Solved Use S Domain Node Voltage Analysis To Find V 2 S And Chegg
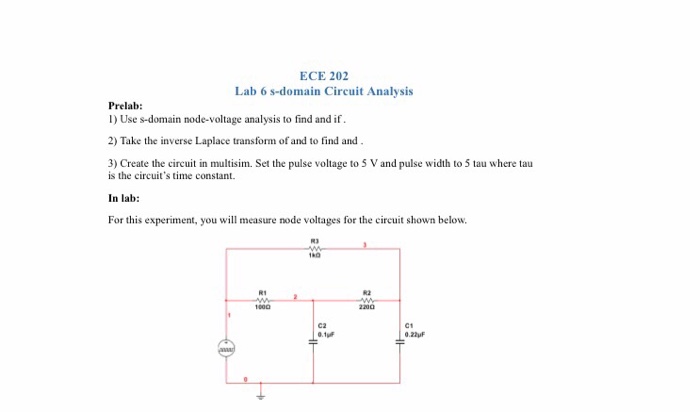
1 Use S Domain Node Voltage Analysis To Find And If Chegg Use s domain node voltage analysis to find v 2 (s) and v 3(s) if v in (t) = 5u(t). take the inverse laplace transform of v 2(s) and v 3(s) to find v 2(t) and v 3(t). create the circuit in multisim. set the pulse voltage to 5 v and pulse width to 5 tau where tau is the circuit's time constant. Solve for vc(t). $% = eq ! % $ sl ! the switch has been open for a long time and is closed at t=0.
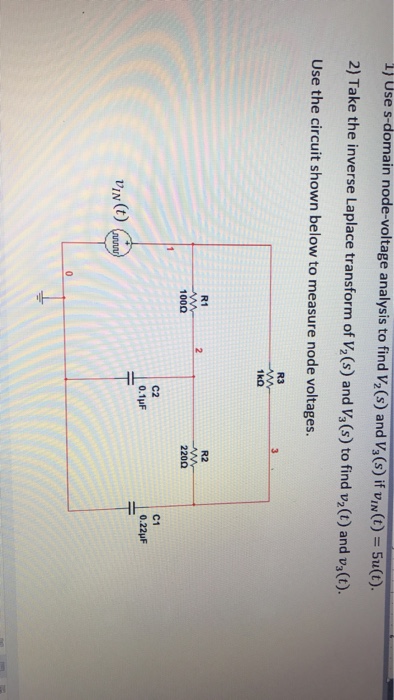
Solved Use S Domain Node Voltage Analysis To Find V 2 S And Chegg Using the laplace transform to solve a second order circuit. the method requires that the circuit be converted from the time domain to the s domain and then solved for v(s). Find out how to transform time domain circuit elements (resistors, capacitors, inductors) into the s domain using laplace transforms. develop the ability to solve linear time invariant (lti) circuits using the s domain techniques, including nodal and mesh analysis. Currents or node voltage due to the need to solve simultaneous differential equations. since laplace allows for algebraic manipulation we can solve a circuit like the one to the right. first find the s domain equivalent circuit… then write the necessary mesh or node equations. General techniques for s domain circuit analysis • node voltage analysis (in s domain) – use kirchhoff’s current law (kcl) – get equations of node voltages – use current sources for initial conditions – voltage source current source • mesh current analysis (in s domain) – use kirchhoff’s voltage law (kvl).
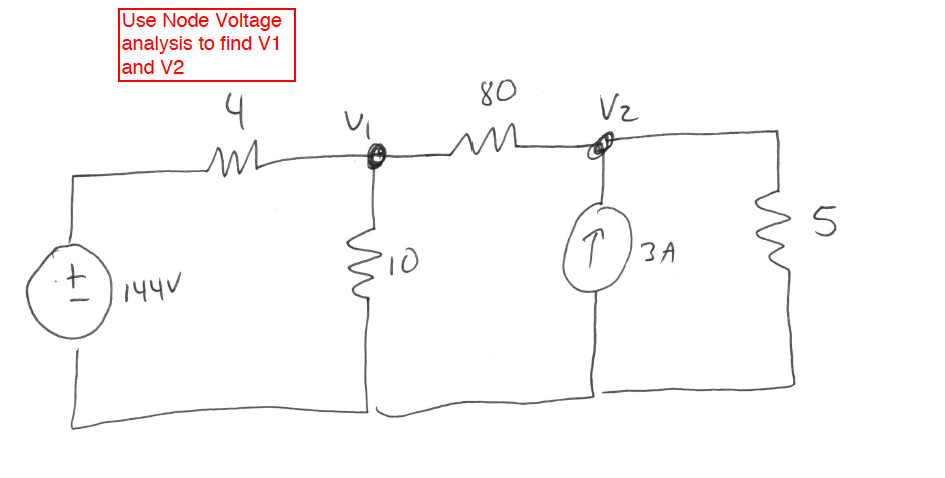
Solved Use Node Voltage Analysis To Find V1 And V2 Chegg Currents or node voltage due to the need to solve simultaneous differential equations. since laplace allows for algebraic manipulation we can solve a circuit like the one to the right. first find the s domain equivalent circuit… then write the necessary mesh or node equations. General techniques for s domain circuit analysis • node voltage analysis (in s domain) – use kirchhoff’s current law (kcl) – get equations of node voltages – use current sources for initial conditions – voltage source current source • mesh current analysis (in s domain) – use kirchhoff’s voltage law (kvl). Use s domain node voltage analysis to find v 2(s) (voltage across c1 ) and v 3(s) (voltage across c2 ) if vin (t)=5u(t). be sure to show (a) the node equations, (b) the method you use to determine the node voltages and (c) your results. you may use matlab or a calculator but indicate what you entered to obtain your results. 3. We will apply **kirchhoff’s current law (kcl)* and ohm’s law to set up and solve the circuit equations. this method is essential in *electrical engineering* for circuit analysis. whether you. Explore solved problems on nodal analysis. master techniques for analyzing electrical circuits using node voltage method. S domain circuit analysis operate directly in the s domain with capacitors, inductors and resistors key feature – linearity is preserved ccts described by odes and their ics order equals number of c plus number of l element by element and source transformation nodal or mesh analysis for s domain cct variables solution via inverse laplace.

Solved Use S Domain Node Voltage Analysis To Find V 2 S Chegg Use s domain node voltage analysis to find v 2(s) (voltage across c1 ) and v 3(s) (voltage across c2 ) if vin (t)=5u(t). be sure to show (a) the node equations, (b) the method you use to determine the node voltages and (c) your results. you may use matlab or a calculator but indicate what you entered to obtain your results. 3. We will apply **kirchhoff’s current law (kcl)* and ohm’s law to set up and solve the circuit equations. this method is essential in *electrical engineering* for circuit analysis. whether you. Explore solved problems on nodal analysis. master techniques for analyzing electrical circuits using node voltage method. S domain circuit analysis operate directly in the s domain with capacitors, inductors and resistors key feature – linearity is preserved ccts described by odes and their ics order equals number of c plus number of l element by element and source transformation nodal or mesh analysis for s domain cct variables solution via inverse laplace.
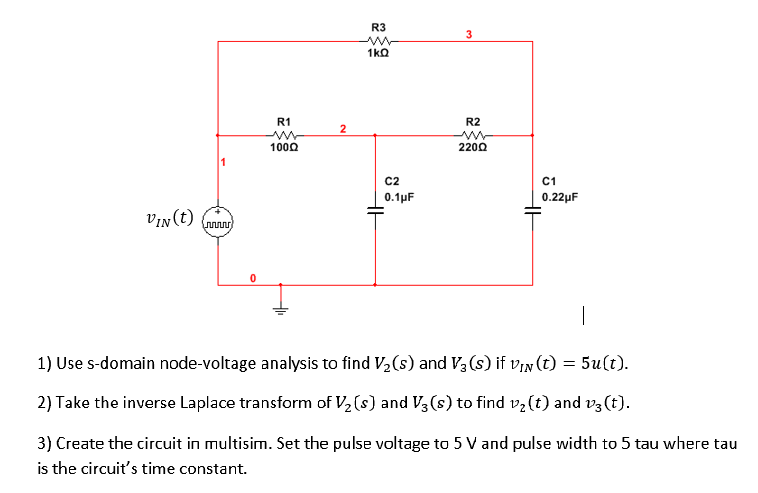
Solved Use S Domain Node Voltage Analysis To Find V 2 S Chegg Explore solved problems on nodal analysis. master techniques for analyzing electrical circuits using node voltage method. S domain circuit analysis operate directly in the s domain with capacitors, inductors and resistors key feature – linearity is preserved ccts described by odes and their ics order equals number of c plus number of l element by element and source transformation nodal or mesh analysis for s domain cct variables solution via inverse laplace.
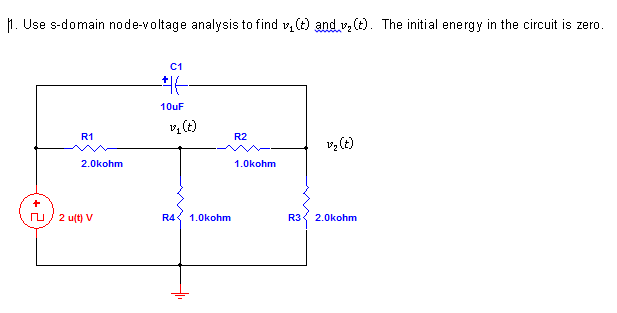
Solved Use S Domain Node Voltage Analysis To Find V 1 T And Chegg
Comments are closed.