The Future Of Data Engineering How Generative Ai Is Revolutionizing The Fieldthe Future Of Data

Generative Ai Revolutionizing Industries And Shaping The Future The class template std::future provides a mechanism to access the result of asynchronous operations: . an asynchronous operation (created via std::async, std::packaged task, or std::promise) can provide a std::future object to the creator of that asynchronous operation. A future

The Future Of Data Engineering How Generative Ai Is Revolutionizing The Fieldthe Future Of Data 2) constructs a shared future that refers to the same shared state, if any, as other. 3,4) transfers the shared state held by other to * this . after the construction, other. valid ( ) == false , and this > valid ( ) returns the same value as other. valid ( ) would have returned before the construction. If the future is the result of a call to std::async that used lazy evaluation, this function returns immediately without waiting. this function may block for longer than timeout duration due to scheduling or resource contention delays. There's not even a guarantee that the shared state of a std::future doesn't lock a mutex to check if it's ready, so it would be impossible to guarantee it was wait free. for gcc's implementation the ready flag is an atomic so there's no mutex lock needed, and if it's ready then wait for returns immediately. Then, the "consumer" will receive this exception instead of data via its std::future. in summary: std::future is an object used in multithreaded programming to receive data or an exception from a different thread; it is one end of a single use, one way communication channel between two threads, std::promise object being the other end. using the.
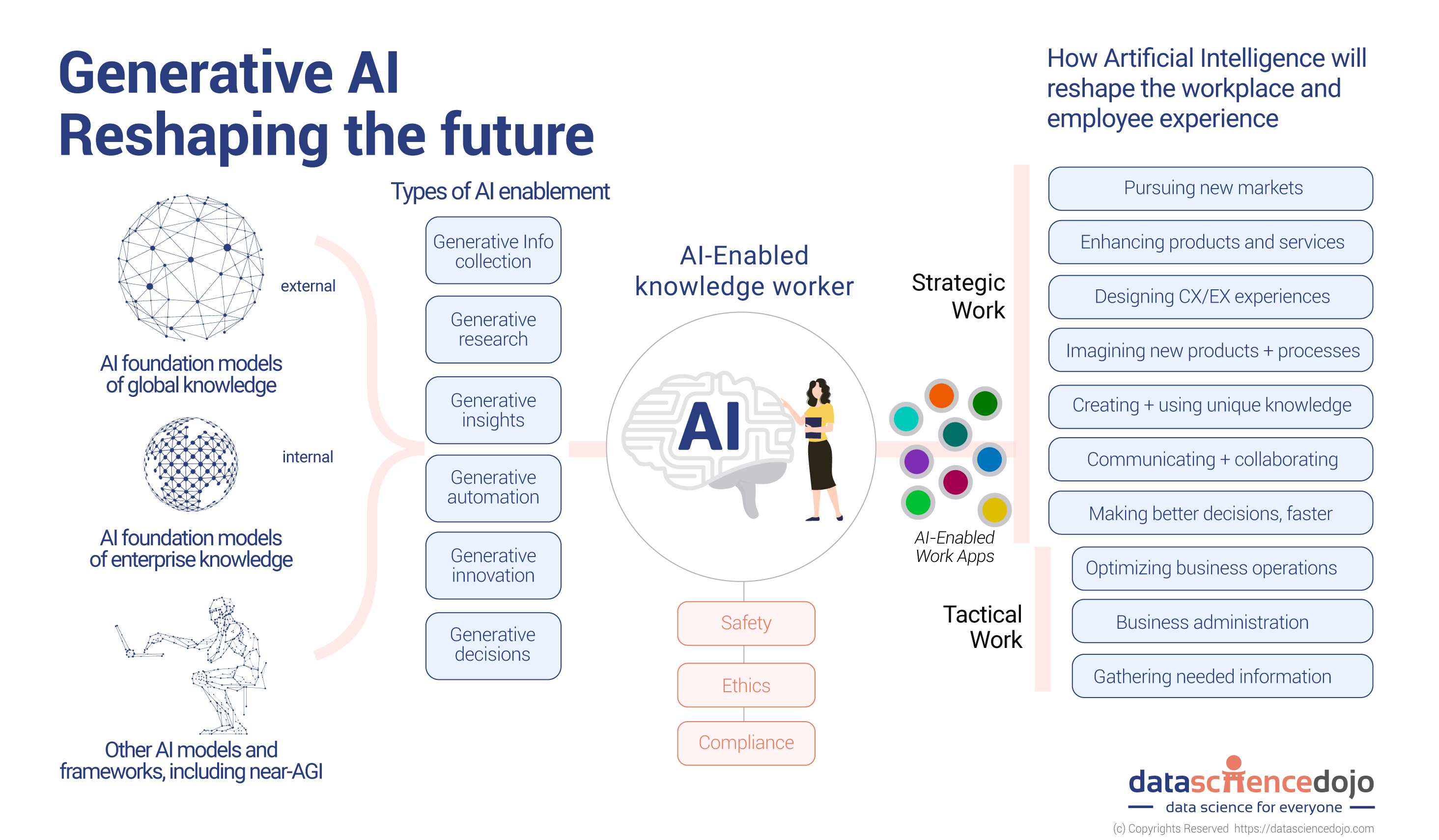
How Is Generative Ai Reshaping The Future Of Work Data Science Dojo There's not even a guarantee that the shared state of a std::future doesn't lock a mutex to check if it's ready, so it would be impossible to guarantee it was wait free. for gcc's implementation the ready flag is an atomic so there's no mutex lock needed, and if it's ready then wait for returns immediately. Then, the "consumer" will receive this exception instead of data via its std::future. in summary: std::future is an object used in multithreaded programming to receive data or an exception from a different thread; it is one end of a single use, one way communication channel between two threads, std::promise object being the other end. using the. Constructs a std::future with the shared state of other using move semantics. after construction, other. valid ( ) == false . 3) std::future is not copyconstructible . Waits for a value (possibly referenced by other futures) that is set asynchronously (class template). Calling wait on the same std::shared future from multiple threads is not safe; the intended use is for each thread that waits on the same shared state to have a copy of a std::shared future. [ edit ] example. The warning tells that in a future seaborn version you will need to write sns.countplot(x=ex emp['dept']). you are encouraged to already do it that way now. without the proper keyword it can quickly get confusing which plot is wanted. –.

Transforming Data Engineering How Generative Ai Is Shaping The Future Constructs a std::future with the shared state of other using move semantics. after construction, other. valid ( ) == false . 3) std::future is not copyconstructible . Waits for a value (possibly referenced by other futures) that is set asynchronously (class template). Calling wait on the same std::shared future from multiple threads is not safe; the intended use is for each thread that waits on the same shared state to have a copy of a std::shared future. [ edit ] example. The warning tells that in a future seaborn version you will need to write sns.countplot(x=ex emp['dept']). you are encouraged to already do it that way now. without the proper keyword it can quickly get confusing which plot is wanted. –.

Guide Generative Ai Data And The Future Of Talent Findem Calling wait on the same std::shared future from multiple threads is not safe; the intended use is for each thread that waits on the same shared state to have a copy of a std::shared future. [ edit ] example. The warning tells that in a future seaborn version you will need to write sns.countplot(x=ex emp['dept']). you are encouraged to already do it that way now. without the proper keyword it can quickly get confusing which plot is wanted. –.
Comments are closed.