Solved Solve For V1 In The Circuit Of The Figure Using Nodal Chegg
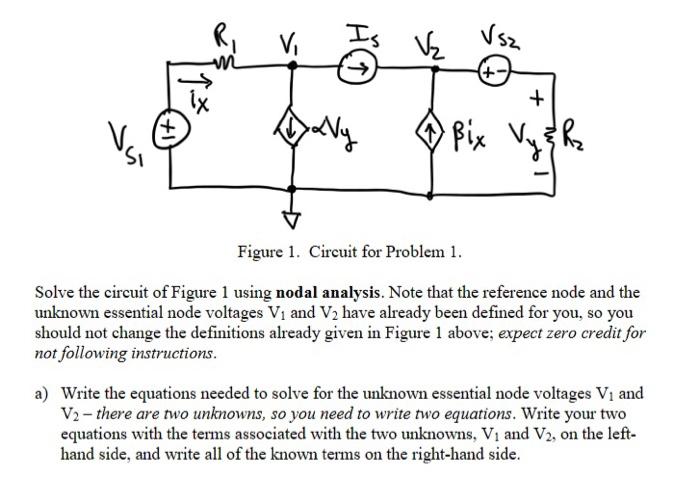
Solved Figure 1 Circuit For Problem 1 Solve The Circuit Of Chegg Using kcl, we can sum up all currents leaving the node. let us now express these currents in terms of voltage and resistance using (i=v r). v 1 3 k v 1 v 2 2 k 6 m = 0 (e q. 1) 3kv 1 2kv 1−v 2 6m= 0 (eq.1) next, we look at the purple node v 2 v 2. again, let us write our kcl expression. Explore solved problems on nodal analysis. master techniques for analyzing electrical circuits using node voltage method.
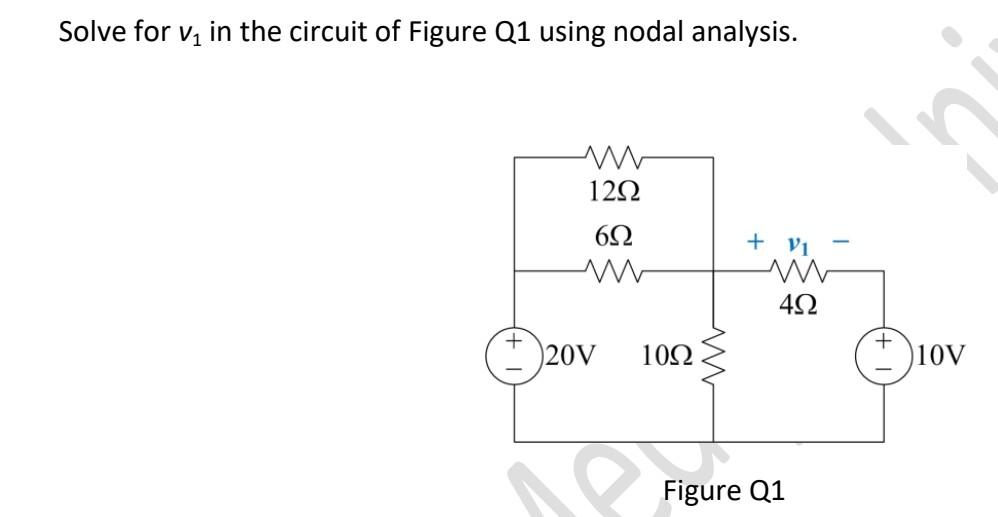
Solved Solve For V1 In The Circuit Of Figure Q1 Using Nodal Chegg Determine ix in the circuit shown in fig. 3.50 using nodal analysis. 1 kΩ 4 kΩ ix 9v 2 kΩ 6v figure 3.50 for prob. 3.1. chapter 3, solution 1 let vx be the voltage at the node between 1 kΩ and 4 kΩ resistors. 9 − vx 6 − vx vk = 1k 4k 2k vx ix = = 3 ma 2k ⎯⎯ → vx = 6 proprietary material. © 2007 the mcgraw hill companies, inc. For the circuit in the figure, find v {1}, v {2} v1,v2 and v {3} v3 using nodal analysis. nodes 1 and 2 form a supernode; so do nodes 1 and 3. hence. but i= v {3} 4 v 3 4 . combining this with (2) and (3) gives. nodes 1 and 2 form a supernode; so do nodes 1 and 3. We will apply **kirchhoff’s current law (kcl)* and ohm’s law to set up and solve the circuit equations. this method is essential in *electrical engineering* for circuit analysis. whether you. To find the values of v1, v2, and v3 in the circuit of figure 1 using nodal analysis, we need to set up and solve a system of linear equations. the steps are as follows: identify the nodes in the circuit. in this case, there are 3 nodes: the top node, the middle node, and the bottom node.

Solved Solve For V1 In The Circuit Of The Figure Using Nodal Chegg We will apply **kirchhoff’s current law (kcl)* and ohm’s law to set up and solve the circuit equations. this method is essential in *electrical engineering* for circuit analysis. whether you. To find the values of v1, v2, and v3 in the circuit of figure 1 using nodal analysis, we need to set up and solve a system of linear equations. the steps are as follows: identify the nodes in the circuit. in this case, there are 3 nodes: the top node, the middle node, and the bottom node. Solution for find v1, v2, and v3 in the circuit shown in figure 1 using nodal analysis to determine the node voltages in the following three different ways: 1. use hand calculation (show find v1, v2, and v3 in the circuit shown in figure 1 using nodal analysis. So the (v1 40) 1 represents the current leaving node 1 along that branch (e.g. if v1 was 50v, then the current would be (50 40) 1 = 10 a leaving towards ground).
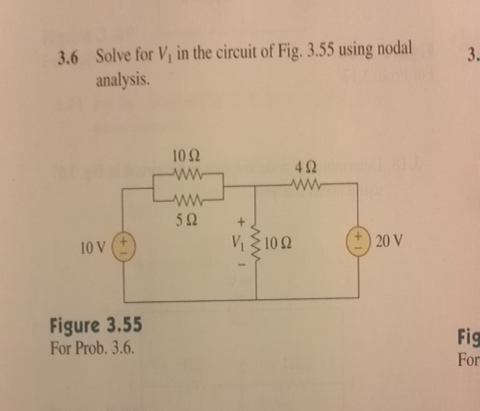
Solved Solve For V In The Circuit Of Fig 3 55 Using Nodal Chegg Solution for find v1, v2, and v3 in the circuit shown in figure 1 using nodal analysis to determine the node voltages in the following three different ways: 1. use hand calculation (show find v1, v2, and v3 in the circuit shown in figure 1 using nodal analysis. So the (v1 40) 1 represents the current leaving node 1 along that branch (e.g. if v1 was 50v, then the current would be (50 40) 1 = 10 a leaving towards ground).
Comments are closed.