Vector Scalar Quantities Pdf

Vector Scalar Quantities Pdf Scalar and vector quantities you will learn: 1. the principles of scalar and vector quantities 2. mathematical combinations of vector quantities 3. unit vectors 1. Operations, vector addition and multiplication of a vector by a scalar. we can add two forces together and the sum of the forces must satisfy the rule for vector addition.

Scalar And Vector Quantities Pdf Euclidean Vector Acceleration A vector of magnitude 10 units is shown with respect to a set x and y axes. what is the correct expression for the components of the vector along the x and y axis? component along the [ axis component along the \ axis. Known as scalar. examples of scalar are time, mass, length, volume, density, temperature, energy, distance, speed etc. the number describing the quantity of a particular scalar is known as its magnitude. the scalars are added subtracted, multiplied and divided by the usual arithmetical laws. 2. classify each quantity as a vector or a scalar. a) 15km2 b) 8m s ne c) 20˚c d) 12km up e) − ⃗ f) 70km h 3. al drove 7km east, then 24km south. a) draw a diagram of al’s movement. b) calculate the magnitude of the displacement vector, to the nearest tenth of a kilometre. Scalar is a physical quantity that is specified by giving only a magnitude or single number. certain quantities, however, cannot be completely specified by a magnitude only.

Vector And Scalar Quantities Pdf 2. classify each quantity as a vector or a scalar. a) 15km2 b) 8m s ne c) 20˚c d) 12km up e) − ⃗ f) 70km h 3. al drove 7km east, then 24km south. a) draw a diagram of al’s movement. b) calculate the magnitude of the displacement vector, to the nearest tenth of a kilometre. Scalar is a physical quantity that is specified by giving only a magnitude or single number. certain quantities, however, cannot be completely specified by a magnitude only. • the word position in this class implies a vector quantity, like the position of an object relative to a reference point or the position change when moving from point a to point b. Speed (a scalar quantity) is the distance travelled every second. , velocity (a vector quantity) is the change of displacement every second. % ˛˝ , ˛ [a unit must always be stated]. [a unit and direction must always be stated, unless the velocity is zero, in which case there is no direction]. Gaining a thorough understanding of scalar and vector quantities, including the skill to decompose vectors into their respective components. exploring the mathematical applications of vector quantities, including multiplication of vector quantities. 3.

Scalar Vector Quantities With Graphical Method Pdf Euclidean Vector Velocity • the word position in this class implies a vector quantity, like the position of an object relative to a reference point or the position change when moving from point a to point b. Speed (a scalar quantity) is the distance travelled every second. , velocity (a vector quantity) is the change of displacement every second. % ˛˝ , ˛ [a unit must always be stated]. [a unit and direction must always be stated, unless the velocity is zero, in which case there is no direction]. Gaining a thorough understanding of scalar and vector quantities, including the skill to decompose vectors into their respective components. exploring the mathematical applications of vector quantities, including multiplication of vector quantities. 3.

Scalar And Vector Quantities Pdf Gaining a thorough understanding of scalar and vector quantities, including the skill to decompose vectors into their respective components. exploring the mathematical applications of vector quantities, including multiplication of vector quantities. 3.
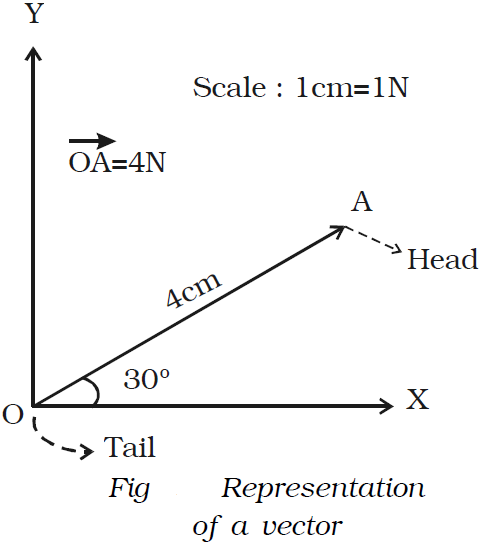
Scalar And Vector Quantities Engineersfield
Comments are closed.