Sampling Distributions 7 2

Chapter 7 Sampling Distributions Pdf Sampling Statistics Standard Deviation Learn about sampling distributions, and how they compare to sample distributions and population distributions. Suppose a srs x1, x2, , x40 was collected. give the approximate sampling distribution of x normally denoted by p x, which indicates that x is a sample proportion.

Chapter 7 Sampling And Sampling Distributions Chapter 7 Sampling And Sampling Distributions The spread of a sampling distribution is affected by the sample size, not the population size. specifically, larger sample sizes result in smaller spread or variability. We have described the mean and standard deviation of the sampling distribution of the sample mean x but not its shape. that's because the shape of the distribution of x depends on the shape of the population distribution. What test can you use to determine if the sample is large enough to assume that the sampling distribution is approximately normal? what condition must be checked?. To see how we use sampling error, we will learn about a new, theoretical distribution known as the sampling distribution.

Chapter 7 Sampling And Sampling Distributions What test can you use to determine if the sample is large enough to assume that the sampling distribution is approximately normal? what condition must be checked?. To see how we use sampling error, we will learn about a new, theoretical distribution known as the sampling distribution. Key chapter 7 practice test. key lecture notes & examples 7.1. 7.2. sampling distribution for the sample mean having established that statistics are random variables with their own distributions, we now focus on the most important statistic in all of statistical inference: the sample mean x. De nition 1 the sampling distribution of a sample statistic is the distrib ution of the values of the statistic created by repeated samples of n observations. The mean of the sampling distribution is the population proportion p, and the standard deviation is the square root of (p (1 p) n). several examples are provided to illustrate calculating probabilities for the sampling distribution.

Chapter 7 Sampling Distributions 7 1 Population Sampling Key chapter 7 practice test. key lecture notes & examples 7.1. 7.2. sampling distribution for the sample mean having established that statistics are random variables with their own distributions, we now focus on the most important statistic in all of statistical inference: the sample mean x. De nition 1 the sampling distribution of a sample statistic is the distrib ution of the values of the statistic created by repeated samples of n observations. The mean of the sampling distribution is the population proportion p, and the standard deviation is the square root of (p (1 p) n). several examples are provided to illustrate calculating probabilities for the sampling distribution.
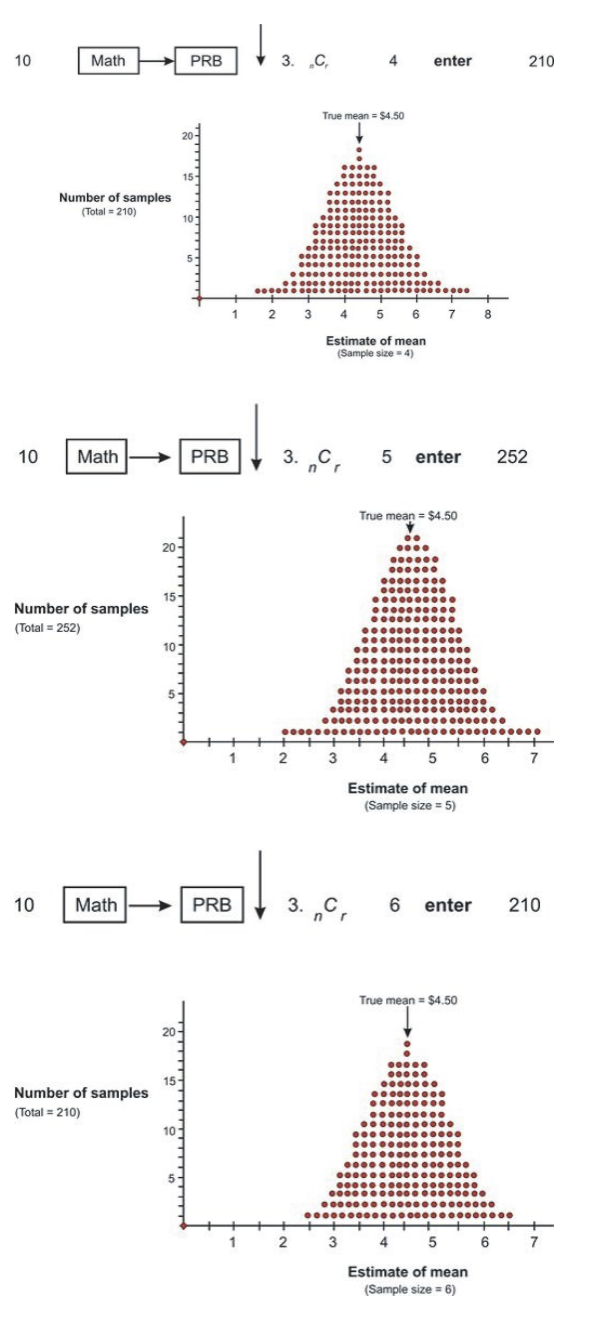
7 6 Sampling Distributions K12 Libretexts De nition 1 the sampling distribution of a sample statistic is the distrib ution of the values of the statistic created by repeated samples of n observations. The mean of the sampling distribution is the population proportion p, and the standard deviation is the square root of (p (1 p) n). several examples are provided to illustrate calculating probabilities for the sampling distribution.
Comments are closed.