Solved Circuit 1 Circuit 2 Chegg
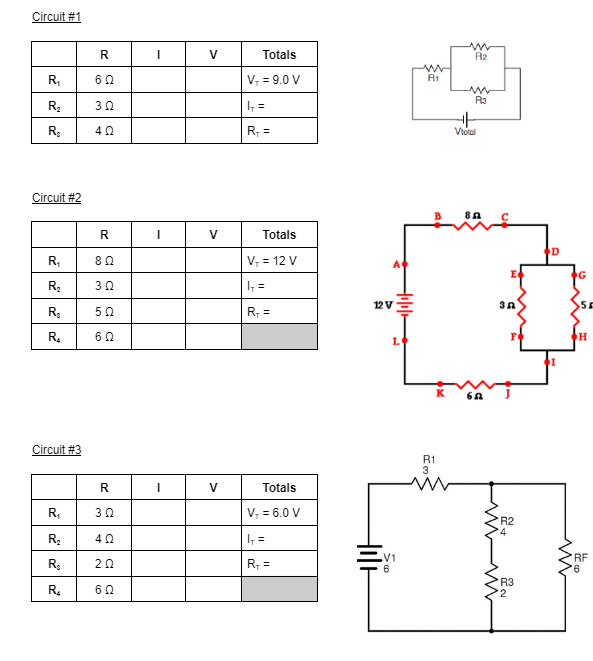
Solved Circuit 1 Circuit 2 Circuit 3 Circuit 4 Chegg What is the value of current through each resistor? what is the voltage across each resistor? what is the total current flowing through the power supply into the entire circuit? what is the power dissipated (as heat) in each resistor? if any value exceeds 2 w, talk with your ta before proceeding to the next step. Circuit 1 circuit 2 for both circuit 1 and circuit 2, you are t o find all the voltages.
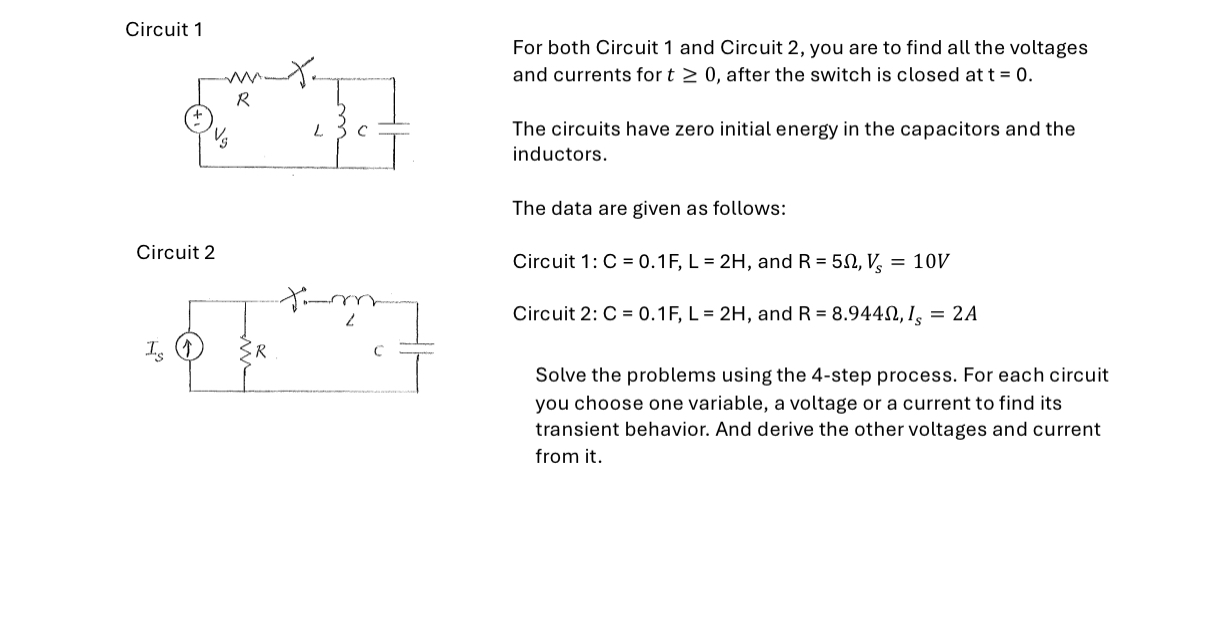
Solved Circuit 1circuit 2for Both Circuit 1 ï And Circuit 2 Chegg Now with a collection of circuit problems and their worked out solutions, take one or two out every day and work it out on your own. refer to the solution and go step by step through it to see how he solved and where you may have messed up. Now, with expert verified solutions from electric circuits 11th edition, you’ll learn how to solve your toughest homework problems. our resource for electric circuits includes answers to chapter exercises, as well as detailed information to walk you through the process step by step. Problem sheet 1 solutions circuit (a) is a parallel circuit: there are only two nodes and all four components are connected between them. ed to exactly tw ow through each. Simplify first order circuits with solved problems to excel in your exams and grasp key concepts easily.
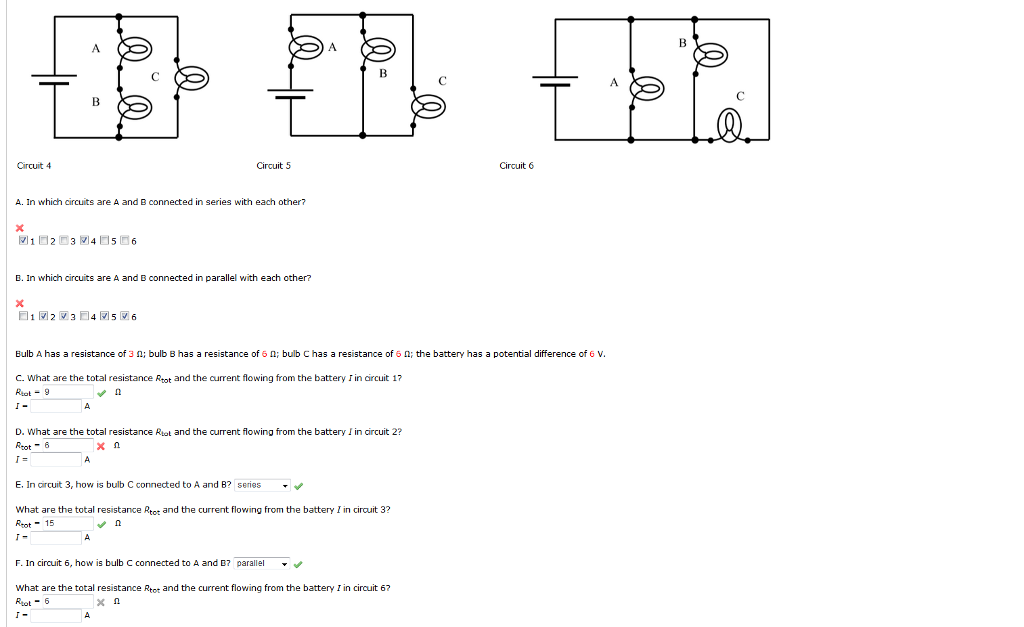
Solved Circuit 1 Circuit 2 Circuit 3 Chegg Problem sheet 1 solutions circuit (a) is a parallel circuit: there are only two nodes and all four components are connected between them. ed to exactly tw ow through each. Simplify first order circuits with solved problems to excel in your exams and grasp key concepts easily. Thevenin's theorem is used to solve the complex circuits consisting of several sources and impedances by converting them into a simple equivalent circuit. The article provides an overview of nodal analysis, a method used in electrical circuit analysis that applies kirchhoff’s current law and source transformation techniques. it also includes a solved example to demonstrate how to apply nodal analysis to calculate currents in a simple circuit. This problem involves a series circuit. in a series circuit, the total resistance is the sum of individual resistances, and the current is the same throughout the circuit. In the following circuits (figs. 3 and 4), assume that|vt h|= 1 v and|id (sat)|= 1 ma when|vgs|= 3v. for problems 3a, 3b, 4a, and 4b, the transistors must have a drain current of 3 ma (|id|= 3 ma).
Comments are closed.