Vectors Gcse Higher Maths

Gcse Vectors Pdf Have you ever seen that happen? maybe you have seen birds struggling against a strong wind that seem to fly sideways. vectors help explain that. In mathematics and physics, vector is a term that refers to quantities that cannot be expressed by a single number (a scalar), or to elements of some vector spaces.

Vectors Cse Questions Gcse Revision Questions Vectors are scalable graphic files that use mathematical formulas to represent shapes, allowing them to be resized without losing quality. they are perfect for designs like logos, illustrations, icons, and more. Vectors in math is a geometric entity that has both magnitude and direction. vectors have an initial point at the point where they start and a terminal point that tells the final position of the point. various operations can be applied to vectors such as addition, subtraction, and multiplication. Because of this, we study vectors, mathematical objects that convey both magnitude and direction information. one "bare bones'' definition of a vector is based on what we wrote above: "a vector is a mathematical object with magnitude and direction parameters.''. This topic covers: vector magnitude vector scaling unit vectors adding & subtracting vectors magnitude & direction form vector applications.

Vectors B Gcse Questions Gcse Revision Questions Because of this, we study vectors, mathematical objects that convey both magnitude and direction information. one "bare bones'' definition of a vector is based on what we wrote above: "a vector is a mathematical object with magnitude and direction parameters.''. This topic covers: vector magnitude vector scaling unit vectors adding & subtracting vectors magnitude & direction form vector applications. Two examples of vectors are those that represent force and velocity. both force and velocity are in a particular direction. the magnitude of the vector would indicate the strength of the force or the speed associated with the velocity. we denote vectors using boldface as in $\vc{a}$ or $\vc{b}$. Vector, in physics, a quantity that has both magnitude and direction. it is typically represented by an arrow whose direction is the same as that of the quantity and whose length is proportional to the quantity’s magnitude. although a vector has magnitude and direction, it does not have position. Vectors, in maths, are objects which have both, magnitude and direction. magnitude defines the size of the vector. magnitude defines the size of the vector. it is represented by a line with an arrow, where the length of the line is the magnitude of the vector and the arrow shows the direction. Vectors are geometric representations of magnitude and direction and can be expressed as arrows in two or three dimensions. vectors are geometric representations of magnitude and direction which are often represented by straight arrows, starting at one point on a coordinate axis and ending at a different point.
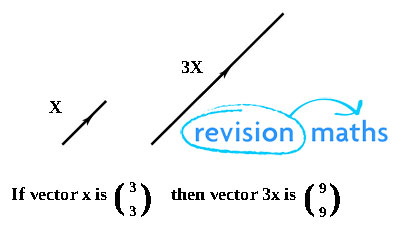
Vectors Maths Gcse Revision Two examples of vectors are those that represent force and velocity. both force and velocity are in a particular direction. the magnitude of the vector would indicate the strength of the force or the speed associated with the velocity. we denote vectors using boldface as in $\vc{a}$ or $\vc{b}$. Vector, in physics, a quantity that has both magnitude and direction. it is typically represented by an arrow whose direction is the same as that of the quantity and whose length is proportional to the quantity’s magnitude. although a vector has magnitude and direction, it does not have position. Vectors, in maths, are objects which have both, magnitude and direction. magnitude defines the size of the vector. magnitude defines the size of the vector. it is represented by a line with an arrow, where the length of the line is the magnitude of the vector and the arrow shows the direction. Vectors are geometric representations of magnitude and direction and can be expressed as arrows in two or three dimensions. vectors are geometric representations of magnitude and direction which are often represented by straight arrows, starting at one point on a coordinate axis and ending at a different point.
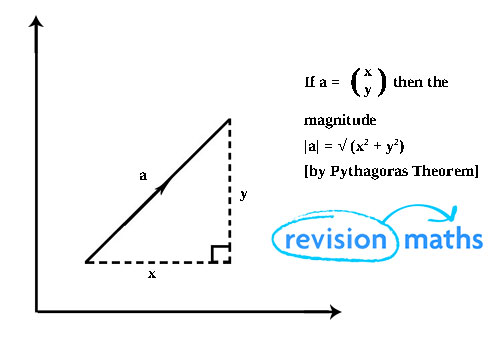
Vectors Maths Gcse Revision Vectors, in maths, are objects which have both, magnitude and direction. magnitude defines the size of the vector. magnitude defines the size of the vector. it is represented by a line with an arrow, where the length of the line is the magnitude of the vector and the arrow shows the direction. Vectors are geometric representations of magnitude and direction and can be expressed as arrows in two or three dimensions. vectors are geometric representations of magnitude and direction which are often represented by straight arrows, starting at one point on a coordinate axis and ending at a different point.
Comments are closed.