Viewdata Viewbag Tempdata In Asp Net Mvc 5
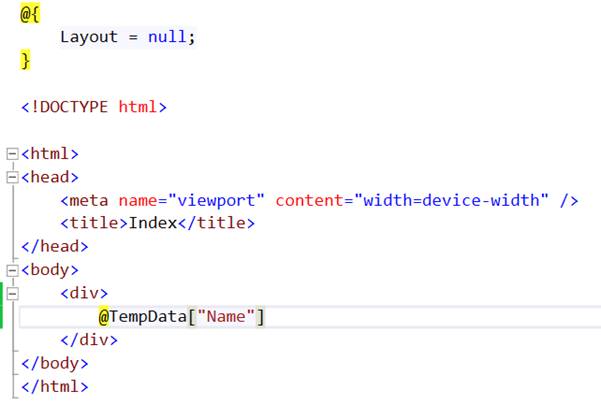
Viewdata Viewbag And Tempdata In Asp Net Mvc Also known as low grade spondylolisthesis, grade 1 spondylolisthesis is found in virtually all patients with degenerative spondylolisthesis. over time, without the appropriate treatment plan, grade 1 degenerative spondylolisthesis is likely to progress into a more severe form of the condition. what causes grade 1 spondylolisthesis?. Degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis (ds) can be treated by several surgical procedures varying from decompression alone to instrumented fusion. [1] instrumented fusion techniques include posterolateral fusion (plf), posterior lumbar interbody fusion (plif), transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (tlif), anterior lumbar interbody fusion (alif) and, more recently, lateral lumbar interbody.
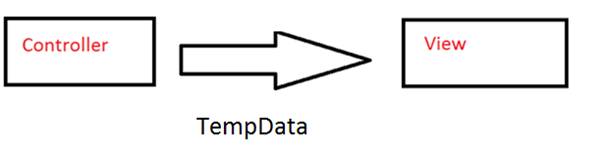
Viewdata Viewbag And Tempdata In Asp Net Mvc Degenerative spondylolisthesis is a common degenerative condition characterized by subluxation of one vertebral body anterior to the adjacent inferior vertebral body with intact pars. often combined with a posterior lumbar interbody fusion or transforaminal interbody fusion. new data shows equivalent outcomes using cortical screw fixation. Purpose to compare the outcomes and characteristics of oblique lumbar interbody fusion stand alone (olif sa) and olif with posterior pedicle screw fixation (olif pps) in the treatment of grade i or grade ii degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis. patients and methods between january 2019 and may 2022, 139 patients with degenerative spondylolisthesis were treated with olif sa (n = 85) or olif. We applied the following inclusion criteria for the selection of articles: (1) surgical method: posterior lumbar fusion surgery; (2) preoperative condition requiring lumbar fusion surgery: ds; (3) intervention in the experimental group: cbt pedicle screw technique (cs); (4) intervention in the control group: conventional ps technique; (5) study. The occurrence of pseudoarthrosis, which refers to a lack of solid fusion between vertebrae, may vary by surgical technique; pseudoarthrosis rates reported in 10–30% of cases with pedicle screw fixation, with pedicle screw fixation being associated with higher fusion rates. 22 patients with higher grade spondylolisthesis and those with high.

Viewdata Viewbag And Tempdata In Asp Net Mvc We applied the following inclusion criteria for the selection of articles: (1) surgical method: posterior lumbar fusion surgery; (2) preoperative condition requiring lumbar fusion surgery: ds; (3) intervention in the experimental group: cbt pedicle screw technique (cs); (4) intervention in the control group: conventional ps technique; (5) study. The occurrence of pseudoarthrosis, which refers to a lack of solid fusion between vertebrae, may vary by surgical technique; pseudoarthrosis rates reported in 10–30% of cases with pedicle screw fixation, with pedicle screw fixation being associated with higher fusion rates. 22 patients with higher grade spondylolisthesis and those with high. Sakaura h, miwa t, yamashita t, et al. posterior lumbar interbody fusion with cortical bone trajectory screw fixation versus posterior lumbar interbody fusion using traditional pedicle screw fixation for degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis: a comparative study[j]. journal of neurosurgery spine. 2016 nov;25(5):591–5. Background to perform a comparative assessment of percutaneous transfacet screws (tfs) and percutaneous bilateral pedicle screws (bps) in oblique lateral interbody fusion (olif) for the treatment of single level degenerative lumbar spine diseases in terms of radiological examinations and clinical outcomes. methods sixty six patients who received single level olif with percutaneous. In a meta analysis of 12 randomized trails included 808, the fusion rate was quite similar in the unilateral versus bilateral pedicle screw fixation in the degenerative lumbar disease. no significant difference in means of clinical outcome. Previous studies have demonstrated that in case of symptomatic degenerative spondylolisthesis, surgical treatment can consist of decompression alone [1,2,3,4,5] however, still many surgeons prefer to add interbody fusion and pedicle screw stabilisation in case of symptomatic unstable spondylolisthesis.
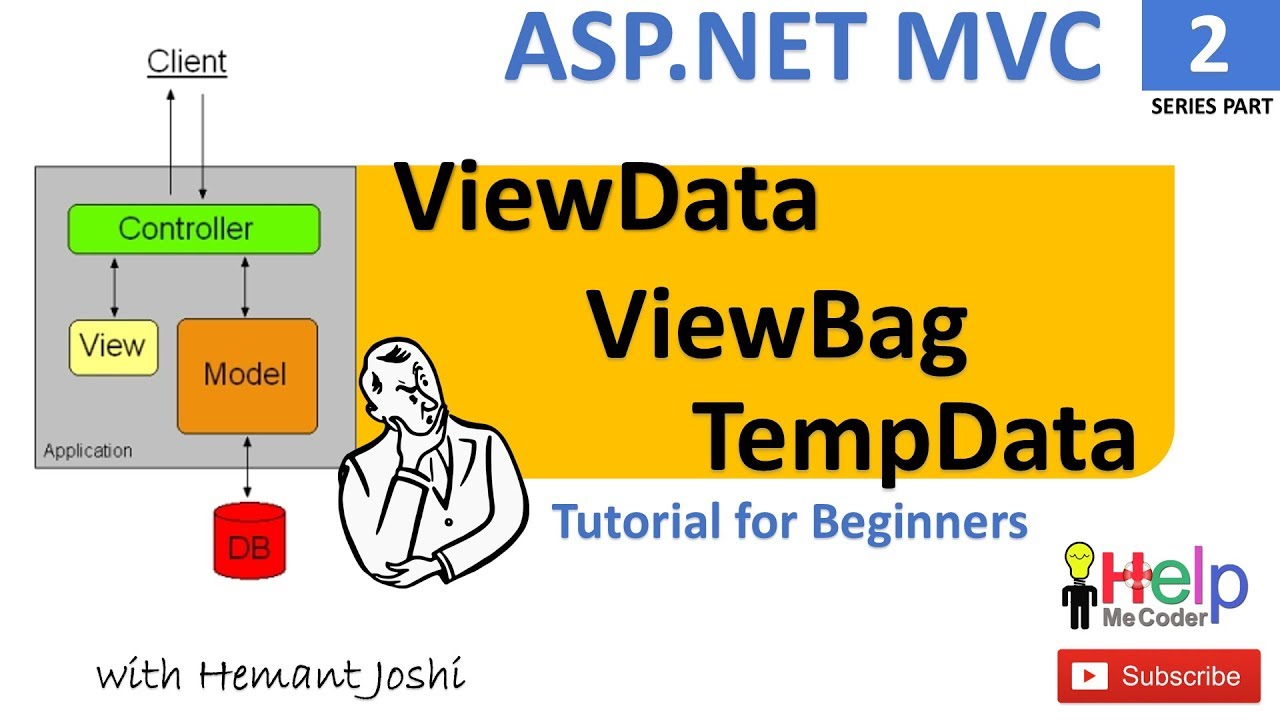
Viewdata Viewbag And Tempdata In Asp Net Mvc Vrogue Sakaura h, miwa t, yamashita t, et al. posterior lumbar interbody fusion with cortical bone trajectory screw fixation versus posterior lumbar interbody fusion using traditional pedicle screw fixation for degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis: a comparative study[j]. journal of neurosurgery spine. 2016 nov;25(5):591–5. Background to perform a comparative assessment of percutaneous transfacet screws (tfs) and percutaneous bilateral pedicle screws (bps) in oblique lateral interbody fusion (olif) for the treatment of single level degenerative lumbar spine diseases in terms of radiological examinations and clinical outcomes. methods sixty six patients who received single level olif with percutaneous. In a meta analysis of 12 randomized trails included 808, the fusion rate was quite similar in the unilateral versus bilateral pedicle screw fixation in the degenerative lumbar disease. no significant difference in means of clinical outcome. Previous studies have demonstrated that in case of symptomatic degenerative spondylolisthesis, surgical treatment can consist of decompression alone [1,2,3,4,5] however, still many surgeons prefer to add interbody fusion and pedicle screw stabilisation in case of symptomatic unstable spondylolisthesis.

Viewdata Viewbag Tempdata In Asp Net Mvc 5 In a meta analysis of 12 randomized trails included 808, the fusion rate was quite similar in the unilateral versus bilateral pedicle screw fixation in the degenerative lumbar disease. no significant difference in means of clinical outcome. Previous studies have demonstrated that in case of symptomatic degenerative spondylolisthesis, surgical treatment can consist of decompression alone [1,2,3,4,5] however, still many surgeons prefer to add interbody fusion and pedicle screw stabilisation in case of symptomatic unstable spondylolisthesis.
Comments are closed.