Type 1 And Type 2 Errors Are You Positive You Know The Difference

Type 1 And Type 2 Errors Are You Positive You Know The Difference Artofit In statistics, a type i error is a false positive conclusion, while a type ii error is a false negative conclusion. making a statistical decision always involves uncertainties, so the risks of making these errors are unavoidable in hypothesis testing. One very simple way of understanding the difference between type 1 and type 2 errors is to think about erroneous test results. as clearly illustrated in the pregnancy example above. another great way is to provide a 'real world' perspective.

Difference Between Type 1 And Type 2 Errors In Statistical Hypothesis Testing How To Interpret It Type i error, or a false positive, is the erroneous rejection of a true null hypothesis in statistical hypothesis testing. a type ii error, or a false negative, is the erroneous failure in bringing about appropriate rejection of a false null hypothesis. [1]. In statistics, type i and type ii errors represent two kinds of errors that can occur when making a decision about a hypothesis based on sample data. understanding these errors is crucial for interpreting the results of hypothesis tests. When you try and reduce type 1 errors, you increase the odds of type 2 errors. therefore, controlling for type 1 and type 2 errors is based on the situation you are in. statistically speaking a reducing α risk (type 1) makes it harder to reject the null hypothesis. Both errors have significant implications in research and decision making. the chances of committing these two types of errors are inversely proportional: that is, decreasing type i error rate increases type ii error rate and vice versa.

Difference Of Type 1 And Type 2 Errors Datajello When you try and reduce type 1 errors, you increase the odds of type 2 errors. therefore, controlling for type 1 and type 2 errors is based on the situation you are in. statistically speaking a reducing α risk (type 1) makes it harder to reject the null hypothesis. Both errors have significant implications in research and decision making. the chances of committing these two types of errors are inversely proportional: that is, decreasing type i error rate increases type ii error rate and vice versa. Type i error or otherwise known as false positives, in essence, the positive result is equivalent to the refusal of the null hypothesis. in contrast, type ii error is also known as false negatives, i.e. negative result, leads to the acceptance of the null hypothesis. Type 1 errors occur when we incorrectly reject a true null hypothesis, while type 2 errors happen when we fail to reject a false null hypothesis. think of type 1 as a "false positive" and type 2 as a "false negative.". A type i error occurs when we reject a null hypothesis that is actually true, while a type ii error happens when we fail to reject a false null hypothesis. get the full details here. A type i error happens when you say that the null hypothesis is false when it actually is true. a type ii error happens when you say that the null hypothesis is true when it actually is.
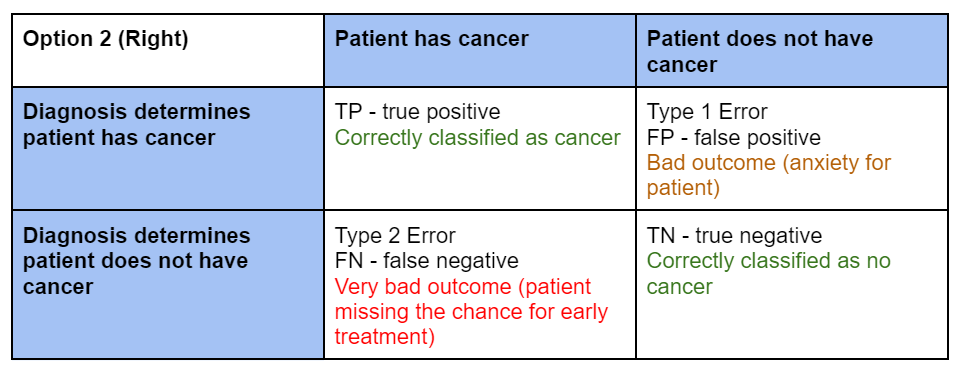
Difference Of Type 1 And Type 2 Errors Datajello Type i error or otherwise known as false positives, in essence, the positive result is equivalent to the refusal of the null hypothesis. in contrast, type ii error is also known as false negatives, i.e. negative result, leads to the acceptance of the null hypothesis. Type 1 errors occur when we incorrectly reject a true null hypothesis, while type 2 errors happen when we fail to reject a false null hypothesis. think of type 1 as a "false positive" and type 2 as a "false negative.". A type i error occurs when we reject a null hypothesis that is actually true, while a type ii error happens when we fail to reject a false null hypothesis. get the full details here. A type i error happens when you say that the null hypothesis is false when it actually is true. a type ii error happens when you say that the null hypothesis is true when it actually is.
Comments are closed.