Solved Use Nodal Analysis To Find Equation For All Voltages Chegg
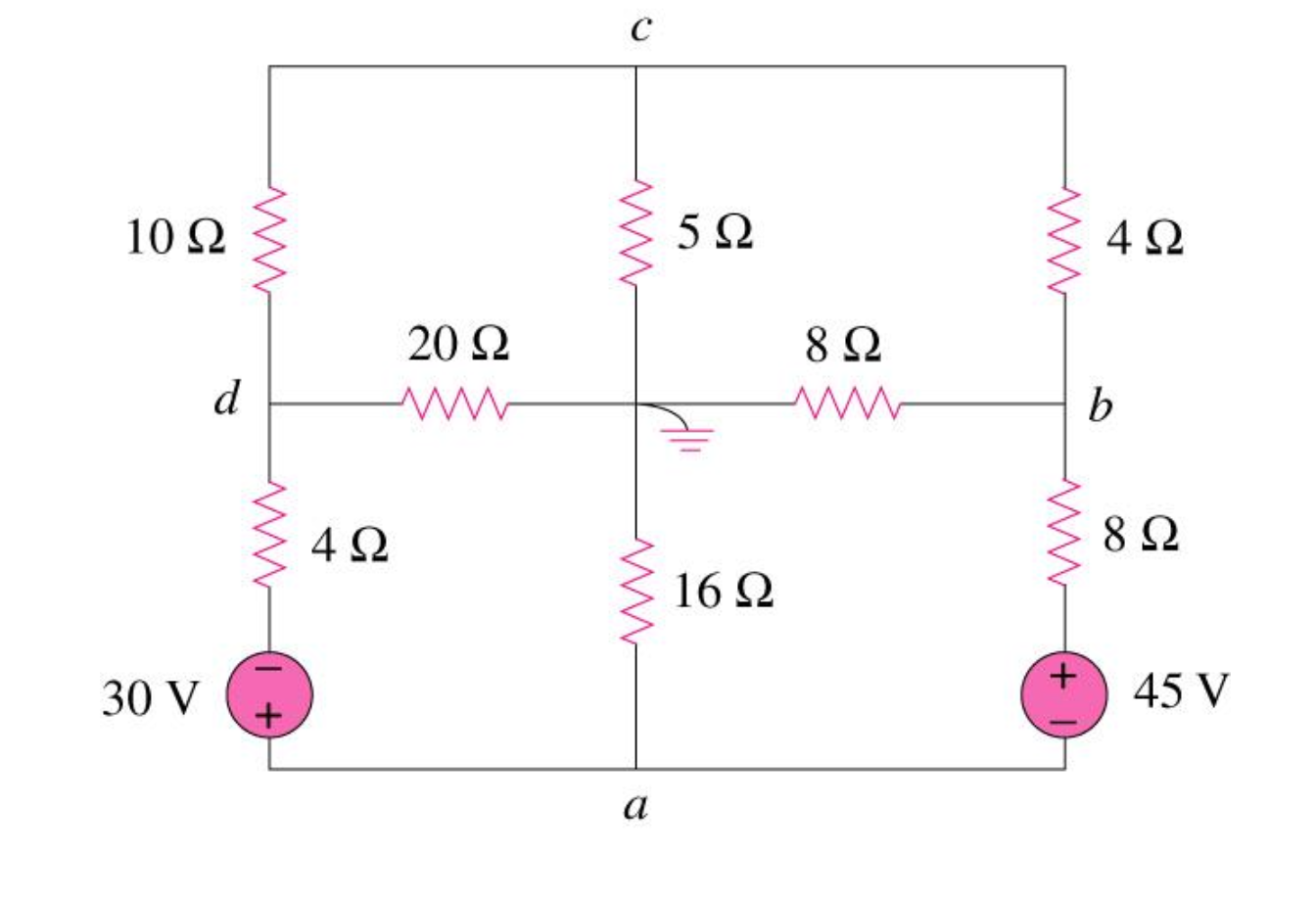
Solved Use Nodal Analysis To Find All The Nodal Voltages If Chegg Here’s the best way to solve it. not the question you’re looking for? post any question and get expert help quickly. Now the system of equations can be solved for the three node voltages and verified using kcl summations at each node. this is left as an exercise.
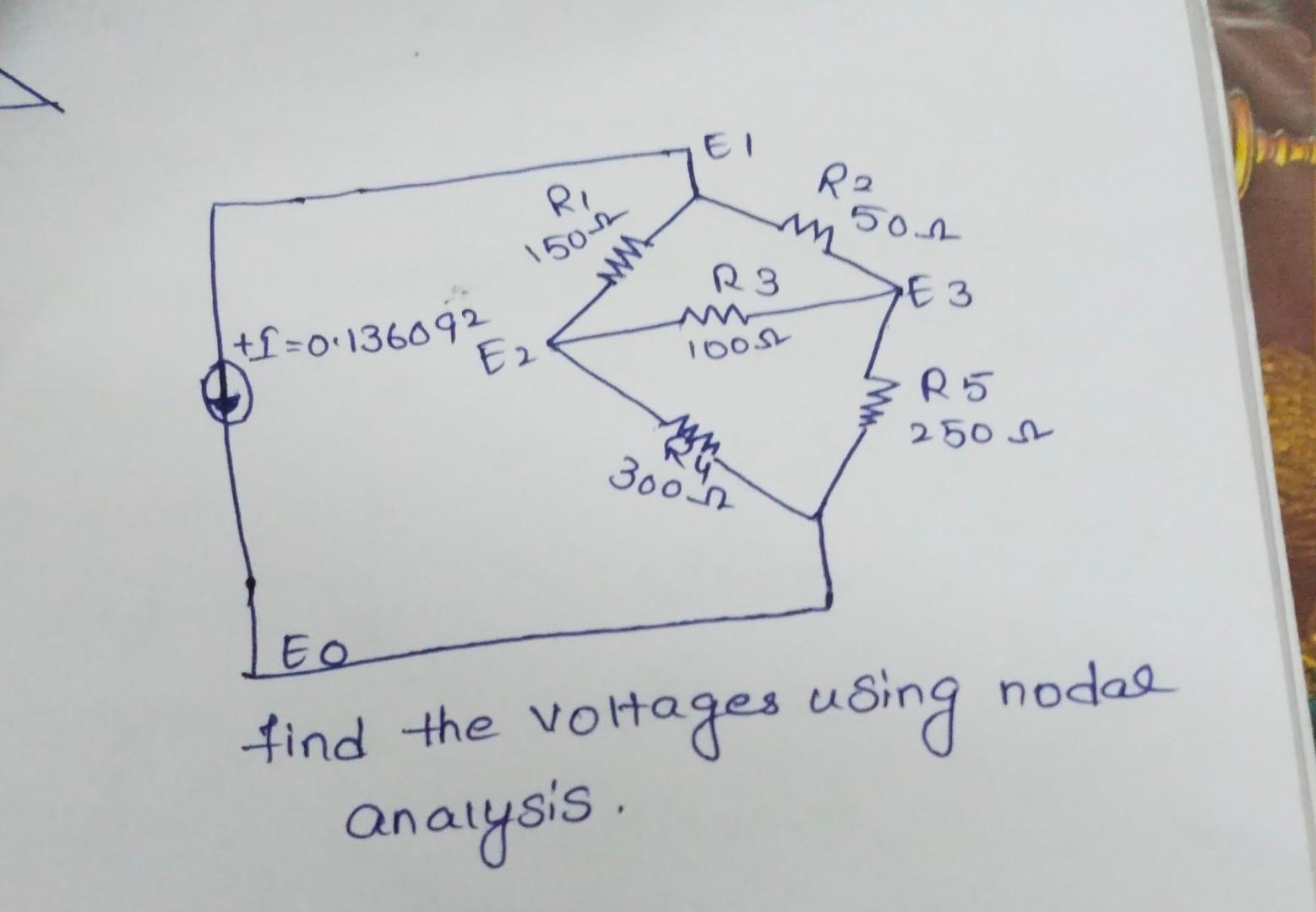
Solved Find The Voltages Using Nodal Analysis Chegg In conclusion, nodal analysis is a systematic approach of solving complex circuits using node voltages. it uses kcl, kvl and ohm's law for forming the equations. when a voltage source is present between two non reference nodes then the node is known as super node. Explore solved problems on nodal analysis. master techniques for analyzing electrical circuits using node voltage method. Converting all voltage sources to equivalent constant current sources allows us to standardize the way we write the kirchhoff’s current law equations. for nodal analysis, we consider source currents to flow into a node. In this method, kirchoff's current law is applied at various nodes in an electric circuit. nodal analysis. using nodal analysis determine the current in the 20 Ω resistor. convert all the voltage sources into their equivalent current sources. i1= 10 10 = 1a. i2= 20 10 = 2a. apply kcl to node 1. example: 30.
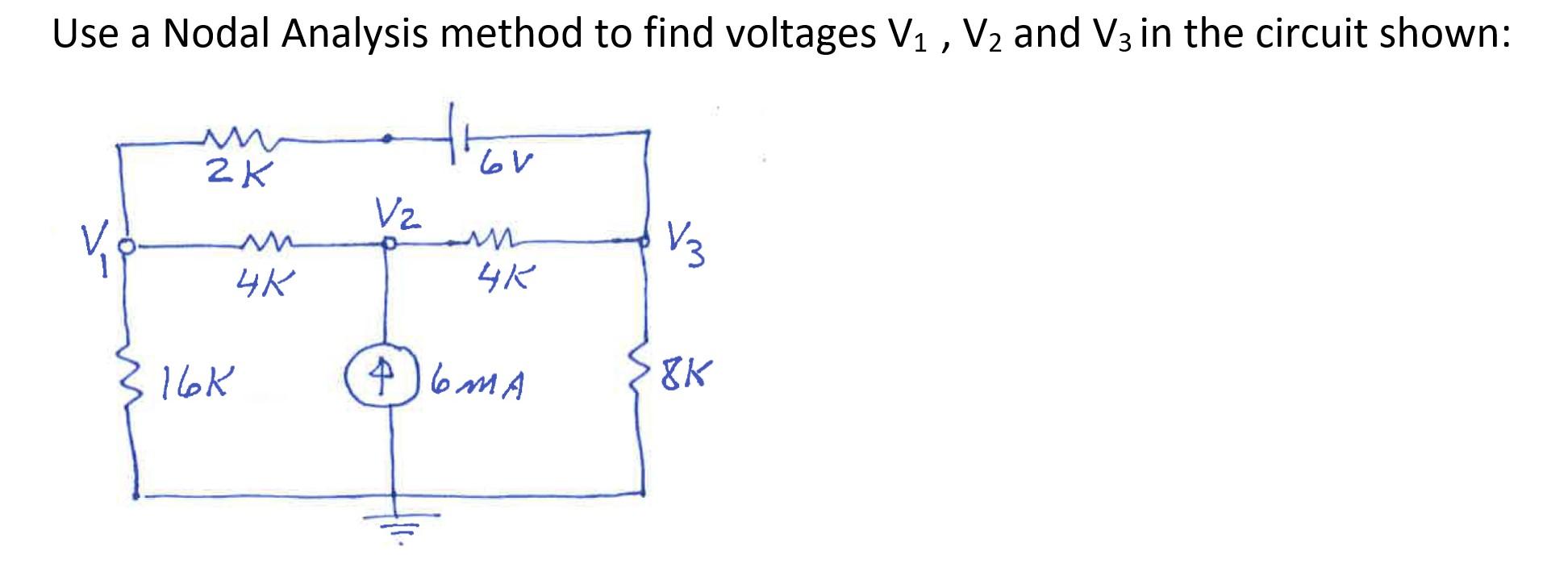
Solved Use A Nodal Analysis Method To Find Voltages V1 V2 Chegg Converting all voltage sources to equivalent constant current sources allows us to standardize the way we write the kirchhoff’s current law equations. for nodal analysis, we consider source currents to flow into a node. In this method, kirchoff's current law is applied at various nodes in an electric circuit. nodal analysis. using nodal analysis determine the current in the 20 Ω resistor. convert all the voltage sources into their equivalent current sources. i1= 10 10 = 1a. i2= 20 10 = 2a. apply kcl to node 1. example: 30. Just as current sources create special cases for mesh analysis, voltage sources create special cases for nodal analysis. we will write a kvl for each voltage supply in a circuit we are analyzing with nodal analysis. Nodal analysis, also known as the node voltage method, is a technique for analyzing circuits by focusing on the voltages at various nodes. nodal analysis is based on the application of the kirchhoff’s current law (kcl). having ‘n’ nodes there will be ‘n 1’ simultaneous equations to solve. Using nodal analysis, write the equations in matrix form. then, solve for each of the node voltages. Is a systematic way to generate multiple equations which can be solved to find the multiple unknowns. these equations are based on basic kirchoff's and ohm's laws.
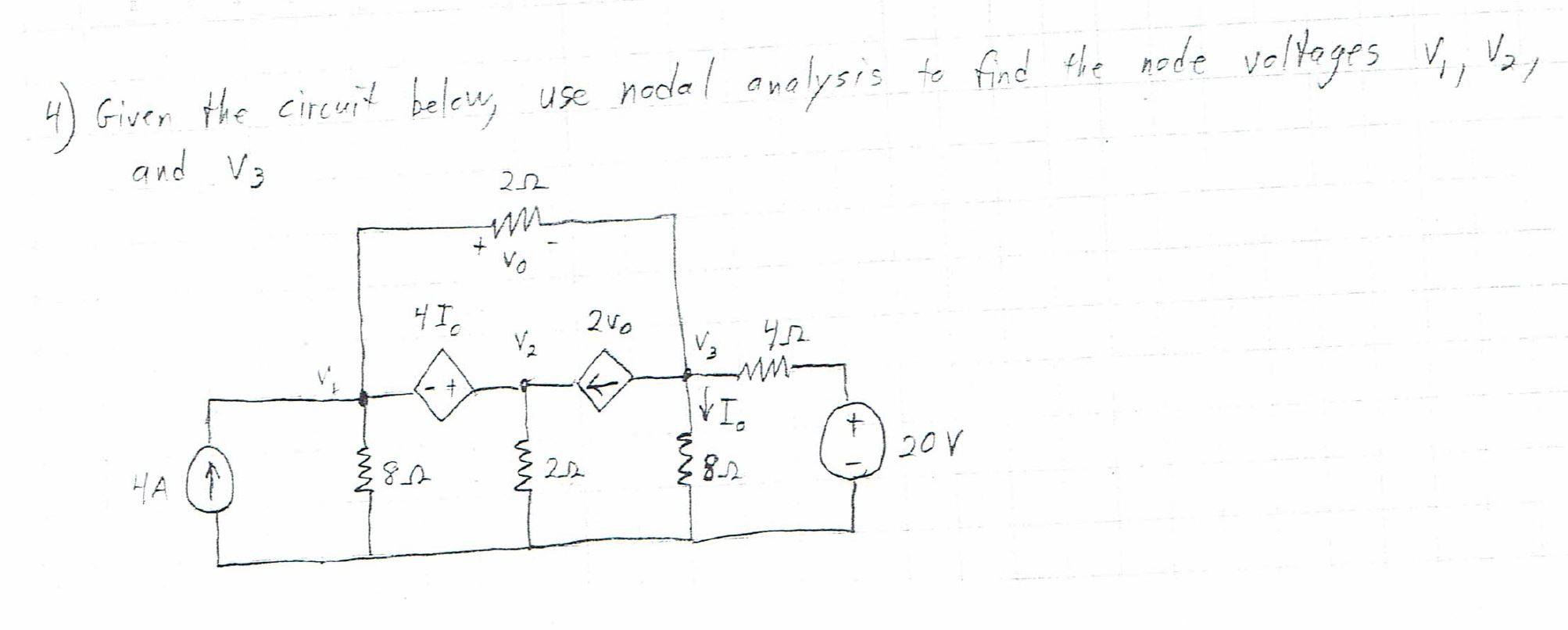
Solved Given The Circuit Below Use Nodal Analysis To Find Chegg Just as current sources create special cases for mesh analysis, voltage sources create special cases for nodal analysis. we will write a kvl for each voltage supply in a circuit we are analyzing with nodal analysis. Nodal analysis, also known as the node voltage method, is a technique for analyzing circuits by focusing on the voltages at various nodes. nodal analysis is based on the application of the kirchhoff’s current law (kcl). having ‘n’ nodes there will be ‘n 1’ simultaneous equations to solve. Using nodal analysis, write the equations in matrix form. then, solve for each of the node voltages. Is a systematic way to generate multiple equations which can be solved to find the multiple unknowns. these equations are based on basic kirchoff's and ohm's laws.
Comments are closed.