What Are Bayesian Belief Networks How Does A Bayesian Belief Network Learn Sirf Padhai

Bayesian Belief Network Pdf A bayesian model is a statistical model made of the pair prior x likelihood = posterior x marginal. bayes' theorem is somewhat secondary to the concept of a prior. Flat priors have a long history in bayesian analysis, stretching back to bayes and laplace. a "vague" prior is highly diffuse though not necessarily flat, and it expresses that a large range of values are plausible, rather than concentrating the probability mass around specific range.

Bayesian Belief Network Pdf Bayesian Network Graph Theory The bayesian, on the other hand, think that we start with some assumption about the parameters (even if unknowingly) and use the data to refine our opinion about those parameters. both are trying to develop a model which can explain the observations and make predictions; the difference is in the assumptions (both actual and philosophical). You're incorrect that hmc is not a markov chain method. per : in mathematics and physics, the hybrid monte carlo algorithm, also known as hamiltonian monte carlo, is a markov chain monte carlo method for obtaining a sequence of random samples from a probability distribution for which direct sampling is difficult. this sequence can be used to approximate the distribution (i.e., to. I understand what the posterior predictive distribution is, and i have been reading about posterior predictive checks, although it isn't clear to me what it does yet. what exactly is the posterior. Which is the best introductory textbook for bayesian statistics? one book per answer, please.

Bayesian Belief Networks Pdf I understand what the posterior predictive distribution is, and i have been reading about posterior predictive checks, although it isn't clear to me what it does yet. what exactly is the posterior. Which is the best introductory textbook for bayesian statistics? one book per answer, please. Confessions of a moderate bayesian, part 4 bayesian statistics by and for non statisticians read part 1: how to get started with bayesian statistics read part 2: frequentist probability vs bayesian probability read part 3: how bayesian inference works in the context of science predictive distributions a predictive distribution is a distribution that we expect for future observations. in other. The bayesian choice for details.) in an interesting twist, some researchers outside the bayesian perspective have been developing procedures called confidence distributions that are probability distributions on the parameter space, constructed by inversion from frequency based procedures without an explicit prior structure or even a dominating. The bayesian landscape when we setup a bayesian inference problem with n n unknowns, we are implicitly creating a n n dimensional space for the prior distributions to exist in. associated with the space is an additional dimension, which we can describe as the surface, or curve, of the space, that reflects the prior probability of a particular. I am looking for uninformative priors for beta distribution to work with a binomial process (hit miss). at first i thought about using $\\alpha=1, \\beta=1$ that generate an uniform pdf, or jeffrey p.

What Are Bayesian Belief Networks How Does A Bayesian Belief Network Learn Sirf Padhai Confessions of a moderate bayesian, part 4 bayesian statistics by and for non statisticians read part 1: how to get started with bayesian statistics read part 2: frequentist probability vs bayesian probability read part 3: how bayesian inference works in the context of science predictive distributions a predictive distribution is a distribution that we expect for future observations. in other. The bayesian choice for details.) in an interesting twist, some researchers outside the bayesian perspective have been developing procedures called confidence distributions that are probability distributions on the parameter space, constructed by inversion from frequency based procedures without an explicit prior structure or even a dominating. The bayesian landscape when we setup a bayesian inference problem with n n unknowns, we are implicitly creating a n n dimensional space for the prior distributions to exist in. associated with the space is an additional dimension, which we can describe as the surface, or curve, of the space, that reflects the prior probability of a particular. I am looking for uninformative priors for beta distribution to work with a binomial process (hit miss). at first i thought about using $\\alpha=1, \\beta=1$ that generate an uniform pdf, or jeffrey p.
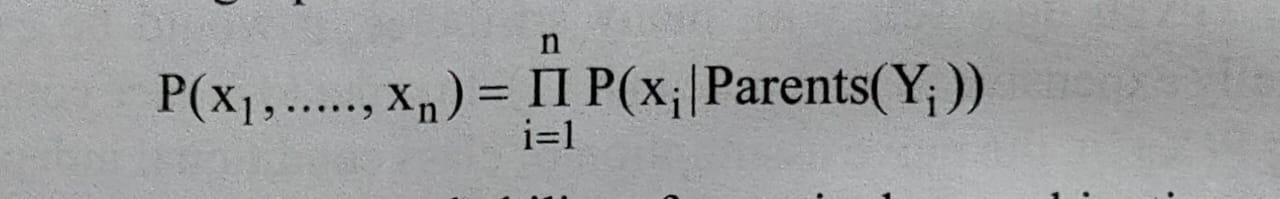
What Are Bayesian Belief Networks How Does A Bayesian Belief Network Learn Sirf Padhai The bayesian landscape when we setup a bayesian inference problem with n n unknowns, we are implicitly creating a n n dimensional space for the prior distributions to exist in. associated with the space is an additional dimension, which we can describe as the surface, or curve, of the space, that reflects the prior probability of a particular. I am looking for uninformative priors for beta distribution to work with a binomial process (hit miss). at first i thought about using $\\alpha=1, \\beta=1$ that generate an uniform pdf, or jeffrey p.

Bayesian Belief Network Bayesian Network Probability Theory
Comments are closed.