Vector Vs Raster Data Gis Explained
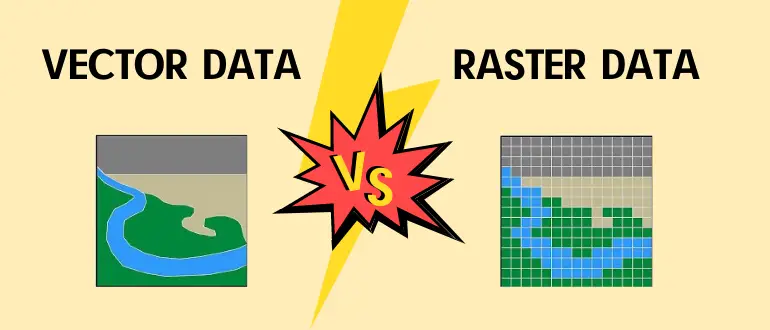
Vector Data Vs Raster Data Which One Should I Choose Definition: vector data is the process of representing real world objects and features within the gis field. this means that anything that you can visually see in a landscape, such as trees, houses, and rivers, can be represented in a gis application. Let’s dive into the key differences between raster and vector data, explore their pros and cons, and see how they are used in real world applications — visually explained for better.
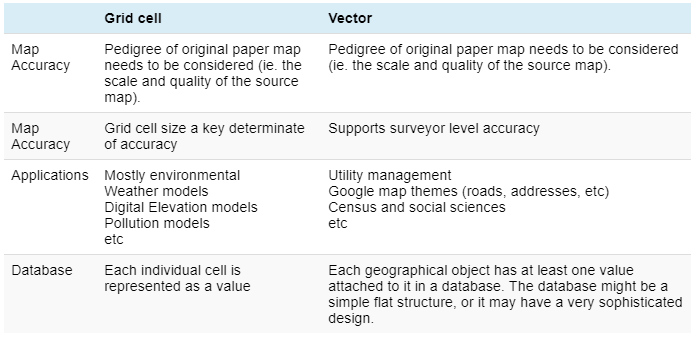
Raster Vs Vector Gis Gis University Raster Vs Vector Gis Understanding the difference between vector and raster data is fundamental for gis. these two types of spatial data are the backbone of gis analyses and mapping, each with its unique characteristics, advantages, and applications. In the gis space, it's important to know what raster and vector data is and the differences between the two. in this article, we explore both of these in detail. The main difference between raster and vector data in gis is how they store spatial information. raster data uses pixels to represent continuous features, while vector data uses geometric shapes to represent specific locations and boundaries. Understanding the nuanced characteristics of these data types is crucial for professionals working in cartography, environmental science, urban planning, and geospatial analysis.
Raster Vs Vector Data Formats In Gis Equator The main difference between raster and vector data in gis is how they store spatial information. raster data uses pixels to represent continuous features, while vector data uses geometric shapes to represent specific locations and boundaries. Understanding the nuanced characteristics of these data types is crucial for professionals working in cartography, environmental science, urban planning, and geospatial analysis. Geospatial data can be represented using either vector data type or raster. the two data types are very different in their internal representation, the operations you can do on them as well as their look and feel. the figures below show a representation of the same geographical location. When it comes to geographic information systems (gis), two main types of data are commonly used: raster data and vector data. each type has its own set of attributes and characteristics that make it suitable for different applications. Compare raster and vector data models in gis. understand their characteristics, advantages, disadvantages, and use cases to choose the best for your needs.
Comments are closed.