Two Types Of Soil Erosion In India Infoupdate Org

Two Types Of Soil Erosion In India Infoupdate Org Explain the two types of soil erosion mostly observed in india earth surface processes and landforms geomorphology journal wiley online library. Two types: khadar (new alluvium) – more fertile bangar (old alluvium) – less fertile black soil (regur or black cotton soil) formed from weathered volcanic rocks; also called lava soil. rich in minerals and has high moisture retention. ideal for cotton and sugarcane cultivation.

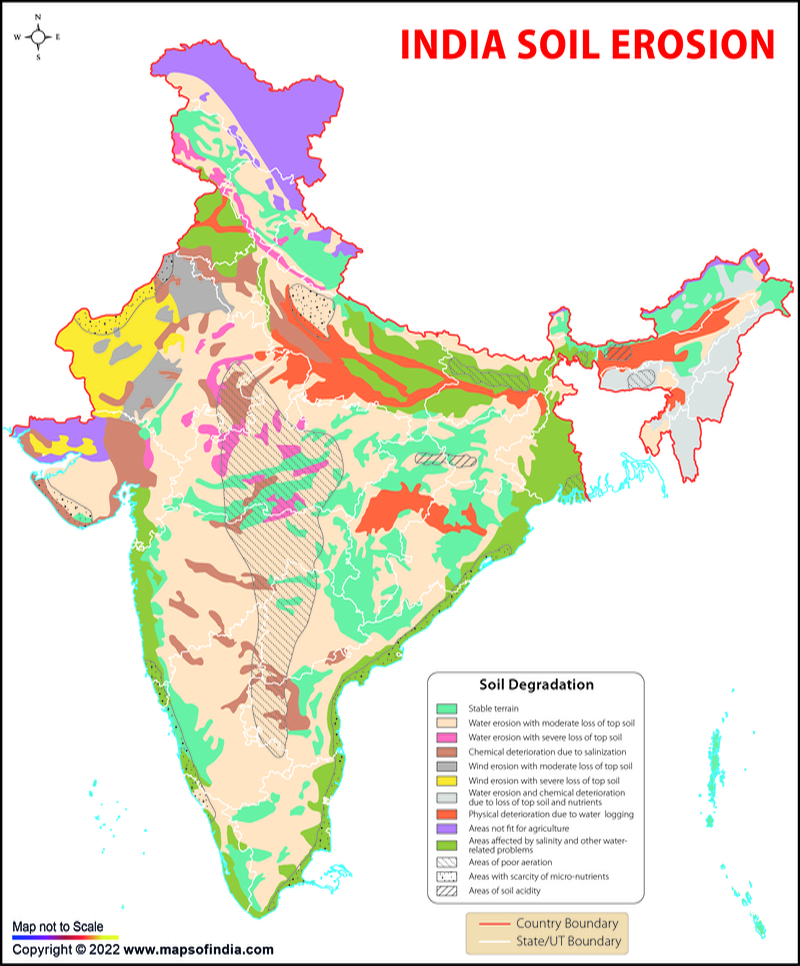
Two Types Of Soil Erosion In India Infoupdate Org Mention any two human activities which are responsible for the process of soil erosion. explain the two types of soil erosion mostly observed in india?. Exploring soil erosion in india: types, causes, effects, and effective remedies to mitigate its environmental impacts and preserve agricultural productivity. In uttar pradesh and bihar also suffer from the problem of soil erosion caused by water. these rivers are carving deep furrows and removing fertile top soil. according to one estimate the ganga river is transporting about 30 million tonnes of eroded material per year from the ganga plain to the bay of bengal. similarly the. Among two main agents of erosion namely water and winds in india about 90 per cent role is played by water. in the case of erosion by water, soil particles are either detached by impacting raindrops or run off water moving over soil surface.

Two Types Of Soil Erosion In India Infoupdate Org In uttar pradesh and bihar also suffer from the problem of soil erosion caused by water. these rivers are carving deep furrows and removing fertile top soil. according to one estimate the ganga river is transporting about 30 million tonnes of eroded material per year from the ganga plain to the bay of bengal. similarly the. Among two main agents of erosion namely water and winds in india about 90 per cent role is played by water. in the case of erosion by water, soil particles are either detached by impacting raindrops or run off water moving over soil surface. Types of soil erosion in india 10 what is soil erosion explain the major type of soil erosion prevailing in india brainly in. A recent study has shed light on the concerning state of soil erosion across india, revealing significant challenges and implications for agricultural productivity and environmental sustainability. Types of soil erosion in india are varied and are responsible for the immense damage of the eco system. the soil surface gets eroded by natural and artificial agents. The two types of natural soil erosion, water and wind erosion, are the major causes of land degradation. approximately 75 billion tons of soil are eroded annually, at a rate that is 13 40 times faster than the natural rate of erosion.

Two Types Of Soil Erosion In India Infoupdate Org Types of soil erosion in india 10 what is soil erosion explain the major type of soil erosion prevailing in india brainly in. A recent study has shed light on the concerning state of soil erosion across india, revealing significant challenges and implications for agricultural productivity and environmental sustainability. Types of soil erosion in india are varied and are responsible for the immense damage of the eco system. the soil surface gets eroded by natural and artificial agents. The two types of natural soil erosion, water and wind erosion, are the major causes of land degradation. approximately 75 billion tons of soil are eroded annually, at a rate that is 13 40 times faster than the natural rate of erosion.

Two Types Of Soil Erosion In India Infoupdate Org Types of soil erosion in india are varied and are responsible for the immense damage of the eco system. the soil surface gets eroded by natural and artificial agents. The two types of natural soil erosion, water and wind erosion, are the major causes of land degradation. approximately 75 billion tons of soil are eroded annually, at a rate that is 13 40 times faster than the natural rate of erosion.
Types Of Soil Erosion In India Infoupdate Org
Comments are closed.