Solved A Pipe With Inner Diameter Di 39mm I And Outer Chegg

Solved A Pipe Has An Inner Diameter Of 100 Mm And An Outer Chegg There are 3 steps to solve this one. Consider a water flow (Ï = 999 kg m³, μ = 1.14x10⠻⠵ kg (m*s)) from the reservoir through the smooth pipe of diameter d = 5 cm and length l = 20 m (sharp edged entrance to the pipe). the water is discharged to atmospheric pressure at the pipe exit at the average velocity of 10 m s.
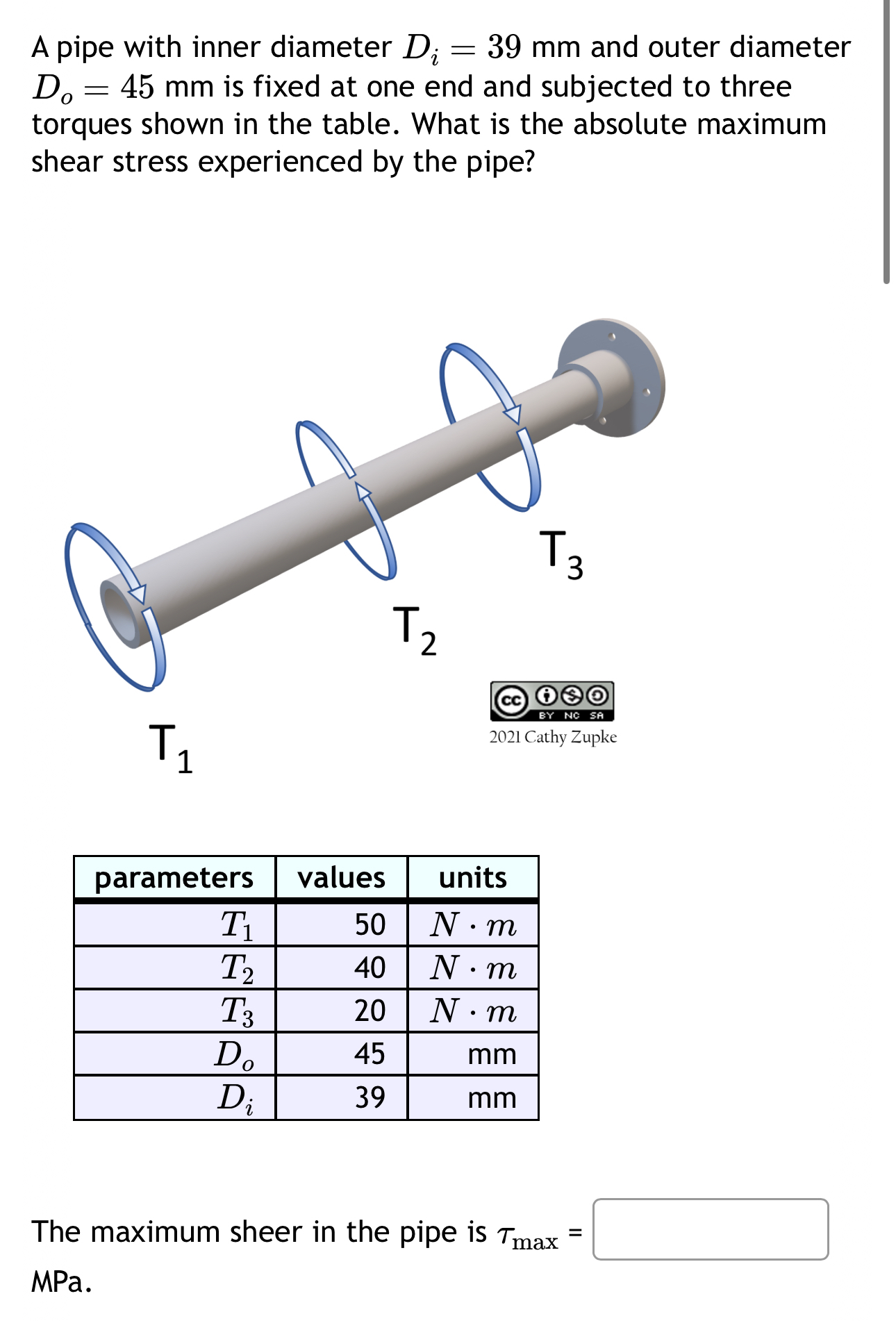
Solved A Pipe With Inner Diameter Di 39mm ï And Outer Chegg Video answer: the answer is that the stress under the applied moment is equal to 35 plus 0.8 r. so, where p is equal to…. We trained chegg’s ai tools using our own step by step homework solutions–you’re not just getting an answer, you’re learning how to solve the problem. Access mechanics of materials, 9th edition 9th edition chapter 14 problem 39p solution now. our solutions are written by chegg experts so you can be assured of the highest quality!. A pipe with inner diameter di=35 mm and outer diameter d0=45 mm is fixed at one end and subjected to three torques shown in the table. what is the absolute maximum shear stress experienced by the pipe?.

Solved A Pipe With Inner Diameter Di 35 Mm And Outer Chegg Access mechanics of materials, 9th edition 9th edition chapter 14 problem 39p solution now. our solutions are written by chegg experts so you can be assured of the highest quality!. A pipe with inner diameter di=35 mm and outer diameter d0=45 mm is fixed at one end and subjected to three torques shown in the table. what is the absolute maximum shear stress experienced by the pipe?. Question: the copper pipe has an outer diameter of 39 mm and an inner diameter of 35 mm. it is tightly secured to the wall at a and three torques are applied to it as shown in (figure 1). part a determine the absolute maximum shear stress developed in the pipe. It requires two primary inputs: the inner diameter and the wall thickness of the object in question. the inner diameter is the distance across the hollow portion of the object, while the wall thickness represents the distance between the inner and outer walls. Cross sectional inside area of a pipe can be calculated as. ai = π (di 2)2. = π di2 4 (1) where. ai = cross sectional inside area of pipe (m2, in2) di = inside diameter (m, in) the cross sectional wall area or area of piping material can be calculated as. am = π (do 2)2 π (di 2)2. The copper pipe has an outer diameter of 39 mm and an inner diameter of 37 mm. it is tightly secured to the wall at a and three torques are applied to it as shown in (figure 1). part a determine the absolute maximum shear stress developed in the pipe express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units.

Solved The Pipe Shown In Figure Has An Inner Diameter Of 80 Chegg Question: the copper pipe has an outer diameter of 39 mm and an inner diameter of 35 mm. it is tightly secured to the wall at a and three torques are applied to it as shown in (figure 1). part a determine the absolute maximum shear stress developed in the pipe. It requires two primary inputs: the inner diameter and the wall thickness of the object in question. the inner diameter is the distance across the hollow portion of the object, while the wall thickness represents the distance between the inner and outer walls. Cross sectional inside area of a pipe can be calculated as. ai = π (di 2)2. = π di2 4 (1) where. ai = cross sectional inside area of pipe (m2, in2) di = inside diameter (m, in) the cross sectional wall area or area of piping material can be calculated as. am = π (do 2)2 π (di 2)2. The copper pipe has an outer diameter of 39 mm and an inner diameter of 37 mm. it is tightly secured to the wall at a and three torques are applied to it as shown in (figure 1). part a determine the absolute maximum shear stress developed in the pipe express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units.
Comments are closed.