Why Biofilms Make Pseudomonas Infections So Hard To Treat
Microbiology School Of Chemistry And Biosciences University Of Bradford Additionally, treatment of these infections is also hindered by the p. aeruginosa ability to form biofilms which protect them from surrounding environmental stresses, impedes phagocytosis and thereby confers capacity for colonization and long term persistence . The accelerating rise of multi drug resistance and resultant difficulties in the treatment of pseudomonas aeruginosa infections are a significant cause of high morbidity and mortality in infected patients.

High Throughput Determination Of The Biofilm Prevention Concentration For Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Planktonic cells are up to a thousand times more susceptible to antibiotics than the same bacterium grown as a biofilm, sauer pointed out. this heightened tolerance is the reason that conventional antibiotic treatment can fail in chronic, biofilm related infections. Biofilm formation leads to multiple antibiotic resistance in p. aeruginosa, posing a significant challenge to conventional single antibiotic therapeutic approaches. it has therefore become particularly important to develop anti biofilm drugs. Along the different layers of the biofilm, the p. aeruginosa population is heterogeneous, exhibiting an extreme ability to adapt his metabolic activity to the local microenvironment. at the deepest layers of the biofilm is a subset of dormant cells, called persister cells. Infections caused by biofilms are notoriously challenging to cure due to the inadequate absorption of antibiotics through the eps matrix, the existence of persister cells, which are naturally.

Pseudomonas 24 Hour Biofilm Growth Under Flow Cell Microsystems Along the different layers of the biofilm, the p. aeruginosa population is heterogeneous, exhibiting an extreme ability to adapt his metabolic activity to the local microenvironment. at the deepest layers of the biofilm is a subset of dormant cells, called persister cells. Infections caused by biofilms are notoriously challenging to cure due to the inadequate absorption of antibiotics through the eps matrix, the existence of persister cells, which are naturally. Its remarkable adaptability and resistance to various antimicrobial treatments make it difficult to eradicate. its persistence is enabled by its ability to form a biofilm. Multidrug resistant p. aeruginosa poses a significant challenge to antibiotics and therapeutic approaches due to its pathogenicity, virulence, and biofilm forming ability mediated by quorum sensing. understanding the pathogenic mechanisms is essential for developing potential drug targets. Genus pseudomonas includes a large number of species that can be encountered in biotechnological processes as well as in the role of serious human or plant pathogens. pseudomonads easily form biofilms on various types of surfaces. Why biofilms are difficult to treat biofilms exhibit resilience to conventional treatments, primarily due to their protective extracellular polymeric substance (eps) matrix. this network of polysaccharides, proteins, and dna acts as a physical barrier, significantly impeding the penetration of antibiotics, disinfectants, and host immune system.
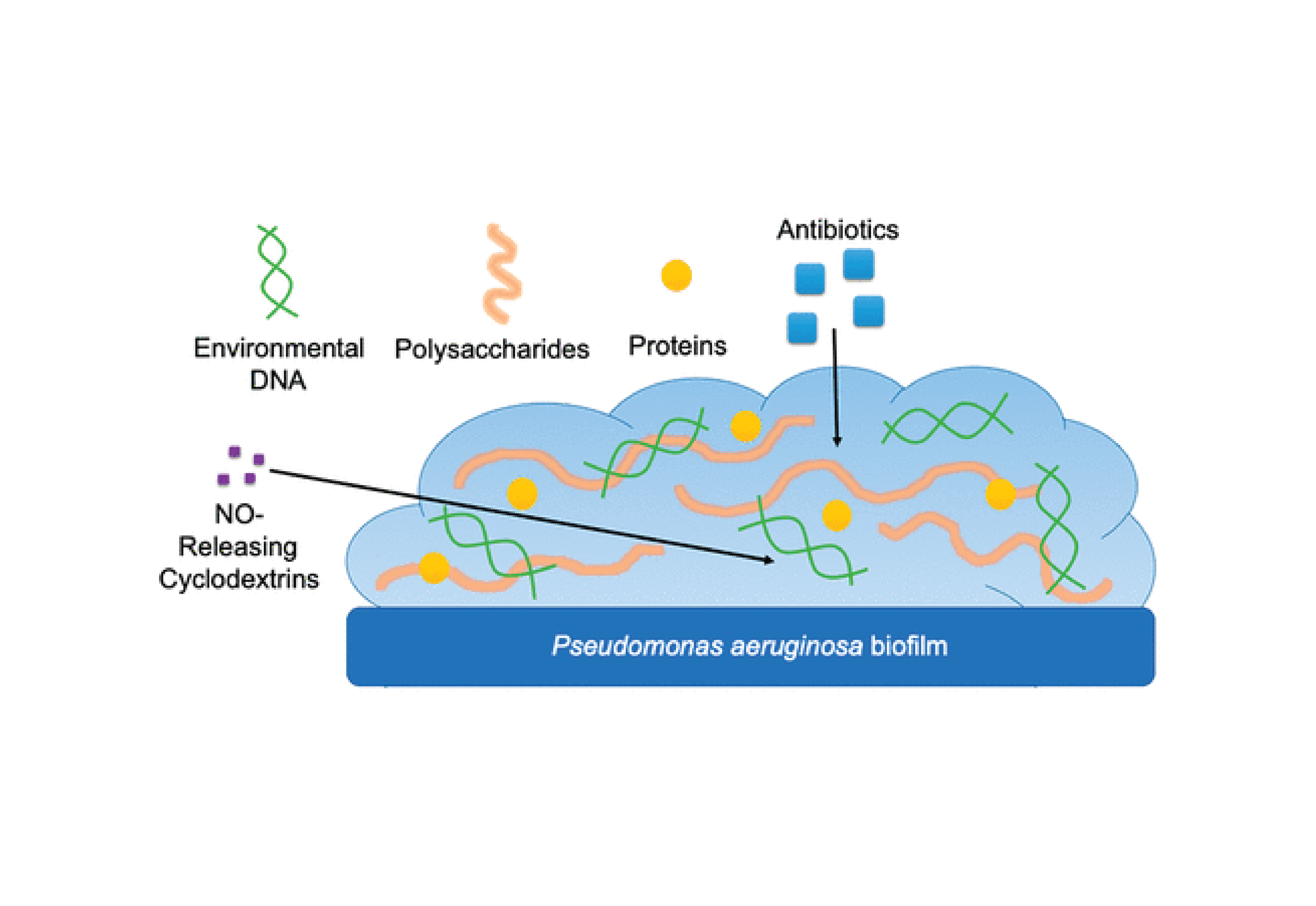
Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Biofilm Eradication Via Nitric Oxide Releasing Cyclodextrins Department Its remarkable adaptability and resistance to various antimicrobial treatments make it difficult to eradicate. its persistence is enabled by its ability to form a biofilm. Multidrug resistant p. aeruginosa poses a significant challenge to antibiotics and therapeutic approaches due to its pathogenicity, virulence, and biofilm forming ability mediated by quorum sensing. understanding the pathogenic mechanisms is essential for developing potential drug targets. Genus pseudomonas includes a large number of species that can be encountered in biotechnological processes as well as in the role of serious human or plant pathogens. pseudomonads easily form biofilms on various types of surfaces. Why biofilms are difficult to treat biofilms exhibit resilience to conventional treatments, primarily due to their protective extracellular polymeric substance (eps) matrix. this network of polysaccharides, proteins, and dna acts as a physical barrier, significantly impeding the penetration of antibiotics, disinfectants, and host immune system.

Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Biofilms And Their Partners In Crime Institute For Bioengineering Of Genus pseudomonas includes a large number of species that can be encountered in biotechnological processes as well as in the role of serious human or plant pathogens. pseudomonads easily form biofilms on various types of surfaces. Why biofilms are difficult to treat biofilms exhibit resilience to conventional treatments, primarily due to their protective extracellular polymeric substance (eps) matrix. this network of polysaccharides, proteins, and dna acts as a physical barrier, significantly impeding the penetration of antibiotics, disinfectants, and host immune system.
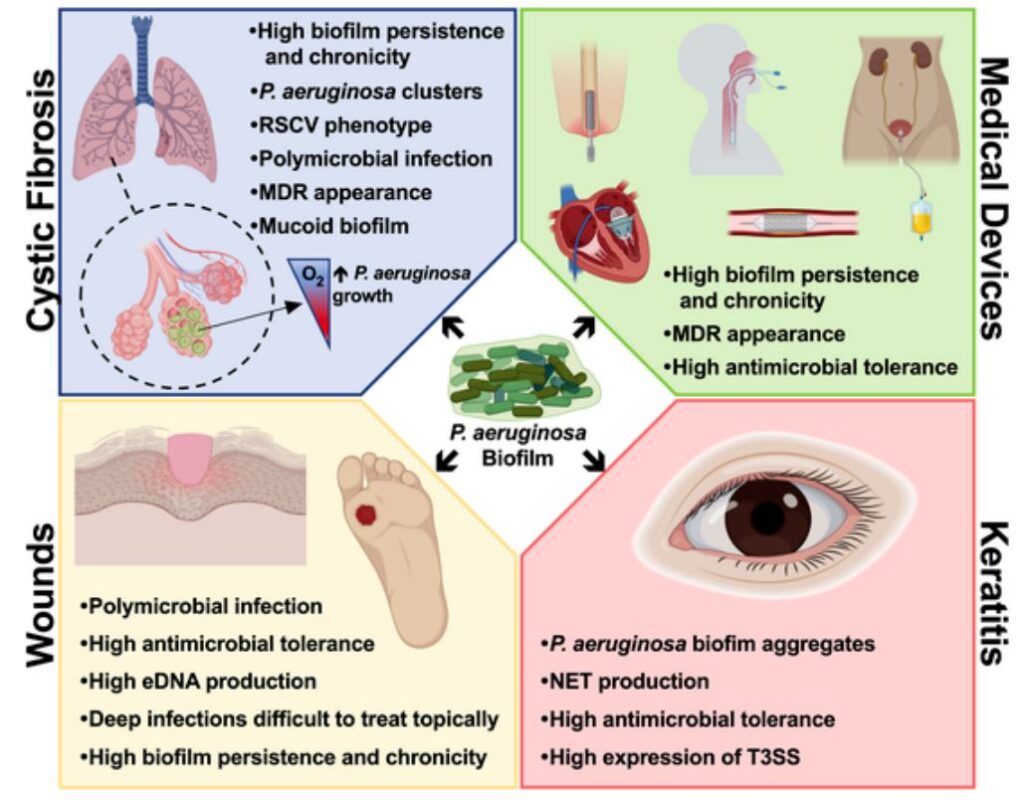
Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Biofilms And Their Partners In Crime Institute For Bioengineering Of
Comments are closed.