Solved 20 Marks Solve The Chinese Postman Problem For The Graph That Is Find The Route Of

Chinese Postman Problem Pdf Vertex Graph Theory Combinatorics Our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. question: (20 marks) solve the chinese postman problem for the graph b c 1 2 3 2 3 3 a d 4 4 g 2 2 . 2 1 f 4 e that is, find the route of the postman (start from any vertex). here’s the best way to solve it. Chinese postman problem is defined for connected and undirected graph. the problem is to find shortest path or circuity that visits every edge of the graph at least once.

The Directed Chinese Postman Problem Pdf Vertex Graph Theory Linear Programming The chinese postman problem requires you to find the route of least weight that starts and finishes at the same vertex and traverses every edge in the graph. some edges may need to be traversed twice and the challenge is to minimise the total weight of these repeated edges. Master the chinese postman problem (cpp) with our detailed guide covering algorithms, complexity analysis, and practical solutions. learn step by step approaches to optimize routing efficiency. In graph theory and combinatorial optimization, guan's route problem, the chinese postman problem, postman tour or route inspection problem is to find a shortest closed path or circuit that visits every edge of an (connected) undirected graph at least once. In this video, we break down the chinese postman problem (also known as the route inspection problem) and guide you step by step through real exam style questions.
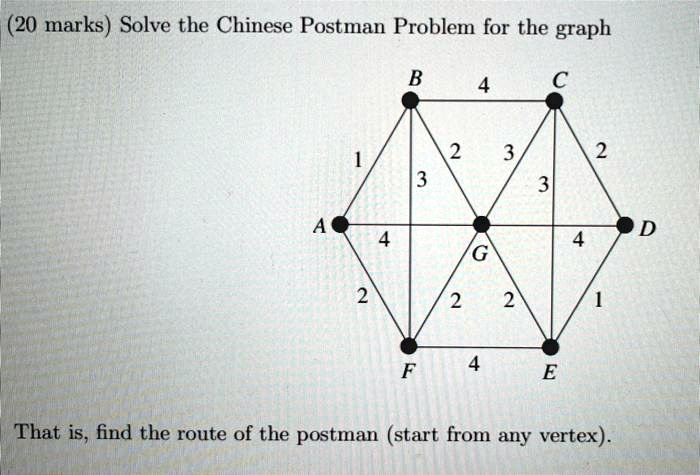
Solved 20 Marks Solve The Chinese Postman Problem For The Graph That Is Find The Route Of In graph theory and combinatorial optimization, guan's route problem, the chinese postman problem, postman tour or route inspection problem is to find a shortest closed path or circuit that visits every edge of an (connected) undirected graph at least once. In this video, we break down the chinese postman problem (also known as the route inspection problem) and guide you step by step through real exam style questions. An ambulance is based at a and has to respond to an emergency at j. use dijkstra’s algorithm to find the minimum distance required to travel from a to j, and state the route. Dive into the world of graph theory and explore the chinese postman problem, its applications, and step by step solutions to optimize route planning. For a graph to be eulerian all the vertices must be of even order. an algorithm for finding an optimal chinese postman route is: list all odd vertices. list all possible pairings of odd vertices. for each pairing find the edges that connect the vertices with the minimum weight. find the pairings such that the sum of the weights is minimised. (i) draw the graph, in its planar form, that is represented by the table. (ii) write down with reasons whether or not it is possible to find an eulerian trail in this graph. (iii) solve the chinese postman problem with reference to this graph if a is to be the starting and finishing point. write down the walk and determine the length of the walk.
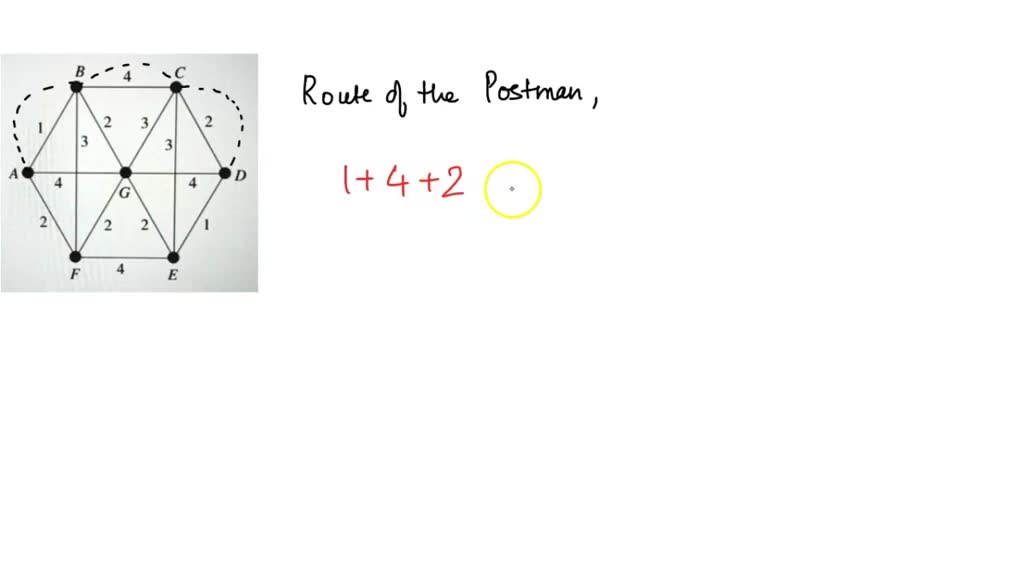
Solved 20 Marks Solve The Chinese Postman Problem For The Graph That Is Find The Route Of An ambulance is based at a and has to respond to an emergency at j. use dijkstra’s algorithm to find the minimum distance required to travel from a to j, and state the route. Dive into the world of graph theory and explore the chinese postman problem, its applications, and step by step solutions to optimize route planning. For a graph to be eulerian all the vertices must be of even order. an algorithm for finding an optimal chinese postman route is: list all odd vertices. list all possible pairings of odd vertices. for each pairing find the edges that connect the vertices with the minimum weight. find the pairings such that the sum of the weights is minimised. (i) draw the graph, in its planar form, that is represented by the table. (ii) write down with reasons whether or not it is possible to find an eulerian trail in this graph. (iii) solve the chinese postman problem with reference to this graph if a is to be the starting and finishing point. write down the walk and determine the length of the walk.
Comments are closed.