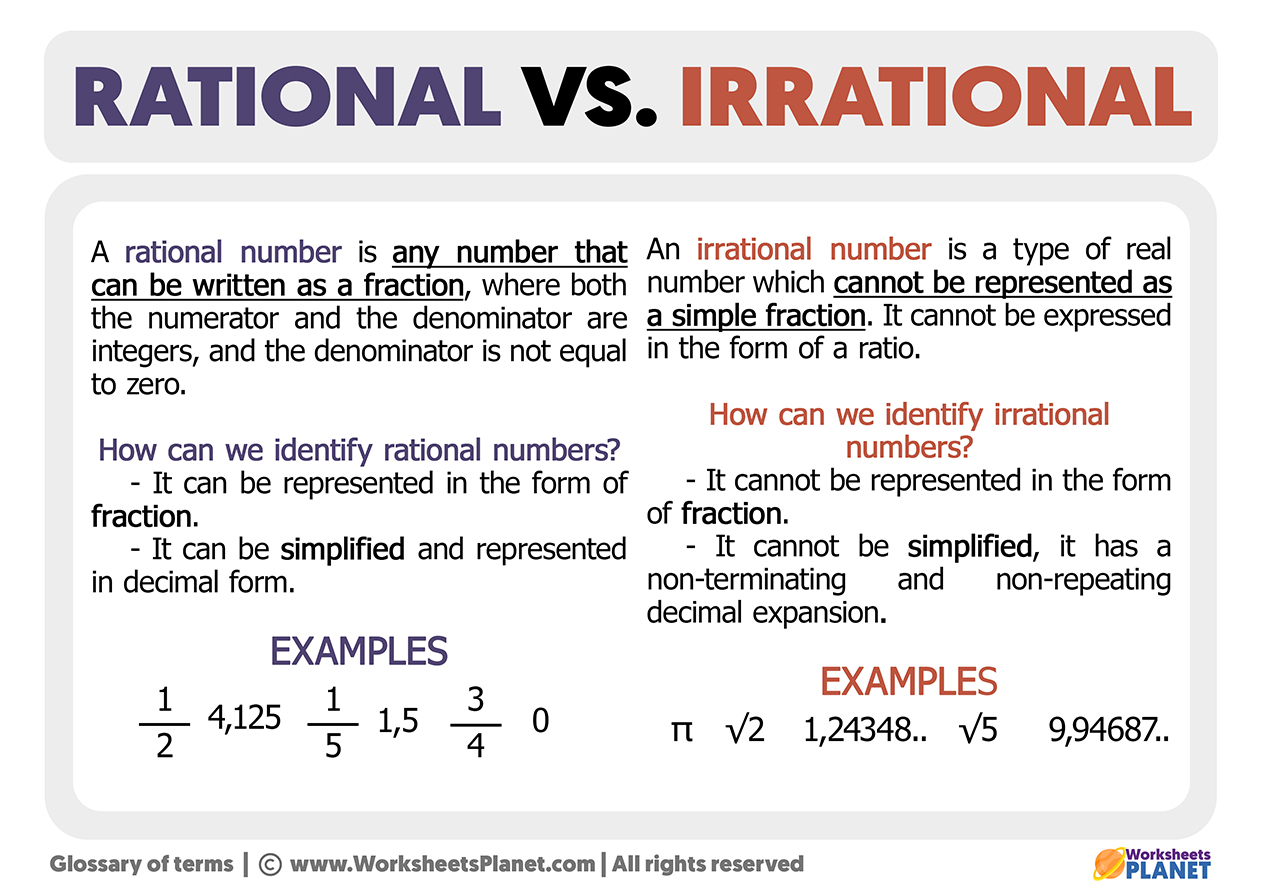
Rational And Irrational Numbers The key difference between rational and irrational numbers is, the rational number is expressed in the form of p q whereas it is not possible for irrational number (though both are real numbers). learn the definitions, more differences and examples based on them. To summarize, real numbers encompass both rational and irrational numbers. Properties of rational and irrational numbers: since rational and irrational numbers are subsets of the real numbers, they possess all of the properties assigned to the real number system. Numbers that can be expressed in the form of p q, where q≠ 0 are rational numbers, numbers that cannot be represented in the p q are irrational numbers. let's learn about the difference between rational and irrational numbers,.

Rational And Irrational Numbers 8th Grade Math Properties of rational and irrational numbers: since rational and irrational numbers are subsets of the real numbers, they possess all of the properties assigned to the real number system. Numbers that can be expressed in the form of p q, where q≠ 0 are rational numbers, numbers that cannot be represented in the p q are irrational numbers. let's learn about the difference between rational and irrational numbers,. Definition : can be expressed as the quotient of two integers (ie a fraction) with a denominator that is not zero. many people are surprised to know that a repeating decimal is a rational number. Learn rational and irrational numbers, its definition with all its properties, differences, how to find rational & irrational numbers using solved examples here. Real numbers (r): real numbers encompass both irrational and rational numbers. they are numbers that can be located on the number line and include integers, fractions, decimals, and square roots of non negative numbers. examples of real numbers are 3, 0, 1.5, 2 , and π. The sum of a rational and an irrational number is always irrational. 5. the product of a non zero rational number and an irrational number is always irrational.

Rational And Irrational Numbers Video Corbettmaths Definition : can be expressed as the quotient of two integers (ie a fraction) with a denominator that is not zero. many people are surprised to know that a repeating decimal is a rational number. Learn rational and irrational numbers, its definition with all its properties, differences, how to find rational & irrational numbers using solved examples here. Real numbers (r): real numbers encompass both irrational and rational numbers. they are numbers that can be located on the number line and include integers, fractions, decimals, and square roots of non negative numbers. examples of real numbers are 3, 0, 1.5, 2 , and π. The sum of a rational and an irrational number is always irrational. 5. the product of a non zero rational number and an irrational number is always irrational.
Comments are closed.