Solved Draw E1 Created By E Q1 At Point C Draw E2 Chegg
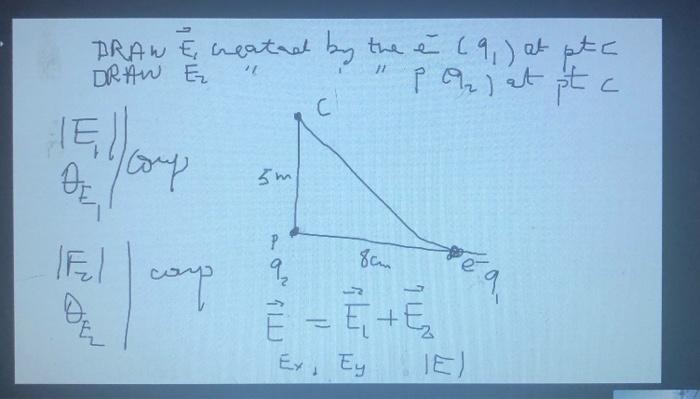
Solved Draw E1 Created By E Q1 At Point C Draw E2 Chegg Draw e1 created by (e ) q1 at point c. draw e2 created by (p) q2 at point c. find the force and direction of e1, e2 and the resultant vector. use the component method as well. your solution’s ready to go! our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. To find the electric field from several point charges we can use superposition and just add the e field contributions separately. to find the net field in the x direction we just sum the individual x axis contributions.

Solved Entered Answer Preview Result Message C1 E 2 X Chegg A positive point charge q 1 creates an electric field of magnitude e 1 at a spot located at a distance r1 from the charge. the charge is replaced by another positive point charge q 2, which creates a field of magnitude e 2 = e 1 at a distance of r2 = 2r1. (a) calculate the electric fields e1 and e2 at p due to charges q1 and q2, expressed in unit vector notation. (b) use the results from the previous question to find the resultant electric field e at p, expressed in unit vector form. A positive point charge q1 creates an electric field of magnitude e1 at a spot located at a distance r1 from the charge. the charge isreplaced by another positive point charge q2, which creates a field of magnitude e2=e1 at a distance of r2=2r1. What is the direction of the electric field at point a? what is the direction of the electric field at point c? c . zero. away from positive charge (right) towards negative charge (right) net e field is to right. add (vectors!) note: this is similar to (but a bit harder than) my earlier example.
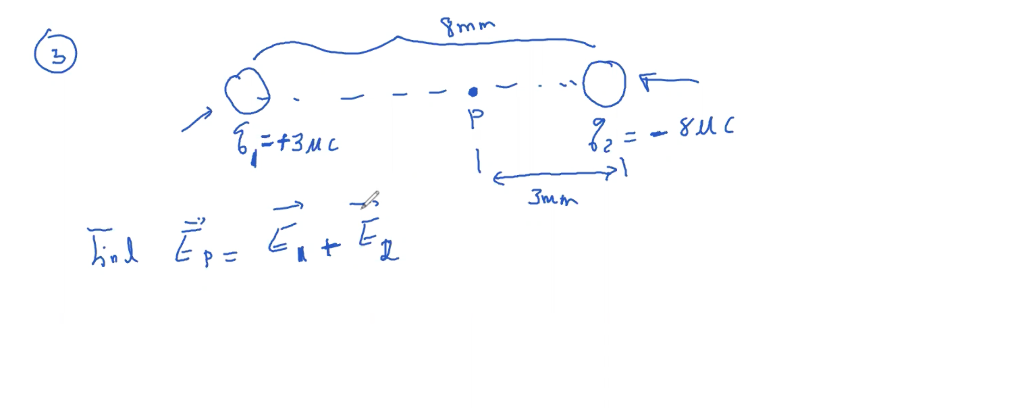
Solved Find Ep E1 E2 Q1 3 μc Q2 8 μc Chegg A positive point charge q1 creates an electric field of magnitude e1 at a spot located at a distance r1 from the charge. the charge isreplaced by another positive point charge q2, which creates a field of magnitude e2=e1 at a distance of r2=2r1. What is the direction of the electric field at point a? what is the direction of the electric field at point c? c . zero. away from positive charge (right) towards negative charge (right) net e field is to right. add (vectors!) note: this is similar to (but a bit harder than) my earlier example. To find the direction of the vector e1 we perform a “thought experiment” that consists in placing a positive test charge at point p and to identify the direction of the force it would experience in presence of charge q 1. The force of gravity points downward and has magnitude mg (m is the mass of the object) and the electrical force acting on the mass has magnitude f = |q|e, where q is the charge of the object and e is the magnitude of the electric field. Calculate the electric fields e1 and e2 at point p due to the charges q1 and q2. express your results in terms of unit vectors (see example 21.6 in the textbook). So the electric field at point a is greater in magnitude compared to the field at point b. further, no electric field line passes through c, which implies that the resultant electric field at c due to these two charges is zero.

Solved A E2 E5p A 0 4 B E1 E3 E4 E5p B 0 8 C E2 E4p C 0 4 Chegg To find the direction of the vector e1 we perform a “thought experiment” that consists in placing a positive test charge at point p and to identify the direction of the force it would experience in presence of charge q 1. The force of gravity points downward and has magnitude mg (m is the mass of the object) and the electrical force acting on the mass has magnitude f = |q|e, where q is the charge of the object and e is the magnitude of the electric field. Calculate the electric fields e1 and e2 at point p due to the charges q1 and q2. express your results in terms of unit vectors (see example 21.6 in the textbook). So the electric field at point a is greater in magnitude compared to the field at point b. further, no electric field line passes through c, which implies that the resultant electric field at c due to these two charges is zero.

Solved A E1 Elimination B E2 Elimination C It Is Chegg Calculate the electric fields e1 and e2 at point p due to the charges q1 and q2. express your results in terms of unit vectors (see example 21.6 in the textbook). So the electric field at point a is greater in magnitude compared to the field at point b. further, no electric field line passes through c, which implies that the resultant electric field at c due to these two charges is zero.
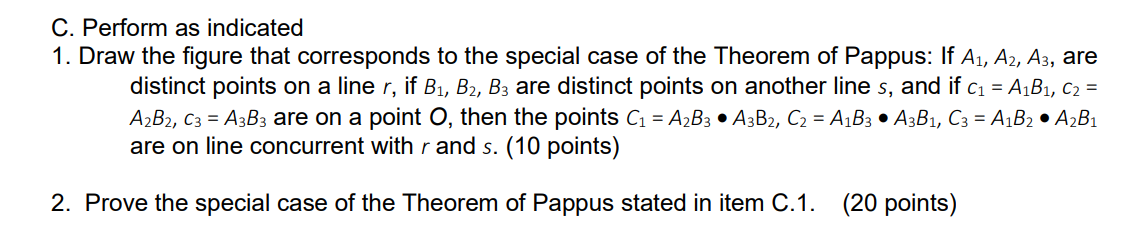
Solved C Perform As Indicated 1 Draw The Figure That Chegg
Comments are closed.