Solved Determine The Voltage Node Equations In The S Domain Chegg

Solved Determine The Voltage Node Equations In The S Domain Chegg Determine the voltage node equations in the s domain this problem has been solved! you'll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core concepts. Kcl at node n3 associated with voltage v3 gives: v2 v3 v3 = r3 r4 0 (4.8) or 111 v2 v3 =0 r3 r3 r4 ⎛⎞ ⎜⎟ ⎝⎠ (4.9) the next step is to solve the simultaneous equations 4.7 and 4.9 for the node voltages v2 and v3. although it is easy to solve eqs. (4.8) and (4.9) directly it is useful to rewrite them in matrix form as follows. 111.

Solved Determine The Voltage Node Equations In The S Domain Chegg Note the source transformation rules apply! switch in place since t= ∞, closed at t=0. solve for vc(t). $% = eq ! % $ sl ! the switch has been open for a long time and is closed at t=0. Use s domain node voltage analysis to find v2 (s) (voltage across c1 ) and v3 (s) (voltage across c2 ) if vin (t)=5u (t). be sure to show (a) the node equations, (b) the method you. your solution’s ready to go! our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. question: 1. While multiple node voltage or mesh current analysis leads to simultaneous dif ferential equations in the time domain, laplace transforms allow us to replace these equations with simultaneous algebraic systems in the s domain. Note that the initial voltage and current transform into equivalent sources in the s domain. the circuit in the s domain is shown in figure 3. figure 3. s domain equivalent of the circuit in figure 1 using kirchhoff's current law to sum the currents out of the top node, the equation is vv s v s s n 4324 4 24 1 =−→1 1.

Solved Find Node Voltage Equations From The S Domain Model Chegg While multiple node voltage or mesh current analysis leads to simultaneous dif ferential equations in the time domain, laplace transforms allow us to replace these equations with simultaneous algebraic systems in the s domain. Note that the initial voltage and current transform into equivalent sources in the s domain. the circuit in the s domain is shown in figure 3. figure 3. s domain equivalent of the circuit in figure 1 using kirchhoff's current law to sum the currents out of the top node, the equation is vv s v s s n 4324 4 24 1 =−→1 1. Formulating node voltage equations step 0: transform the circuit into the s domain using current sources to represent capacitor and inductor initial conditions. Question: problem 3 phasor domain node voltage method v˙s=60∠0∘v ω=2000r s use the node voltage method to determine a) the node voltage equation at node v0 b) the node voltage equation at node v1 c) the values of v0 and v1 d) v5(t)v1(t) and v0(t) e) plot the signals from partd on the some time axis and label the significant values. Solve for vc(t). the switch has been open for a long time and is closed at t=0. As the resistor values and currents are known, simultaneous equation solution techniques may be used to solve for the node voltages. once again, there will be as many equations as node voltages. it is very important that the terms “line up” when the final system of equations is written out.
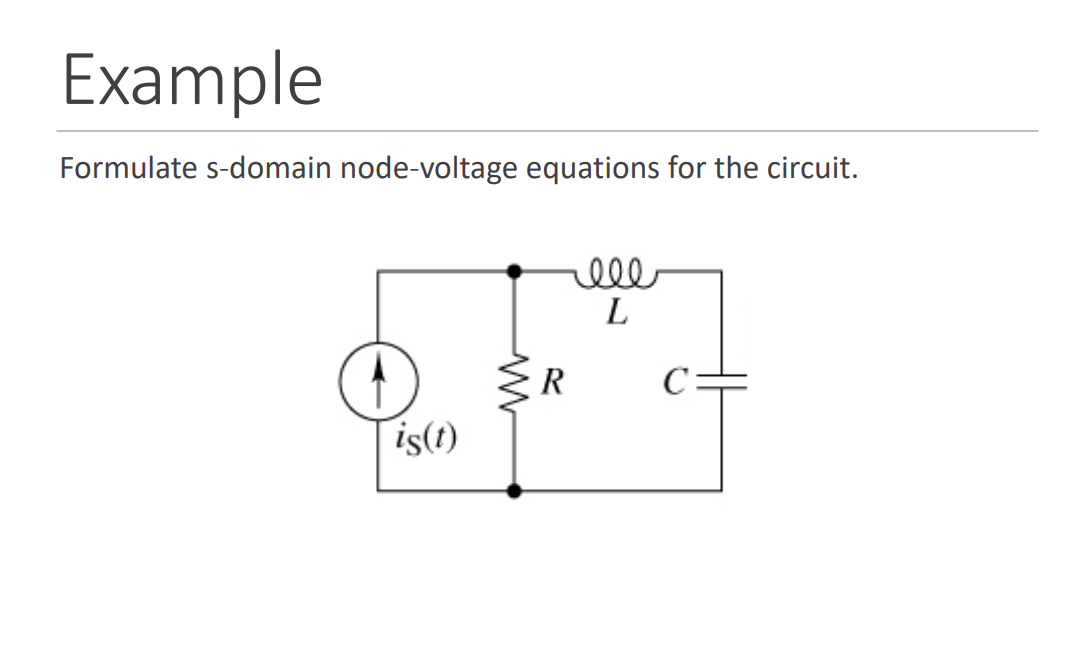
Exampleformulate S Domain Node Voltage Equations For Chegg Formulating node voltage equations step 0: transform the circuit into the s domain using current sources to represent capacitor and inductor initial conditions. Question: problem 3 phasor domain node voltage method v˙s=60∠0∘v ω=2000r s use the node voltage method to determine a) the node voltage equation at node v0 b) the node voltage equation at node v1 c) the values of v0 and v1 d) v5(t)v1(t) and v0(t) e) plot the signals from partd on the some time axis and label the significant values. Solve for vc(t). the switch has been open for a long time and is closed at t=0. As the resistor values and currents are known, simultaneous equation solution techniques may be used to solve for the node voltages. once again, there will be as many equations as node voltages. it is very important that the terms “line up” when the final system of equations is written out.

Solved A For The Circuit In The Figure Write The Equations Chegg Solve for vc(t). the switch has been open for a long time and is closed at t=0. As the resistor values and currents are known, simultaneous equation solution techniques may be used to solve for the node voltages. once again, there will be as many equations as node voltages. it is very important that the terms “line up” when the final system of equations is written out.

Solved 3 51 Obtain The Node Voltage Equations For The Chegg
Comments are closed.