Solved Standard Normal Distribution Table Page 1 Negative Chegg
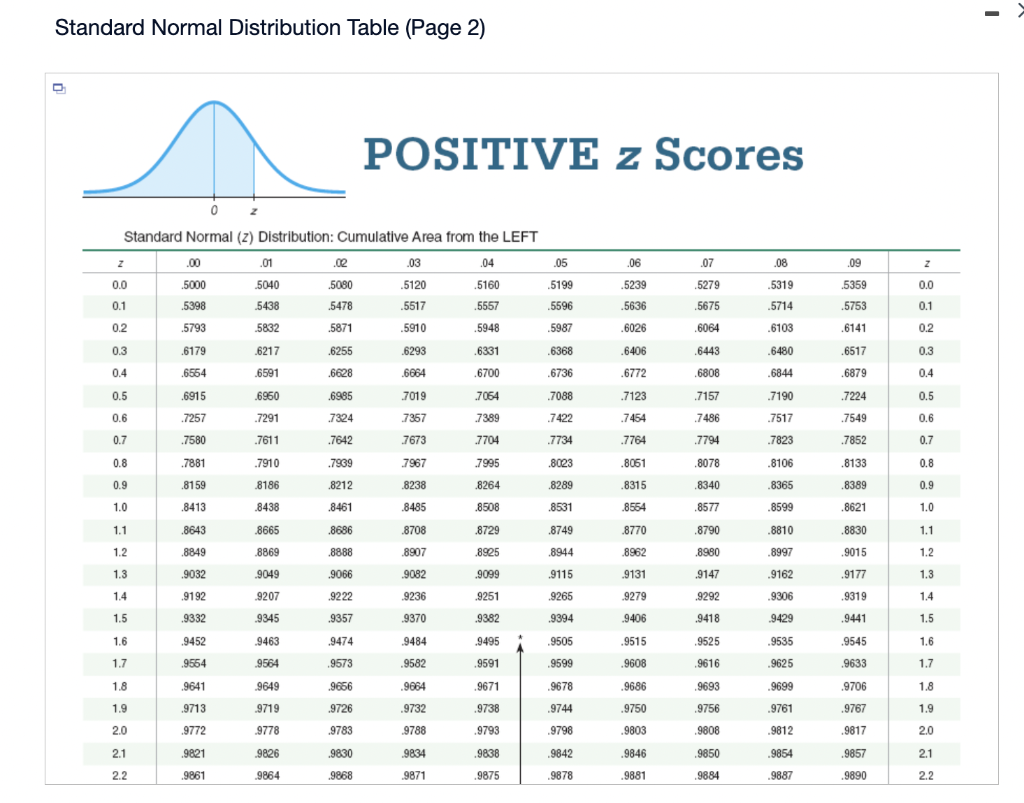
Solved Standard Normal Distribution Table Page 1 Negative Chegg Our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. Cumulative probabilities for negative z values are shown in the following table: z .00 .01 .02 .03 .04 .05 .06 .07 .08 .09 3.0 .0013 .0013 .0013 .0012 .0012 .0011 .0011 .0011 .0010 .0010.

Solved Standard Normal Distribution Table Page 1 Negative Chegg Start at the row for 0.4, and read along until 0.45: there is the value 0.1736. and 0.1736 is 17.36% so 17.36% of the population are between 0 and 0.45 standard deviations from the mean. because the curve is symmetrical, the same table can be used for values going either direction, so a negative 0.45 also has an area of 0.1736. Use the standard normal table to find the z score that corresponds to the given percentile. the area is not in the table, use the entry closest to the area. if the area is halfway between two entries, use the z score halfway between the corresponding z scores. if convenient, use technology to find the z score. p86 click to view page 1 of the table. Since the standard normal probability distribution is a continuous probability distribution, probabilities are given by the area under the graph. the z table gives the area under the standard normal distribution to the left of different z values. Standard normal cumulative probability table cumulative probabilities for negative z values are shown in the following table: z 0.00 0.01 0.02 0.03 0.04 0.05 0.06 0.07 0.08 0.09.
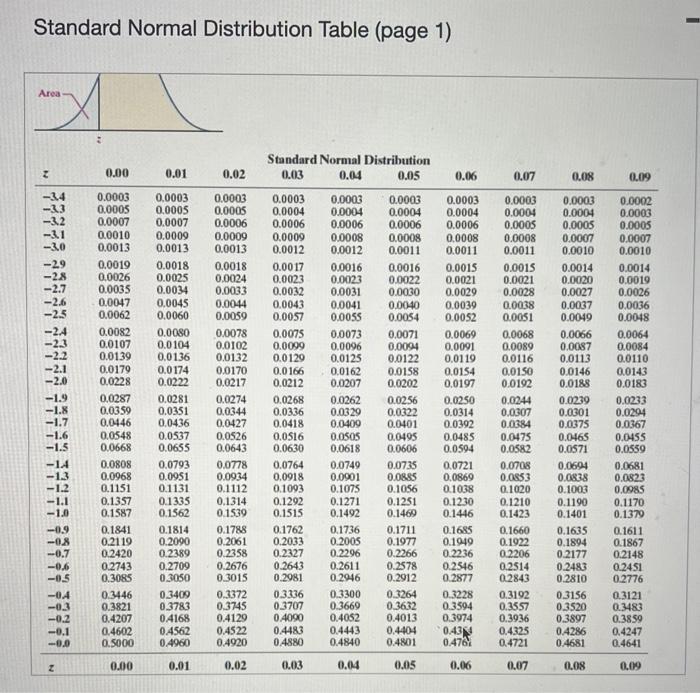
Solved Standard Normal Distribution Table Page Chegg Since the standard normal probability distribution is a continuous probability distribution, probabilities are given by the area under the graph. the z table gives the area under the standard normal distribution to the left of different z values. Standard normal cumulative probability table cumulative probabilities for negative z values are shown in the following table: z 0.00 0.01 0.02 0.03 0.04 0.05 0.06 0.07 0.08 0.09. Negative z score table: used when the z score is negative and below the mean. a negative z score table allows you to find the percentage or probability of all values occurring below a given negative z score in a standard normal distribution. 14.0.1: standard normal probability distribution z table last updated; save as pdf page id 46162. This ai generated tip is based on chegg's full solution. sign up to see more! since part (a) is already given as "this is a two tailed test," for part (b), determine the p value by using the z score of and consult the standard normal distribution table. Notice that the z table doesn't show areas for negative values of z. example: find the area under the standard normal distribution below z = 1: there are a couple of ways to do this one. one way is to realize that since the total area is 1, the area below z = 1 is equal to 1 minus the area above z= 1 which we know from before is 0.1587.
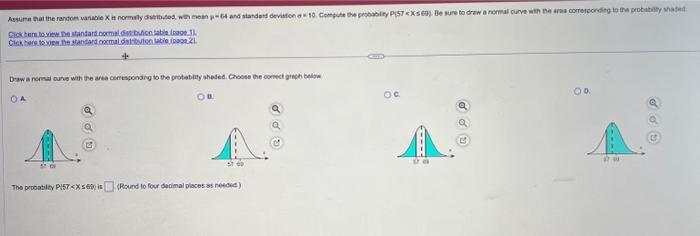
Solved Standard Normal Distribution Table Page Chegg Negative z score table: used when the z score is negative and below the mean. a negative z score table allows you to find the percentage or probability of all values occurring below a given negative z score in a standard normal distribution. 14.0.1: standard normal probability distribution z table last updated; save as pdf page id 46162. This ai generated tip is based on chegg's full solution. sign up to see more! since part (a) is already given as "this is a two tailed test," for part (b), determine the p value by using the z score of and consult the standard normal distribution table. Notice that the z table doesn't show areas for negative values of z. example: find the area under the standard normal distribution below z = 1: there are a couple of ways to do this one. one way is to realize that since the total area is 1, the area below z = 1 is equal to 1 minus the area above z= 1 which we know from before is 0.1587.
Solved Standard Normal Distribution Table Page 1 Standard Chegg This ai generated tip is based on chegg's full solution. sign up to see more! since part (a) is already given as "this is a two tailed test," for part (b), determine the p value by using the z score of and consult the standard normal distribution table. Notice that the z table doesn't show areas for negative values of z. example: find the area under the standard normal distribution below z = 1: there are a couple of ways to do this one. one way is to realize that since the total area is 1, the area below z = 1 is equal to 1 minus the area above z= 1 which we know from before is 0.1587.

Solved Standard Normal Distribution Table Page Chegg
Comments are closed.