Solving Single Autonomous Differential Equations Using Graphical Methods Math Insight

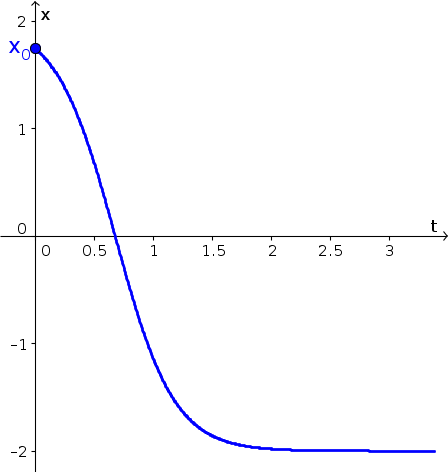
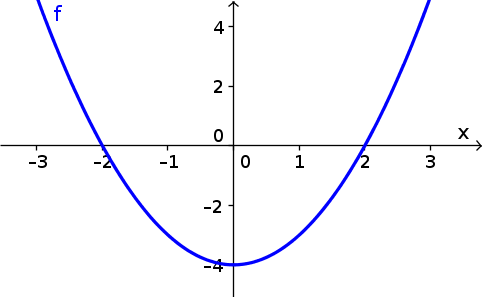
Autonomous Differential Equations Pdf Differential Equations Equations The graphical method for solving differential equations involves two different types of graphs. the first is a plot of the function defining the differential equation. since our differential equation can be written as $u'(t)=f(u)$ for $f(u)=1 u^2 9$, we plot $f$, shown below. 16.4: graphical solutions of autonomous equations is shared under a not declared license and was authored, remixed, and or curated by libretexts.
Solving Single Autonomous Differential Equations Using Graphical Methods Math Insight Solutions to differential equations can be graphed in a variety of ways, each giving different insight into the structure of the solutions. we begin by asking what object is to be graphed. do we first solve the differential equation and then graph the solution as was done previously?. See mathinsight.org solving single autonomous differential equations graphical for context. In our world things change, and describing how they change often ends up as a differential equation. real world examples where differential equations are used include population growth, electrodynamics, heat flow, planetary movement, economic systems and much more! solving. a differential equation can be a very natural way of describing something. Graphical and numerical methods the world of differential equations is large (very large). this page aims to see what is already done and what remains to do. chapters 1 and 2 concentrated on equations we can solve. compared to digging for coal or drilling for oil, this was the equivalent of picking up gold. solutions were wait ing for us.
Solving Single Autonomous Differential Equations Using Graphical Methods Math Insight In our world things change, and describing how they change often ends up as a differential equation. real world examples where differential equations are used include population growth, electrodynamics, heat flow, planetary movement, economic systems and much more! solving. a differential equation can be a very natural way of describing something. Graphical and numerical methods the world of differential equations is large (very large). this page aims to see what is already done and what remains to do. chapters 1 and 2 concentrated on equations we can solve. compared to digging for coal or drilling for oil, this was the equivalent of picking up gold. solutions were wait ing for us. 1.1 simple differential equations and explicit solutions 1.2 graphical solutions using calculus 1.3 slope fields and isoclines 1.4 functions and power series expansions. Go to: worksheet: solving single autonomous differential equations using graphical methods. We begin our discussion of the numerical integration of differential equations with the single first order differential equation of the form: the equation is first order since only the first derivative of the function appears in the equation. An autonomous system is a system of ordinary differential equations of the form = (()) where x takes values in n dimensional euclidean space; t is often interpreted as time it is distinguished from systems of differential equations of the form = ((),) in which the law governing the evolution of the system does not depend solely on the system's current state but also the parameter t, again.

Solving Single Autonomous Differential Equations Using Graphical Methods Math Insight 1.1 simple differential equations and explicit solutions 1.2 graphical solutions using calculus 1.3 slope fields and isoclines 1.4 functions and power series expansions. Go to: worksheet: solving single autonomous differential equations using graphical methods. We begin our discussion of the numerical integration of differential equations with the single first order differential equation of the form: the equation is first order since only the first derivative of the function appears in the equation. An autonomous system is a system of ordinary differential equations of the form = (()) where x takes values in n dimensional euclidean space; t is often interpreted as time it is distinguished from systems of differential equations of the form = ((),) in which the law governing the evolution of the system does not depend solely on the system's current state but also the parameter t, again.

Lecture 1 1d Autonomous Differential Equations Ws Pdf Pdf Differential Equations Equations We begin our discussion of the numerical integration of differential equations with the single first order differential equation of the form: the equation is first order since only the first derivative of the function appears in the equation. An autonomous system is a system of ordinary differential equations of the form = (()) where x takes values in n dimensional euclidean space; t is often interpreted as time it is distinguished from systems of differential equations of the form = ((),) in which the law governing the evolution of the system does not depend solely on the system's current state but also the parameter t, again.
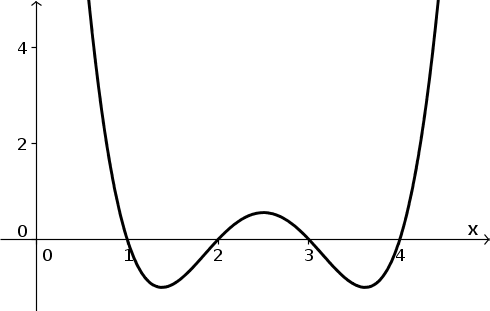
Image Autonomous Differential Equation Example Function 1 Math Insight
Comments are closed.