Solved Value 10 00 Points Problem 03 017 Nodal Analysis Chegg
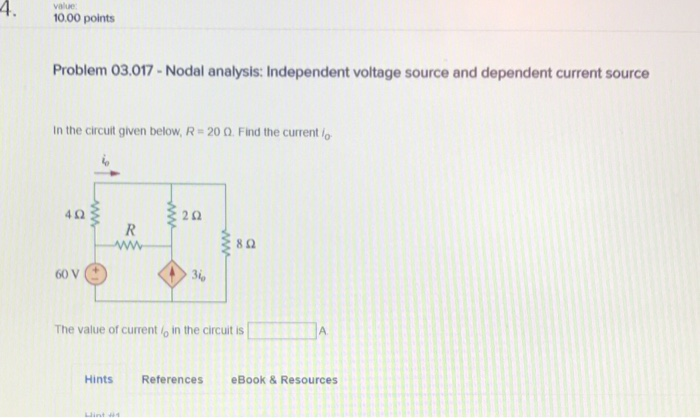
Solved Value 10 00 Points Problem 03 017 Nodal Analysis Chegg Value 10.00 points problem 03.017 nodal analysis: independent voltage source and dependent current source in the circuit given below, r = 20 . find the current lo w 60 v hints references your solution’s ready to go!. In this method, kirchoff's current law is applied at various nodes in an electric circuit. nodal analysis. using nodal analysis determine the current in the 20 Ω resistor. convert all the voltage sources into their equivalent current sources. i1= 10 10 = 1a. i2= 20 10 = 2a. apply kcl to node 1. example: 30.

Solved 1 Value 10 00 Points Problem 03 006 Nodal Chegg Problem 10.017 nodal analysis of a circuit with current sources determine the current i o in the circuit given below using nodal analysis, where v s = 110 20° v. please report your answer so the magnitude is positive and all angles are in the range of negative 180 degrees to positive 180 degrees. Explore solved problems on nodal analysis. master techniques for analyzing electrical circuits using node voltage method. Figure 3.77. circuit for problem 1 2. use nodal analysis to compute the voltage in the circuit of figure 3.78. answer: figure 3.78. circuit for problem 2 3. use nodal analysis to compute the current through the resistor and the power supplied (or absorbed) by the dependent source shown in figure 3.79. answers: 4. In this article, we will understand the nodal analysis with solved examples. we will discuss nodes and their types. we will discuss the procedure for nodal analysis along with some rules.
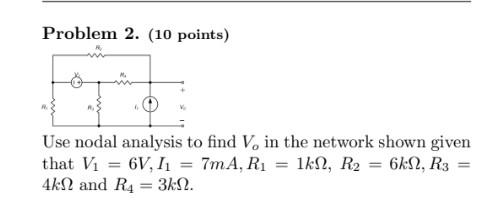
Solved Problem 2 10 Points Use Nodal Analysis To Find Vo Chegg Figure 3.77. circuit for problem 1 2. use nodal analysis to compute the voltage in the circuit of figure 3.78. answer: figure 3.78. circuit for problem 2 3. use nodal analysis to compute the current through the resistor and the power supplied (or absorbed) by the dependent source shown in figure 3.79. answers: 4. In this article, we will understand the nodal analysis with solved examples. we will discuss nodes and their types. we will discuss the procedure for nodal analysis along with some rules. We can use determinants to solve for the voltages. we can write equation 2 directly by noting that the positive voltage term on the left hand side of the equation is the unknown voltage for the node in question multiplied by the sum of the conductance connected to that node. For example, the circuit in figure 7.2.9 could be solved using nodal analysis by converting the voltage source and the associated resistance into a current source. that is, \(e r 1\) would be converted into a source \(i 3\) with a parallel resistor \(r 1\). Nodal analysis is based on the application of the kirchhoff’s current law (kcl). having ‘n’ nodes there will be ‘n 1’ simultaneous equations to solve. solving ‘n 1’ equations all the nodes voltages can be obtained. Nodal analysis steps 1) if the circuit doesn't already have a ground, label one node as ground (zero voltage). if the ground can be defined as one side of a voltage source, that will make the following steps easier.

Solved Problem 1 30 Points A Using The Nodal Analysis Chegg We can use determinants to solve for the voltages. we can write equation 2 directly by noting that the positive voltage term on the left hand side of the equation is the unknown voltage for the node in question multiplied by the sum of the conductance connected to that node. For example, the circuit in figure 7.2.9 could be solved using nodal analysis by converting the voltage source and the associated resistance into a current source. that is, \(e r 1\) would be converted into a source \(i 3\) with a parallel resistor \(r 1\). Nodal analysis is based on the application of the kirchhoff’s current law (kcl). having ‘n’ nodes there will be ‘n 1’ simultaneous equations to solve. solving ‘n 1’ equations all the nodes voltages can be obtained. Nodal analysis steps 1) if the circuit doesn't already have a ground, label one node as ground (zero voltage). if the ground can be defined as one side of a voltage source, that will make the following steps easier.
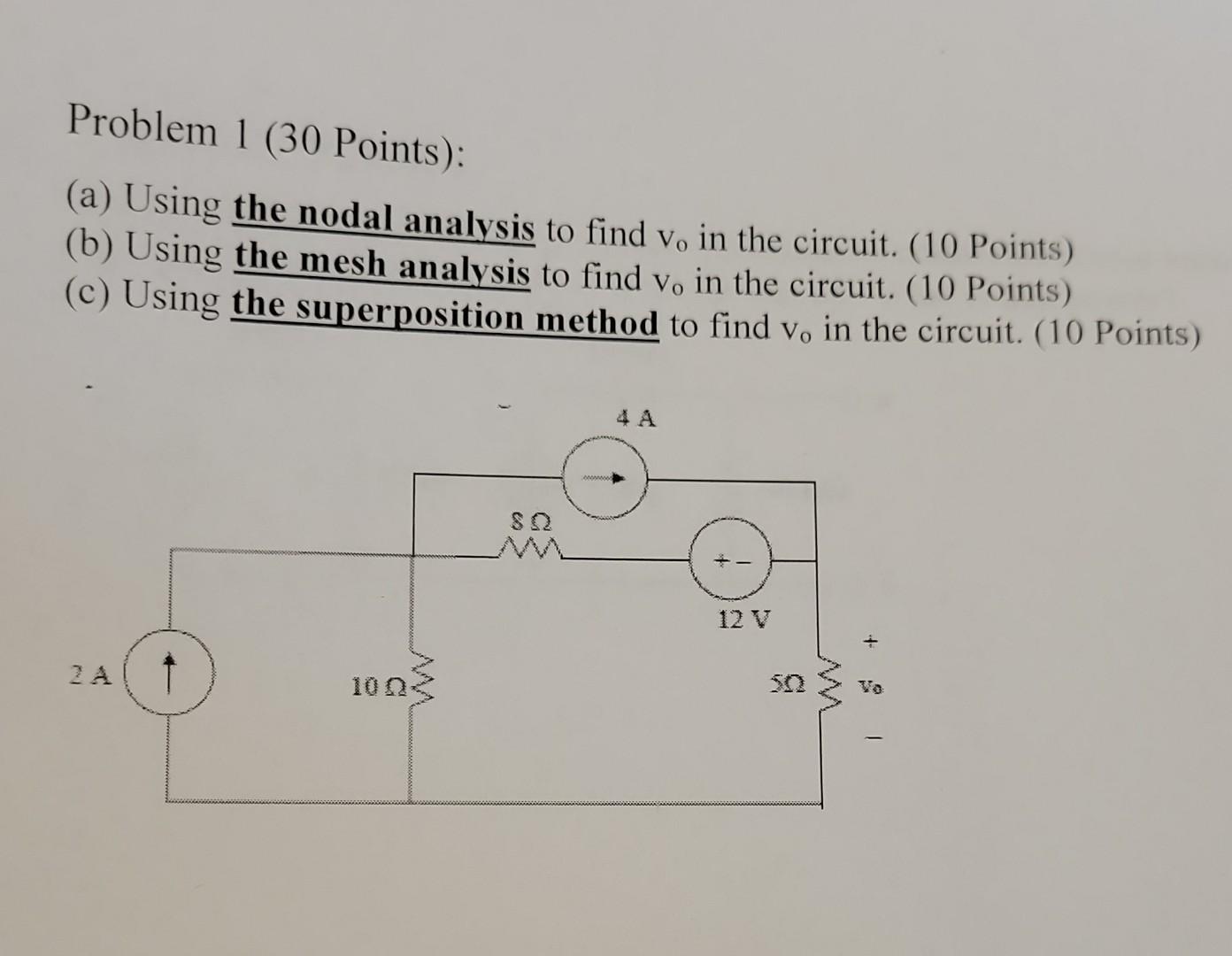
Problem 1 30 Points A Using The Nodal Analysis Chegg Nodal analysis is based on the application of the kirchhoff’s current law (kcl). having ‘n’ nodes there will be ‘n 1’ simultaneous equations to solve. solving ‘n 1’ equations all the nodes voltages can be obtained. Nodal analysis steps 1) if the circuit doesn't already have a ground, label one node as ground (zero voltage). if the ground can be defined as one side of a voltage source, that will make the following steps easier.
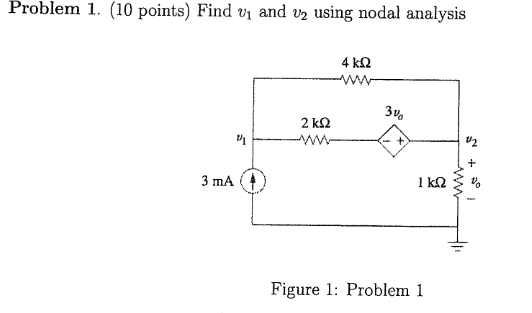
Solved Problem 1 10 Points Find V1 And V2 Using Nodal Chegg
Comments are closed.