What Is Value In Lean Value Added Vs Non Value Added Work

Value Added Analysis Value Added Process Vs Non Value Added Value Added Vs Non Value Added When it comes to value added vs. non value added operations, how can i tell the difference? lean provides ways to identify areas of non value added and value added actions. learn how to identify what adds value in a process and eliminate what does not. Value added vs. non value added are key concepts in process improvement methodologies, particularly in lean manufacturing and six sigma. value added (va) activities are those that, in the eyes of the customer, enhance the product or service, making it worth more or more desirable.
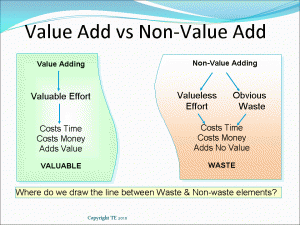
Value Add Vs Non Value Adding Processes Non value added (nva) processes are those that do not provide much if any, value to the product or solution under development. this could take the form of something as simple and mundane as shuffling items around a workspace more than necessary. Value added steps in a process are those in which you add something to a product or service for which the customer would be willing to pay. these activities are where you gain the most from expending your resources when providing a product or service. take the sun card, for example. Lean waste refers to all activities that do not add any value to the product or service and respectfully to your customers. simply put, non value added activities are everything a customer would not be willing to pay for; hence, they bring waste (inefficiencies) to your process. however, does this mean all waste is redundant?. In a manufacturing organization, the value added activities are those that transform the product from raw material to its finished form for which the customer is willing to pay. it is, of course, essential to strike a balance between modification and budget monitoring.
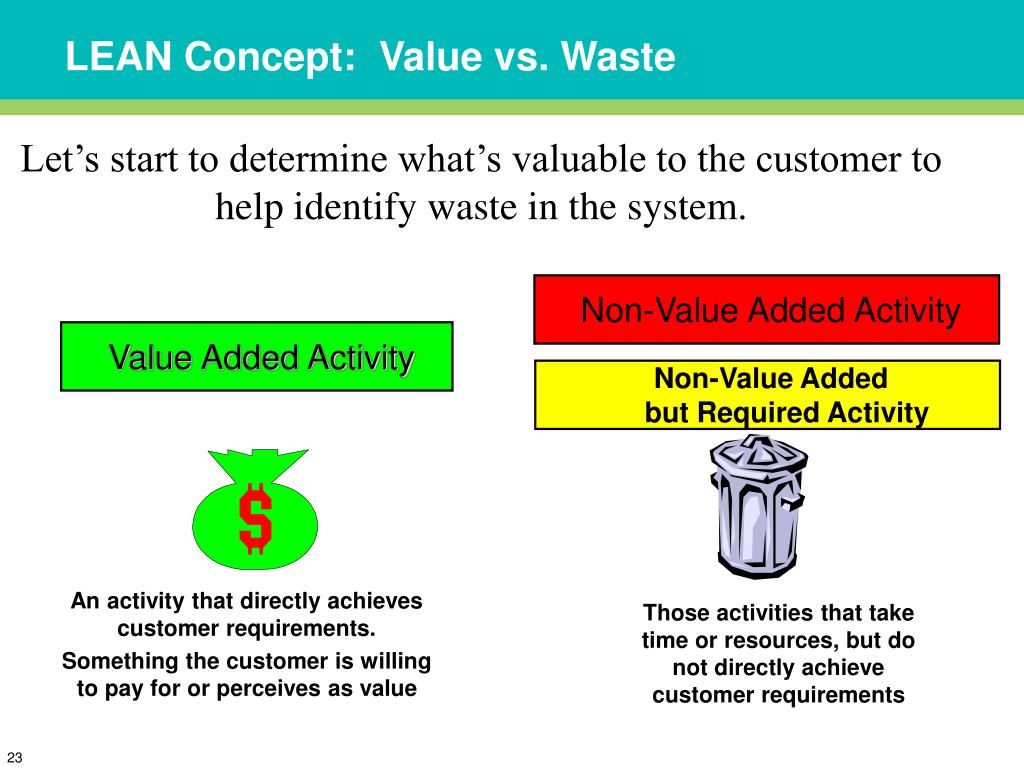
Ppt An Introduction To Lean And Six Sigma For Ahq By Asq Powerpoint Presentation Id 3280616 Lean waste refers to all activities that do not add any value to the product or service and respectfully to your customers. simply put, non value added activities are everything a customer would not be willing to pay for; hence, they bring waste (inefficiencies) to your process. however, does this mean all waste is redundant?. In a manufacturing organization, the value added activities are those that transform the product from raw material to its finished form for which the customer is willing to pay. it is, of course, essential to strike a balance between modification and budget monitoring. Value added and non value added concepts are pretty straightforward on the surface, truly understanding the differences can impact efficiency, waste reduction, and customer satisfaction. for any organization looking to drive continuous improvement, mastering these core concepts is essential. Lean manufacturing focuses on delivering value by eliminating waste but how does lean define "value?" discover the difference between value and waste thro. “only an activity that physically changes the shape or character of a product or assembly can add value.” “any activity that does not change the product or assembly is waste.” however even this can fall short in some areas, consider the case of conducting a roughing cut, or in over polishing a surface that will never been seen. What is value and how do we identify activities that add value and those that do not add value? value can simply be defined as something a customer is willing to pay to receive. if a customer is not willing to pay for it, then there is no value.

Fundamentals Of Lean Methodology Explained With Examp Vrogue Co Value added and non value added concepts are pretty straightforward on the surface, truly understanding the differences can impact efficiency, waste reduction, and customer satisfaction. for any organization looking to drive continuous improvement, mastering these core concepts is essential. Lean manufacturing focuses on delivering value by eliminating waste but how does lean define "value?" discover the difference between value and waste thro. “only an activity that physically changes the shape or character of a product or assembly can add value.” “any activity that does not change the product or assembly is waste.” however even this can fall short in some areas, consider the case of conducting a roughing cut, or in over polishing a surface that will never been seen. What is value and how do we identify activities that add value and those that do not add value? value can simply be defined as something a customer is willing to pay to receive. if a customer is not willing to pay for it, then there is no value.
Comments are closed.