Skeleton Of The Face Dental Anatomy Facial Bones Human Anatomy And

Facial Bones Anatomy 1 Diagram Quizlet Figure 1 identifies the various bone structures of the head and face. correctly visualizing the bone structures of the face and head aids in palpation techniques when conducting a head and neck examination on the patient. The facial skeleton comprises 14 distinct bones that form the structural framework of the human face. these bones create the foundation for facial expressions, mastication, and sensory organ protection while housing vital structures for breathing and speech.

Human Anatomy Facial Bones Features Diagram Quizlet Learn what are the bones of the face, how many are there, their names, & location. facial skeleton viscerocranium structure & anatomy with labeled pictures. In human anatomy and development, the facial skeleton is sometimes called the membranous viscerocranium, which comprises the mandible and dermatocranial elements that are not part of the braincase. in the human skull, the facial skeleton consists of fourteen bones in the face: [1][2]. The 14 facial bones are integral to shaping the face and providing structural support for soft tissues. this article explores the names, locations, and functions of these bones in detail. The facial skeleton is composed of 14 individual bones. most of these bones are paired, meaning they exist on both the left and right sides of the face, except for two unpaired bones—the vomer and mandible.

Human Facial Bones Labeled Anatomy 3d Stock Illustration 2192527931 Shutterstock The 14 facial bones are integral to shaping the face and providing structural support for soft tissues. this article explores the names, locations, and functions of these bones in detail. The facial skeleton is composed of 14 individual bones. most of these bones are paired, meaning they exist on both the left and right sides of the face, except for two unpaired bones—the vomer and mandible. The facial skeleton serves to protect the brain, house and protect the sense organs of smell, sight, and taste, and provide a framework for the soft tissues of the face to facilitate eating,. The facial bones, also known as the viscerocranium, form the framework of the face and support many essential functions such as breathing, eating, and communication. they contribute to the nasal cavity, orbits, and oral cavity, while also giving shape and definition to the face. These bones provide the structure and shape of the face, protect vital sensory organs, and serve as attachment sites for facial muscles. unlike cranial bones, which primarily protect the brain, facial bones contribute to the formation of the orbits, nasal cavity, oral cavity, and jaw. Explore the intricate structures of facial bones, understanding their functions and significance in human anatomy.
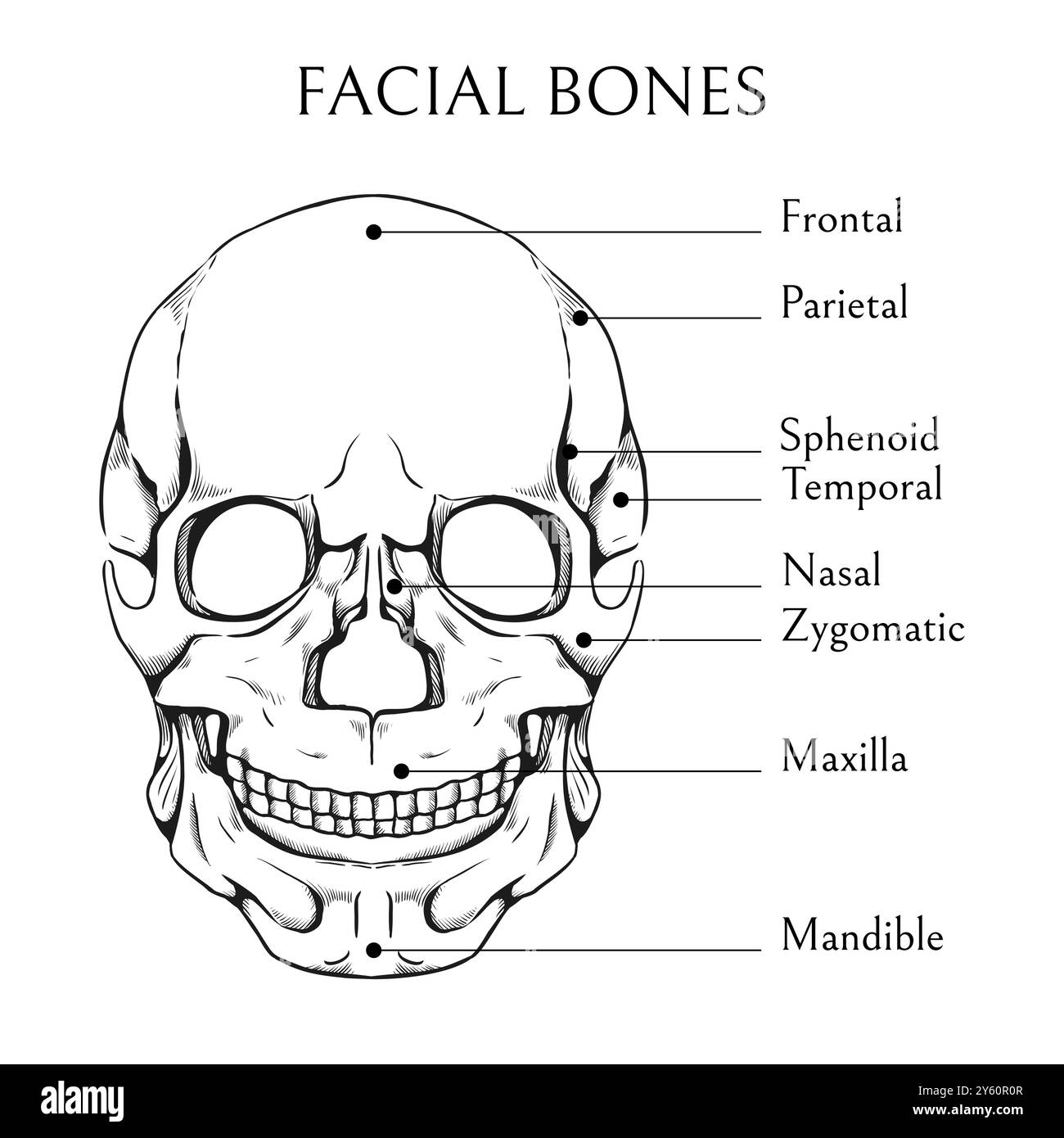
Hand Drawn Facial Bones Human Skull Sketch Medical Educational Banner Skeleton Engraving The facial skeleton serves to protect the brain, house and protect the sense organs of smell, sight, and taste, and provide a framework for the soft tissues of the face to facilitate eating,. The facial bones, also known as the viscerocranium, form the framework of the face and support many essential functions such as breathing, eating, and communication. they contribute to the nasal cavity, orbits, and oral cavity, while also giving shape and definition to the face. These bones provide the structure and shape of the face, protect vital sensory organs, and serve as attachment sites for facial muscles. unlike cranial bones, which primarily protect the brain, facial bones contribute to the formation of the orbits, nasal cavity, oral cavity, and jaw. Explore the intricate structures of facial bones, understanding their functions and significance in human anatomy.
Comments are closed.