What Is Transpiration
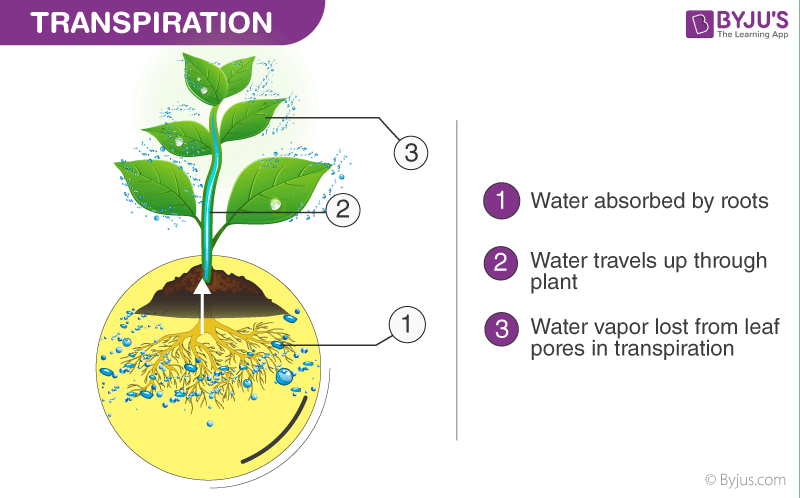
Transpiration In Plants Types Factors And Significance Transpiration is the evaporation of water from plants. most of the water absorbed by the roots of a plant—as much as 99.5 percent—is not used for growth or metabolism; it is excess water, and it leaves the plant through transpiration. Evapotranspiration is the sum of all processes by which water moves from the land surface to the atmosphere via evaporation and transpiration.

Transpiration Definition Image Flippy The basic difference between evaporation and transpiration is that evaporation is a physical process involving the loss of water from any exposed surface of liquid while transpiration is the biological process of losing water from the aerial parts of the plant. Transpiration is the process of water movement through a plant and its evaporation from aerial parts, such as leaves, stems and flowers. it is a passive process that requires no energy expense by the plant. [1]. Transpiration, in botany, a plant’s loss of water, mainly through the stomata of leaves. stomatal openings are necessary to admit carbon dioxide to the leaf interior and to allow oxygen to escape during photosynthesis. Transpiration is the process where water moves through a plant and then evaporates from its aerial parts, such as leaves, stems, and flowers. this occurs primarily through microscopic pores called stomata, located on the underside of leaves.

Transpiration Bonsai Science Transpiration, in botany, a plant’s loss of water, mainly through the stomata of leaves. stomatal openings are necessary to admit carbon dioxide to the leaf interior and to allow oxygen to escape during photosynthesis. Transpiration is the process where water moves through a plant and then evaporates from its aerial parts, such as leaves, stems, and flowers. this occurs primarily through microscopic pores called stomata, located on the underside of leaves. Stomatal transpiration it is the happening that happens through the stomata. the epidermis of leaves and green stems have various stomata. these are liable for around 80 90% of the complete water that happened. Transpirationthe loss of water from leaves by evaporation through the stomata. xylem vesselsnarrow, hollow, dead tubes with lignin, responsible for the transport of water and minerals in plants . Transpiration is the key process that allows plants to regulate moisture and temperature. this fascinating phenomenon involves water vapor escaping from tiny openings in leaves, helping maintain a plant’s internal balance. Transpiration —the loss of water vapor to the atmosphere through stomata—is a passive process, meaning that metabolic energy in the form of atp is not required for water movement. the energy driving transpiration is the difference in energy between the water in the soil and the water in the atmosphere. however, transpiration is tightly controlled.

Transpiration Survival World Stomatal transpiration it is the happening that happens through the stomata. the epidermis of leaves and green stems have various stomata. these are liable for around 80 90% of the complete water that happened. Transpirationthe loss of water from leaves by evaporation through the stomata. xylem vesselsnarrow, hollow, dead tubes with lignin, responsible for the transport of water and minerals in plants . Transpiration is the key process that allows plants to regulate moisture and temperature. this fascinating phenomenon involves water vapor escaping from tiny openings in leaves, helping maintain a plant’s internal balance. Transpiration —the loss of water vapor to the atmosphere through stomata—is a passive process, meaning that metabolic energy in the form of atp is not required for water movement. the energy driving transpiration is the difference in energy between the water in the soil and the water in the atmosphere. however, transpiration is tightly controlled.
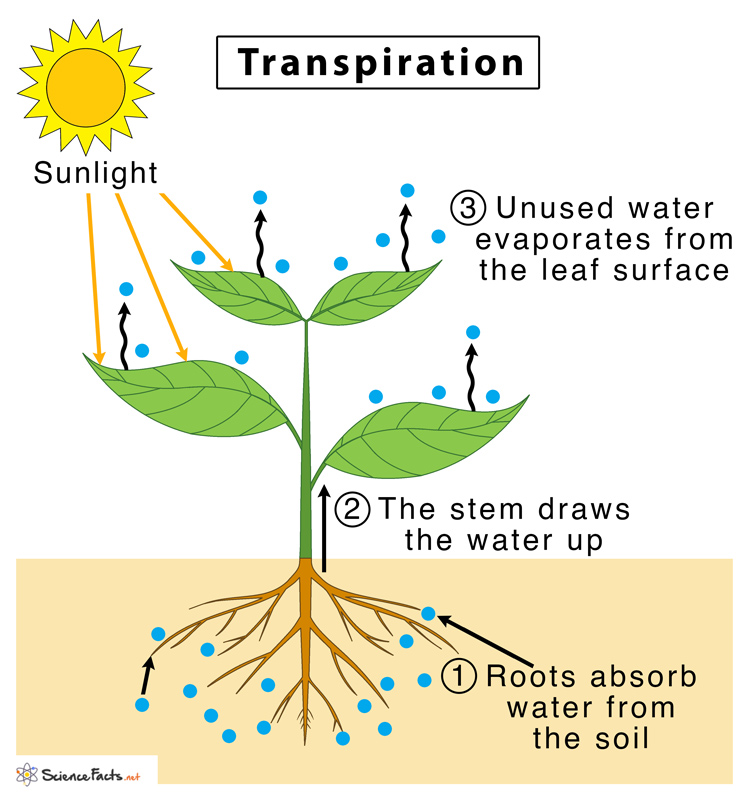
Transpiration Definition Factors Types And Importance Transpiration is the key process that allows plants to regulate moisture and temperature. this fascinating phenomenon involves water vapor escaping from tiny openings in leaves, helping maintain a plant’s internal balance. Transpiration —the loss of water vapor to the atmosphere through stomata—is a passive process, meaning that metabolic energy in the form of atp is not required for water movement. the energy driving transpiration is the difference in energy between the water in the soil and the water in the atmosphere. however, transpiration is tightly controlled.

Transpiration Definition
Comments are closed.