Type 1 And Type 2 Errors Explained Differences And Examples Amplitude

Type 1 And Type 2 Errors Explained Differences And Examples Amplitude Type 1 & type 2 errors explained differences & examples. understanding type 1 and type 2 errors is essential. knowing what and how to manage them can help improve your testing and minimize future mistakes. Type i & type ii errors | differences, examples, visualizations. published on january 18, 2021 by pritha bhandari. revised on june 22, 2023. in statistics, a type i error is a false positive conclusion, while a type ii error is a false negative conclusion.

Type 1 And Type 2 Errors Explained Differences And Examples Amplitude Type 1 error, in statistical hypothesis testing, is the error caused by rejecting a null hypothesis when it is true. type ii error is the error that occurs when the null hypothesis is accepted when it is not true. Type 1 errors lead to false positives and unnecessary actions. type 2 errors result in missed detections, which may be more dangerous in critical settings. there’s no perfect fix—balancing α and β is key, based on the stakes of the situation. In statistics, type i and type ii errors represent two kinds of errors that can occur when making a decision about a hypothesis based on sample data. understanding these errors is crucial for interpreting the results of hypothesis tests. Type i error, or a false positive, is the erroneous rejection of a true null hypothesis in statistical hypothesis testing. a type ii error, or a false negative, is the erroneous failure in bringing about appropriate rejection of a false null hypothesis. [1].

Type 1 And Type 2 Errors Explained Differences And Examples Amplitude In statistics, type i and type ii errors represent two kinds of errors that can occur when making a decision about a hypothesis based on sample data. understanding these errors is crucial for interpreting the results of hypothesis tests. Type i error, or a false positive, is the erroneous rejection of a true null hypothesis in statistical hypothesis testing. a type ii error, or a false negative, is the erroneous failure in bringing about appropriate rejection of a false null hypothesis. [1]. Type i errors are like false alarms, while type ii errors are like missed opportunities. both errors can impact the validity and reliability of psychological findings, so researchers strive to minimize them to draw accurate conclusions from their studies. In statistics we call these two types of mistakes a type i and ii error. figure 8 5 is a diagram to see the four possible jury decisions and two errors. type i error is rejecting h0 when h0 is true, and type ii error is failing to reject h 0 when h 0 is false. From all of this we can conclude that it is important to understand the difference between type i and type ii errors when performing hypothesis testing, so that you can reduce them previously to the study in relation to what you are looking for. The figure in the above example shows the trade off between type i and type ii errors. the gold area gives [latex]\alpha[ latex], the probability of the type i error; and the blue area gives [latex]\beta[ latex], the probability of the type ii error.

Type 1 And Type 2 Errors With Examples Complete Clarity In 10 Min Hypothesis Type 1 Error Type i errors are like false alarms, while type ii errors are like missed opportunities. both errors can impact the validity and reliability of psychological findings, so researchers strive to minimize them to draw accurate conclusions from their studies. In statistics we call these two types of mistakes a type i and ii error. figure 8 5 is a diagram to see the four possible jury decisions and two errors. type i error is rejecting h0 when h0 is true, and type ii error is failing to reject h 0 when h 0 is false. From all of this we can conclude that it is important to understand the difference between type i and type ii errors when performing hypothesis testing, so that you can reduce them previously to the study in relation to what you are looking for. The figure in the above example shows the trade off between type i and type ii errors. the gold area gives [latex]\alpha[ latex], the probability of the type i error; and the blue area gives [latex]\beta[ latex], the probability of the type ii error.
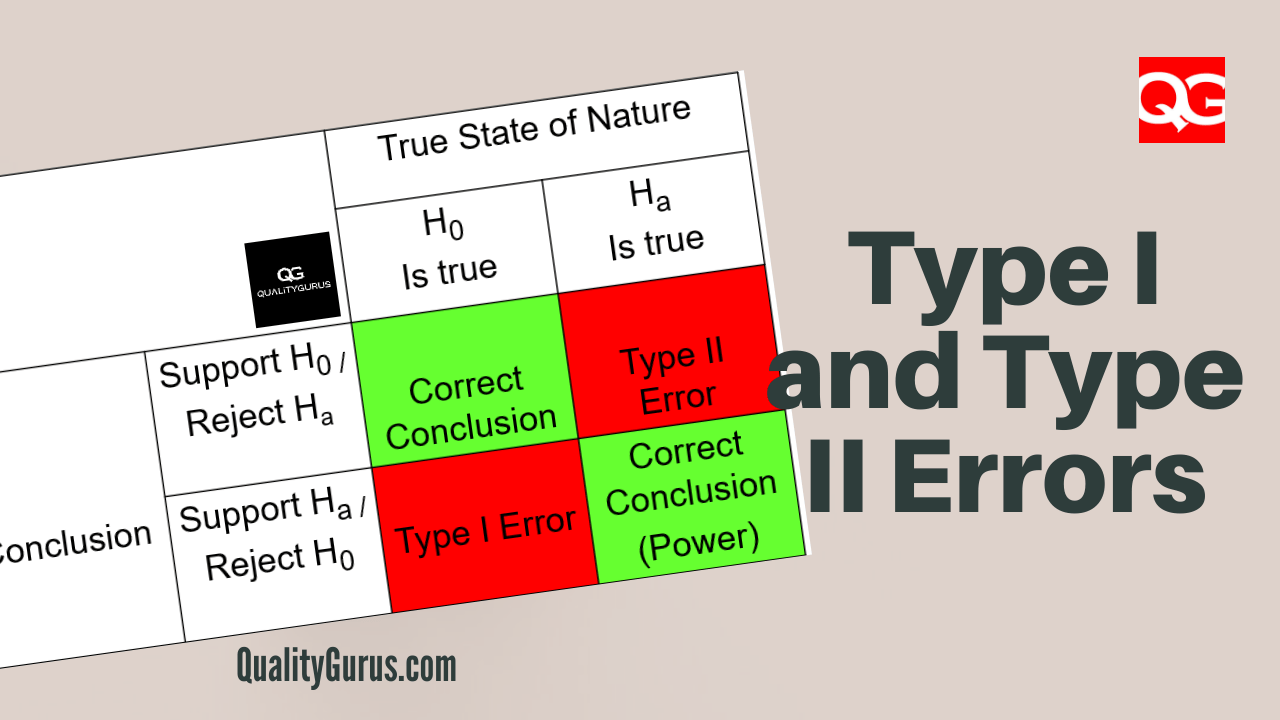
Type I And Type Ii Errors Explained Quality Gurus From all of this we can conclude that it is important to understand the difference between type i and type ii errors when performing hypothesis testing, so that you can reduce them previously to the study in relation to what you are looking for. The figure in the above example shows the trade off between type i and type ii errors. the gold area gives [latex]\alpha[ latex], the probability of the type i error; and the blue area gives [latex]\beta[ latex], the probability of the type ii error.
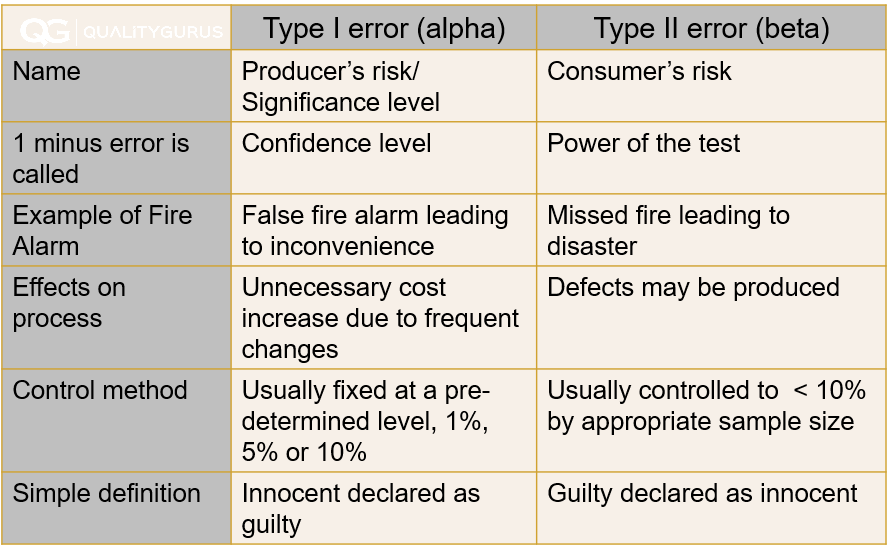
Type I And Type Ii Errors Explained Quality Gurus
Comments are closed.